filmov
tv
MRI Scan Animation : How magnetic resonance imaging works

Показать описание
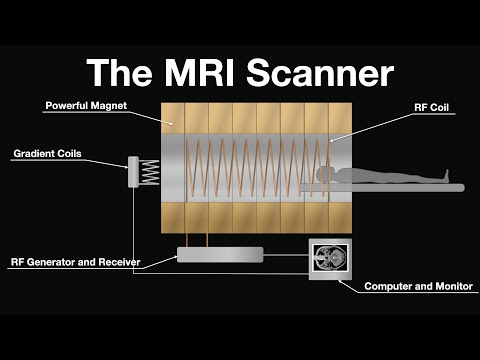
This animation explains how a MRI scan is obtained. It covers how the magnetic resonance signal is produced and detected in the body using powerful magnets and radiofrequency pulses. The role of key components (magnets, gradient coils, and RF coil) are linked to the processes taking place in the body. The animation explains how the MRI signal is localised in image slices of the body using gradient coils. Methods of detecting tissue contrast are introduced, though not explained in detail since the aim of this animation is to introduce the primary concepts of producing an image (proton density, transverse relaxation time, RF pulse sequences and delayed application of localisation fields).
A link to a free quiz on the content of the video is shown at 7:59. Test yourself and check you grasped the main points.
Relevant concepts: nuclear magnetic resonance imaging, protons, precession, Larmor frequency, magnetic field strength, relaxation, phase, transverse and longitudinal vectors, e.m.f., induction and Fourier transformations.
Essential learning for A-Level physics, and medical physics courses at university.
OCR physics A, AQA A-Level physics, Edexcel A-Levrl physics
A link to a free quiz on the content of the video is shown at 7:59. Test yourself and check you grasped the main points.
Relevant concepts: nuclear magnetic resonance imaging, protons, precession, Larmor frequency, magnetic field strength, relaxation, phase, transverse and longitudinal vectors, e.m.f., induction and Fourier transformations.
Essential learning for A-Level physics, and medical physics courses at university.
OCR physics A, AQA A-Level physics, Edexcel A-Levrl physics
Комментарии
 0:03:49
0:03:49
 0:07:00
0:07:00
 0:03:11
0:03:11
 0:08:15
0:08:15
 0:01:21
0:01:21
 0:17:53
0:17:53
 0:10:33
0:10:33
 0:10:04
0:10:04
 0:01:01
0:01:01
 0:00:06
0:00:06
 0:03:33
0:03:33
 0:01:00
0:01:00
 0:03:05
0:03:05
 0:00:05
0:00:05
 0:03:13
0:03:13
 0:01:01
0:01:01
 0:04:37
0:04:37
 0:00:53
0:00:53
 0:19:26
0:19:26
 0:03:57
0:03:57
 0:02:25
0:02:25
 0:04:34
0:04:34
 0:00:24
0:00:24
 0:01:17
0:01:17