filmov
tv
Crisper Cas9 Gene (DNA) editing System

Показать описание
CRISPR-Cas9 is a revolutionary gene editing technology that acts like a precise pair of molecular scissors for DNA. Here's a short explanation:
How it works:
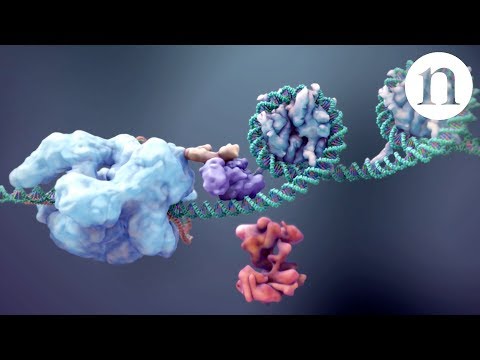
* Guide RNA (gRNA): A short, synthetic RNA molecule is designed to be complementary to a specific target DNA sequence you want to edit. It acts like a "homing device," guiding the Cas9 enzyme to the correct location in the genome.
* Cas9 Enzyme: This is a bacterial enzyme (a nuclease) that can cut DNA. It travels along the DNA until it encounters the sequence that matches the gRNA.
* Target Recognition: The gRNA binds to the complementary DNA sequence, telling Cas9 where to make the cut.
* Double-Strand Break (DSB): Once the gRNA guides it to the target, Cas9 creates a precise double-strand break in the DNA.
* Cellular Repair: The cell's natural DNA repair mechanisms kick in to fix this break. There are two main pathways:
* Non-homologous End Joining (NHEJ): This often leads to small insertions or deletions (indels) at the break site, which can disrupt a gene.
* Homologous Recombination (HR): If a donor DNA template with the desired change is provided, the cell can use it to repair the break, precisely inserting the new genetic information.
In short, CRISPR-Cas9 allows scientists to precisely target and cut specific DNA sequences in a genome, enabling them to delete, insert, or modify genes with relative ease and efficiency. This has vast implications for research and potential therapeutic applications.
#muhammadumerfarooqbiology
#crisper
#geneediting
How it works:
* Guide RNA (gRNA): A short, synthetic RNA molecule is designed to be complementary to a specific target DNA sequence you want to edit. It acts like a "homing device," guiding the Cas9 enzyme to the correct location in the genome.
* Cas9 Enzyme: This is a bacterial enzyme (a nuclease) that can cut DNA. It travels along the DNA until it encounters the sequence that matches the gRNA.
* Target Recognition: The gRNA binds to the complementary DNA sequence, telling Cas9 where to make the cut.
* Double-Strand Break (DSB): Once the gRNA guides it to the target, Cas9 creates a precise double-strand break in the DNA.
* Cellular Repair: The cell's natural DNA repair mechanisms kick in to fix this break. There are two main pathways:
* Non-homologous End Joining (NHEJ): This often leads to small insertions or deletions (indels) at the break site, which can disrupt a gene.
* Homologous Recombination (HR): If a donor DNA template with the desired change is provided, the cell can use it to repair the break, precisely inserting the new genetic information.
In short, CRISPR-Cas9 allows scientists to precisely target and cut specific DNA sequences in a genome, enabling them to delete, insert, or modify genes with relative ease and efficiency. This has vast implications for research and potential therapeutic applications.
#muhammadumerfarooqbiology
#crisper
#geneediting
 0:04:13
0:04:13
 0:14:27
0:14:27
 0:05:29
0:05:29
 0:01:39
0:01:39
 0:04:32
0:04:32
 0:03:14
0:03:14
 0:04:22
0:04:22
 0:05:14
0:05:14
 0:00:54
0:00:54
 0:00:36
0:00:36
 0:01:14
0:01:14
 0:10:02
0:10:02
 0:05:25
0:05:25
 0:09:44
0:09:44
 0:06:07
0:06:07
 0:09:19
0:09:19
 0:13:45
0:13:45
 0:01:18
0:01:18
 0:07:46
0:07:46
 0:14:00
0:14:00
 0:00:41
0:00:41
 0:16:42
0:16:42
 0:10:14
0:10:14
 0:07:21
0:07:21