filmov
tv
Find the Value of X & Y in this Right Triangle | Fast & Easy Explanation

Показать описание
Find the value of x and y
Solving Two - Step Equations - How to Find the Value of X!
Find the value of x
Find the value of x
Find the value of x in the triangle.
Find the value of x. (4^x=128)
Determinate find the value of x good and easy example(PART-1)
Finding the value of x using supplementary angles - Free Math Videos
Proportion|find the value of x #maths #education #proportion #findthevalueofx
Find the measure of three angles by determining the value of x
Find the Value of x, and the Missing Angle Measures
Solving an equation for y and x
Algebra - How To Solve Equations Quickly!
Find the Value of X | Linear Equation Combine Same Terms [CSE Math]
Find the value of X | Solve the given Equation and Inequality
Solving algebra fractions to find the value of x
Find the value of x, Logarithms
Applying the Relationship of Corresponding Angles to Find the Value of x
Proportions: What value for X makes the proportion true?
Pythagorean Theorem Easy Way-Find Value of X using Pythagorean Theorem
Simple Equation | How to find the Value of x? | Genius Learning Point
Solve for X. Find the value of X
TAGALOG MATH Simple Algebra Finding The Value of X | Tagalog Math Tutorial Algebra | MathGaling
How to Solve One-Step Equations | One-Step Equation Steps | Math with Mr. J
Комментарии
 0:04:55
0:04:55
 0:08:59
0:08:59
 0:03:01
0:03:01
 0:04:15
0:04:15
 0:12:28
0:12:28
 0:04:46
0:04:46
 0:04:26
0:04:26
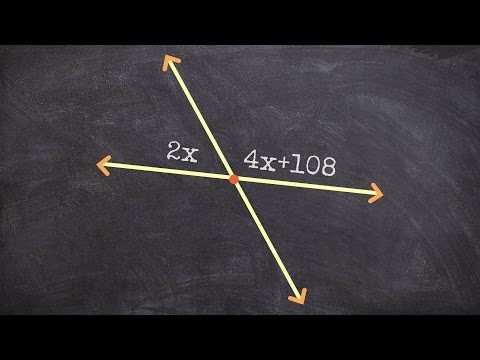 0:03:05
0:03:05
 0:01:00
0:01:00
 0:01:09
0:01:09
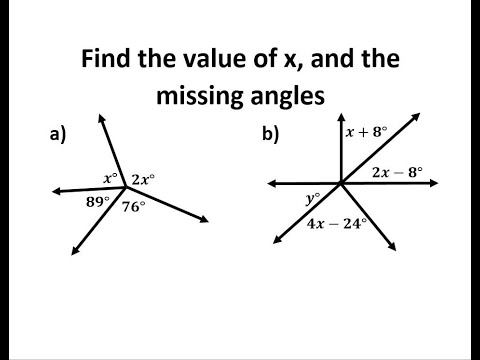 0:10:07
0:10:07
 0:03:47
0:03:47
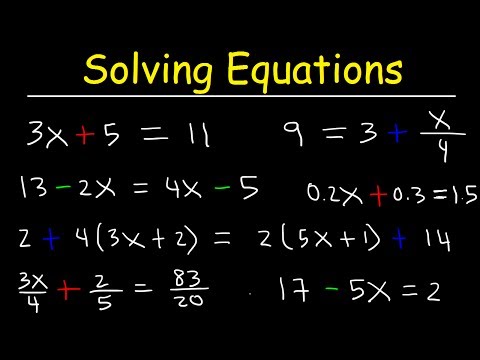 0:25:05
0:25:05
 0:07:23
0:07:23
 0:16:37
0:16:37
 0:06:56
0:06:56
 0:06:42
0:06:42
 0:02:01
0:02:01
 0:02:42
0:02:42
 0:02:42
0:02:42
 0:26:40
0:26:40
 0:15:51
0:15:51
 0:31:45
0:31:45
 0:06:54
0:06:54