filmov
tv
Find the value of right angle triangle | Pythagoras' theorem | triangle | right angle triangle

Показать описание
a theorem attributed to Pythagoras that the square on the hypotenuse of a right-angled triangle is equal in area to the sum of the squares on the other two sides.
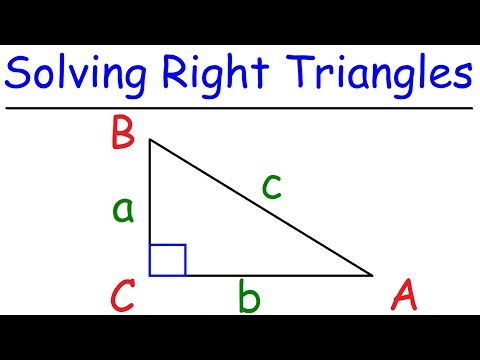
In mathematics, the Pythagorean theorem, or Pythagoras' theorem, is a fundamental relation in Euclidean geometry among the three sides of a right triangle. It states that the area of the square whose side is the hypotenuse (the side opposite the right angle) is equal to the sum of the areas of the squares on the other two sides. This theorem can be written as an equation relating the lengths of the sides a, b and c, often called the Pythagorean equation.
In mathematics, the Pythagorean theorem, or Pythagoras' theorem, is a fundamental relation in Euclidean geometry among the three sides of a right triangle. It states that the area of the square whose side is the hypotenuse (the side opposite the right angle) is equal to the sum of the areas of the squares on the other two sides. This theorem can be written as an equation relating the lengths of the sides a, b and c, often called the Pythagorean equation.
Pythagorean Theorem | MathHelp.com
Pythagorean Theorem Easy Way-Find Value of X using Pythagorean Theorem
Finding the Value of the Underlined Digit | Decimal Place Value | Math with Mr. J
If Given a Semicircle with a Right Triangle, Find the Value of the Line Segment X | Easy Tutorial
Find the Value of X in this Purple Right Triangle | Step-by-Step Tutorial
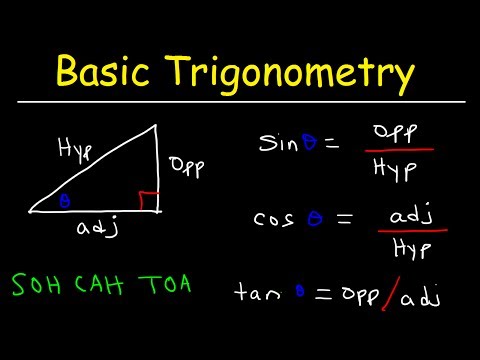
Trigonometry: Solving Right Triangles... How? (NancyPi)
Trigonometry - How To Solve Right Triangles
How To Calculate The Missing Side Length of a Triangle
Taking it to the max: optimization problems
Find the value of right angle triangle | Pythagoras' theorem | triangle | right angle triangle
how to find the value of x in a right angled triangle.#youtubeshorts #mathstricks #mathlover #maths
Find value of x, for the right-angled triangle| Leaving Cert Maths |Quadratic Eq
Find the Value of X & Y in this Right Triangle | Fast & Easy Explanation
Find the measure of three angles by determining the value of x
Find the value of h, with the provided measurements in this diagram.
Joyce Meyer: Find Value in Every Season of Life | Praise on TBN
Find the value of x in the triangle.
Trigonometry For Beginners!
In the given right angled triangle angle B= 90°.find the value of x.Simple equation class 7 maths.
If angleAOB is a right angle, find the value of x in each of the following diagrams: | 6 | ANGL...
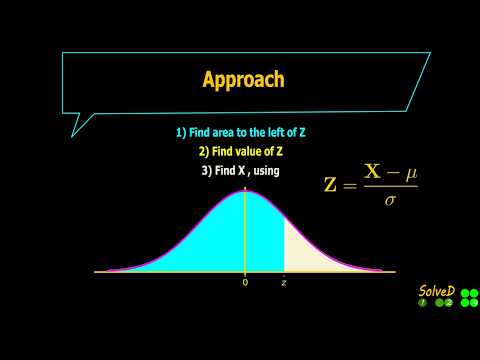
Find X value from given right side area| Standard Normal Distribution Curve| Leaving Cert Maths |
Finding the Value of the Underlined Digit | Whole Number Place Value | Math with Mr. J
Find value of x, right angled triangle in a semi-circle| EXAM Question| Leaving Cert Maths |
Calculus - How to find the value of a one sided limit using the graph
Комментарии
 0:01:57
0:01:57
 0:02:42
0:02:42
 0:03:20
0:03:20
 0:06:47
0:06:47
 0:05:53
0:05:53
 0:13:29
0:13:29
 0:11:00
0:11:00
 0:29:56
0:29:56
 1:01:41
1:01:41
 0:00:48
0:00:48
 0:00:16
0:00:16
 0:02:10
0:02:10
 0:08:01
0:08:01
 0:01:09
0:01:09
 0:03:42
0:03:42
 0:16:10
0:16:10
 0:12:28
0:12:28
 0:21:52
0:21:52
 0:05:35
0:05:35
 0:01:30
0:01:30
 0:02:06
0:02:06
 0:03:11
0:03:11
 0:02:42
0:02:42
 0:04:04
0:04:04