filmov
tv
Excel 2013 Statistical Analysis #43: Simple Random Sampling in Excel: Process & Theory
Показать описание
Topics in this video:
1. (00:12) Chapter explanation
2. (01:57) Discussion about Samples, Point Estimates and Sampling Error
3. (03:50) Why take samples rather than use all the population items?
4. (05:10) What do we use samples for? Answering Research Questions!
5. (06:01) Learn about Sample Population and Target Population
6. (08:58) What is a Frame? Frame = List of items in population
7. (10:58) Simple Random Sampling: use when you have a finite population where you can create a frame.
8. (11:33) Random Sampling: use when you have a finite population or on-going process where you cannot create a frame. Two important points must hold true before selecting n items in a random way: 1) All items must be from same population (Samples = Target) and 2) Items must be selected Independently (without bias)
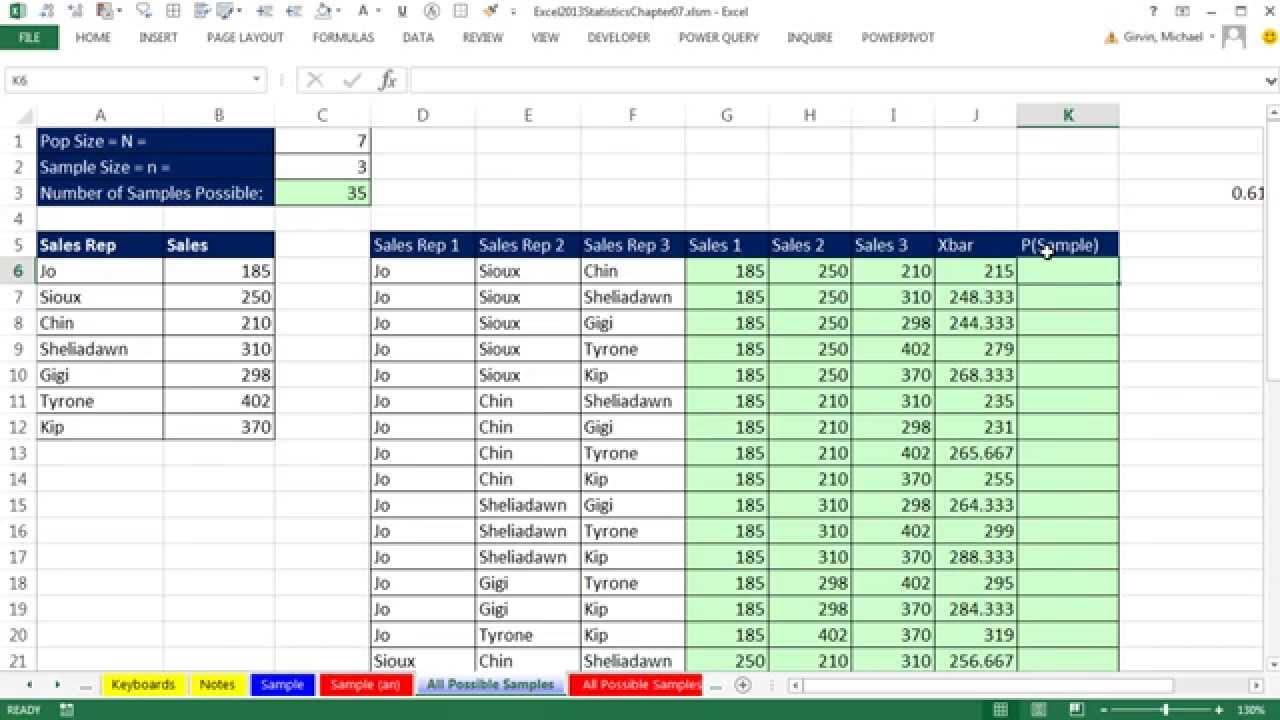
9. (13:25) Define Simple Random Sampling and do a few tests in Excel to prove to ourselves that the definition makes sense. We will look at one sample and the sampling error, then we will list all possible samples and then calculate the probability that we could get any one sample.
10. (16:20) Use VLOOKUP to list all numbers for all possible samples
11. (17:58) Calculate Sample Mean, Xbar, for every one of the possible samples
12. (18:18) Calculate probability of each sample (part of definition of Simple Random Sample)
13. (19:30) Introduction to RAND function
14. (20:36) Create Simple Random Sample using RAND Excel function (0 greater than or equal to 15 digit Number less than 1), the Sort Feature and Copy & Paste.
15. (23:12) Create Simple Random Sample using RAND, SMALL and VLOOKUPO Excel functions
16. (25:53) Conclusion
1. (00:12) Chapter explanation
2. (01:57) Discussion about Samples, Point Estimates and Sampling Error
3. (03:50) Why take samples rather than use all the population items?
4. (05:10) What do we use samples for? Answering Research Questions!
5. (06:01) Learn about Sample Population and Target Population
6. (08:58) What is a Frame? Frame = List of items in population
7. (10:58) Simple Random Sampling: use when you have a finite population where you can create a frame.
8. (11:33) Random Sampling: use when you have a finite population or on-going process where you cannot create a frame. Two important points must hold true before selecting n items in a random way: 1) All items must be from same population (Samples = Target) and 2) Items must be selected Independently (without bias)
9. (13:25) Define Simple Random Sampling and do a few tests in Excel to prove to ourselves that the definition makes sense. We will look at one sample and the sampling error, then we will list all possible samples and then calculate the probability that we could get any one sample.
10. (16:20) Use VLOOKUP to list all numbers for all possible samples
11. (17:58) Calculate Sample Mean, Xbar, for every one of the possible samples
12. (18:18) Calculate probability of each sample (part of definition of Simple Random Sample)
13. (19:30) Introduction to RAND function
14. (20:36) Create Simple Random Sample using RAND Excel function (0 greater than or equal to 15 digit Number less than 1), the Sort Feature and Copy & Paste.
15. (23:12) Create Simple Random Sample using RAND, SMALL and VLOOKUPO Excel functions
16. (25:53) Conclusion
Комментарии
 0:26:57
0:26:57
 2:22:43
2:22:43
 0:15:48
0:15:48
 0:05:31
0:05:31
 0:43:39
0:43:39
 0:02:03
0:02:03
 0:45:39
0:45:39
 0:41:39
0:41:39
 0:54:43
0:54:43
 0:11:28
0:11:28
 0:24:16
0:24:16
 0:09:54
0:09:54
 0:20:17
0:20:17
 0:41:36
0:41:36
 0:19:28
0:19:28
 0:16:40
0:16:40
 0:05:23
0:05:23
 0:30:11
0:30:11
 0:25:55
0:25:55
 0:00:32
0:00:32
 0:15:13
0:15:13
 0:00:21
0:00:21
 0:03:05
0:03:05
 0:05:10
0:05:10