filmov
tv
ELISA Test : All types with Mechanism discussed in details : Microbiology

Показать описание
ELISA - Enzyme Linked Immunosorbent Assay
Different Types of Elisa and their principles.All types of ELISA test.
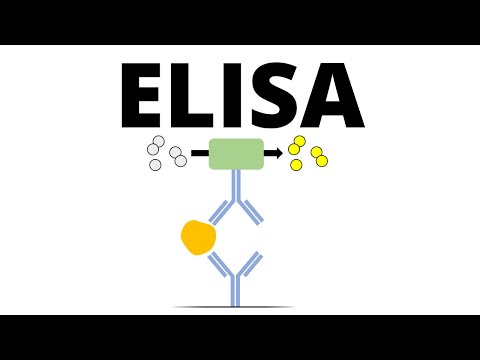
The enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) (/ɪˈlaɪzə/, /ˌiːˈlaɪzə/) is a commonly used analytical biochemistry assay, first described by Engvall and Perlmann in 1971.[1] The assay uses a solid-phase enzyme immunoassay (EIA) to detect the presence of a ligand (commonly a protein) in a liquid sample using antibodies directed against the protein to be measured. ELISA has been used as a diagnostic tool in medicine, plant pathology, and biotechnology, as well as a quality control check in various industries.
In the most simple form of an ELISA, antigens from the sample are attached to a surface. Then, a matching antibody is applied over the surface so it can bind to the antigen. This antibody is linked to an enzyme, and in the final step, a substance containing the enzyme's substrate is added. The subsequent reaction produces a detectable signal, most commonly a color change.
Performing an ELISA involves at least one antibody with specificity for a particular antigen. The sample with an unknown amount of antigen is immobilized on a solid support (usually a polystyrene microtiter plate) either non-specifically (via adsorption to the surface) or specifically (via capture by another antibody specific to the same antigen, in a "sandwich" ELISA). After the antigen is immobilized, the detection antibody is added, forming a complex with the antigen. The detection antibody can be covalently linked to an enzyme or can itself be detected by a secondary antibody that is linked to an enzyme through bioconjugation. Between each step, the plate is typically washed with a mild detergent solution to remove any proteins or antibodies that are non-specifically bound. After the final wash step, the plate is developed by adding an enzymatic substrate to produce a visible signal, which indicates the quantity of antigen in the sample.
Of note, ELISA can perform other forms of ligand binding assays instead of strictly "immuno" assays, though the name carried the original "immuno" because of the common use and history of development of this method. The technique essentially requires any ligating reagent that can be immobilized on the solid phase along with a detection reagent that will bind specifically and use an enzyme to generate a signal that can be properly quantified. In between the washes, only the ligand and its specific binding counterparts remain specifically bound or "immunosorbed" by antigen-antibody interactions to the solid phase, while the nonspecific or unbound components are washed away. Unlike other spectrophotometric wet lab assay formats where the same reaction well (e.g., a cuvette) can be reused after washing, the ELISA plates have the reaction products immunosorbed on the solid phase, which is part of the plate, and so are not easily reusable.
Contents
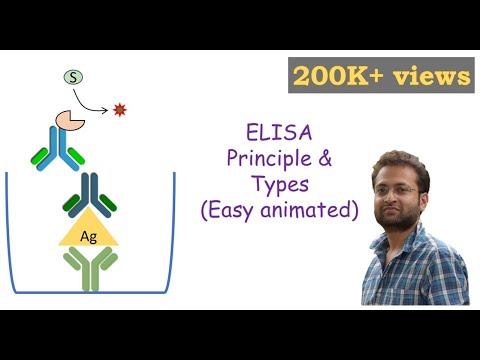
1 Principle
2 History
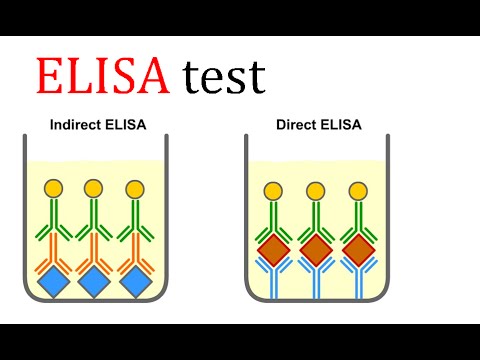
3 Types
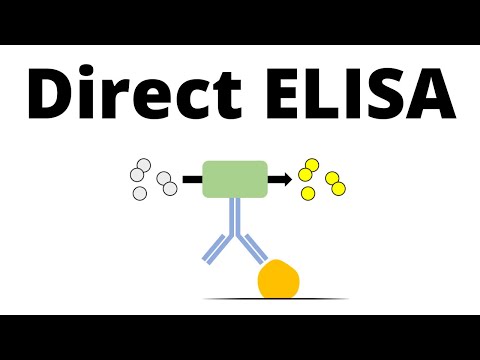
3.1 Direct ELISA[18]
3.2 Sandwich ELISA
3.3 Competitive ELISA
3.4 Reverse ELISA
4 Commonly used enzymatic markers
5 Applications
6 See also
7 Notes and references
8 External links
Different Types of Elisa and their principles.All types of ELISA test.
The enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) (/ɪˈlaɪzə/, /ˌiːˈlaɪzə/) is a commonly used analytical biochemistry assay, first described by Engvall and Perlmann in 1971.[1] The assay uses a solid-phase enzyme immunoassay (EIA) to detect the presence of a ligand (commonly a protein) in a liquid sample using antibodies directed against the protein to be measured. ELISA has been used as a diagnostic tool in medicine, plant pathology, and biotechnology, as well as a quality control check in various industries.
In the most simple form of an ELISA, antigens from the sample are attached to a surface. Then, a matching antibody is applied over the surface so it can bind to the antigen. This antibody is linked to an enzyme, and in the final step, a substance containing the enzyme's substrate is added. The subsequent reaction produces a detectable signal, most commonly a color change.
Performing an ELISA involves at least one antibody with specificity for a particular antigen. The sample with an unknown amount of antigen is immobilized on a solid support (usually a polystyrene microtiter plate) either non-specifically (via adsorption to the surface) or specifically (via capture by another antibody specific to the same antigen, in a "sandwich" ELISA). After the antigen is immobilized, the detection antibody is added, forming a complex with the antigen. The detection antibody can be covalently linked to an enzyme or can itself be detected by a secondary antibody that is linked to an enzyme through bioconjugation. Between each step, the plate is typically washed with a mild detergent solution to remove any proteins or antibodies that are non-specifically bound. After the final wash step, the plate is developed by adding an enzymatic substrate to produce a visible signal, which indicates the quantity of antigen in the sample.
Of note, ELISA can perform other forms of ligand binding assays instead of strictly "immuno" assays, though the name carried the original "immuno" because of the common use and history of development of this method. The technique essentially requires any ligating reagent that can be immobilized on the solid phase along with a detection reagent that will bind specifically and use an enzyme to generate a signal that can be properly quantified. In between the washes, only the ligand and its specific binding counterparts remain specifically bound or "immunosorbed" by antigen-antibody interactions to the solid phase, while the nonspecific or unbound components are washed away. Unlike other spectrophotometric wet lab assay formats where the same reaction well (e.g., a cuvette) can be reused after washing, the ELISA plates have the reaction products immunosorbed on the solid phase, which is part of the plate, and so are not easily reusable.
Contents
1 Principle
2 History
3 Types
3.1 Direct ELISA[18]
3.2 Sandwich ELISA
3.3 Competitive ELISA
3.4 Reverse ELISA
4 Commonly used enzymatic markers
5 Applications
6 See also
7 Notes and references
8 External links
Комментарии
 0:08:44
0:08:44
 0:01:58
0:01:58
 0:03:15
0:03:15
 0:10:36
0:10:36
 0:06:45
0:06:45
 0:01:33
0:01:33
 0:06:02
0:06:02
 1:04:38
1:04:38
 1:05:56
1:05:56
 0:00:06
0:00:06
 0:07:04
0:07:04
 0:03:32
0:03:32
 0:14:59
0:14:59
 0:03:27
0:03:27
 0:01:26
0:01:26
 0:06:58
0:06:58
 0:00:37
0:00:37
 0:02:27
0:02:27
 0:12:28
0:12:28
 0:01:40
0:01:40
 0:04:51
0:04:51
 0:15:59
0:15:59
 0:08:07
0:08:07
 0:04:42
0:04:42