filmov
tv
What is Crystal Field Stabilization Energy? @Diarasacademy

Показать описание
What is Crystal Field Stabilization Energy?
Answer:
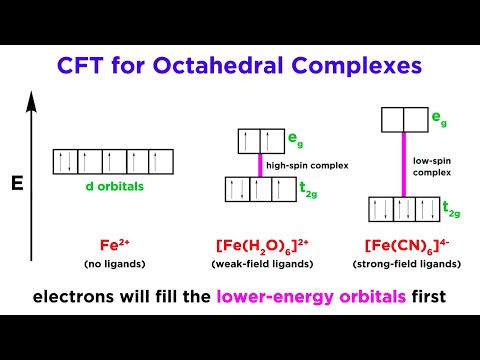
Crystal Field Stabilization Energy (CFSE) is the energy difference between the energy of an electron in a degenerate d-orbital in a free ion and in the crystal field of a coordination complex.
Definition:
Crystal Field Stabilization Energy refers to the energy stabilization that results from the splitting of degenerate d-orbitals into two sets, labeled as "eg" and "t2g", in the presence of a ligand field in coordination complexes. The arrangement of ligands around the metal ion creates an electrostatic field, which causes this splitting. The specific arrangement of electrons in the split d-orbitals leads to a stabilization (or sometimes destabilization) of the complex, which is quantified as CFSE.
Example:
In an octahedral complex like [Fe(CN)6]4-, the "t2g" orbitals are lower in energy than the "eg" orbitals, and the CFSE can be calculated based on the electron configuration in these orbitals.
Fascinating Fact:
The concept of CFSE is essential for understanding the color, magnetism, and stability of coordination complexes in transition metal chemistry.
Key Takeaway:
Crystal Field Stabilization Energy is a critical concept for predicting the properties of coordination complexes, with applications in catalysis, materials science, and bioinorganic chemistry. Stabilize your knowledge with @Diara’s Academy! Don’t forget to like, comment, and share to spread the knowledge!
Keywords: Crystal Field Stabilization Energy, CFSE, d-orbital splitting, coordination complexes, transition metals, STEM learning, @Diara’s Academy.
Hashtags:
#CrystalFieldStabilizationEnergy #CFSE #CoordinationComplexes #TransitionMetals #ChemistryEducation #STEMLearning #DiaraAcademy #LearnChemistry #ScienceExplained #InorganicChemistry #ChemistryFacts
Answer:
Crystal Field Stabilization Energy (CFSE) is the energy difference between the energy of an electron in a degenerate d-orbital in a free ion and in the crystal field of a coordination complex.
Definition:
Crystal Field Stabilization Energy refers to the energy stabilization that results from the splitting of degenerate d-orbitals into two sets, labeled as "eg" and "t2g", in the presence of a ligand field in coordination complexes. The arrangement of ligands around the metal ion creates an electrostatic field, which causes this splitting. The specific arrangement of electrons in the split d-orbitals leads to a stabilization (or sometimes destabilization) of the complex, which is quantified as CFSE.
Example:
In an octahedral complex like [Fe(CN)6]4-, the "t2g" orbitals are lower in energy than the "eg" orbitals, and the CFSE can be calculated based on the electron configuration in these orbitals.
Fascinating Fact:
The concept of CFSE is essential for understanding the color, magnetism, and stability of coordination complexes in transition metal chemistry.
Key Takeaway:
Crystal Field Stabilization Energy is a critical concept for predicting the properties of coordination complexes, with applications in catalysis, materials science, and bioinorganic chemistry. Stabilize your knowledge with @Diara’s Academy! Don’t forget to like, comment, and share to spread the knowledge!
Keywords: Crystal Field Stabilization Energy, CFSE, d-orbital splitting, coordination complexes, transition metals, STEM learning, @Diara’s Academy.
Hashtags:
#CrystalFieldStabilizationEnergy #CFSE #CoordinationComplexes #TransitionMetals #ChemistryEducation #STEMLearning #DiaraAcademy #LearnChemistry #ScienceExplained #InorganicChemistry #ChemistryFacts
 0:07:42
0:07:42
 0:21:56
0:21:56
 0:02:43
0:02:43
 0:07:42
0:07:42
 0:53:35
0:53:35
 0:15:32
0:15:32
 0:17:15
0:17:15
 0:00:58
0:00:58
 0:08:43
0:08:43
 0:06:59
0:06:59
 0:23:25
0:23:25
 0:00:31
0:00:31
 0:08:32
0:08:32
 0:07:45
0:07:45
 0:00:16
0:00:16
 0:00:16
0:00:16
 0:03:57
0:03:57
 0:15:18
0:15:18
 0:00:14
0:00:14
 0:06:39
0:06:39
 0:16:22
0:16:22
 0:07:51
0:07:51
 0:14:08
0:14:08
 0:25:41
0:25:41