filmov
tv
What Causes Light to Refract?

Показать описание
Observe what occurs when light travels from the air, through a liquid.
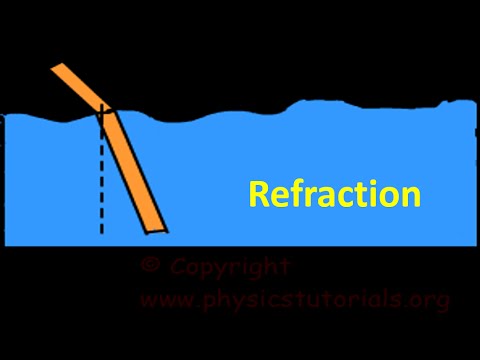
When waves pass through one medium into another medium of different density, the speed of the waves changes. The change in speed causes the waves to change direction. This change in speed and direction is
called refraction.
The amount of light that is refracted depends on the difference in density between the two mediums. The greater the difference in densities between two mediums, the more light bends as it passes through them. Look at the pencil in the glass of water below. The change in density as light moves from the air to the water bends the light waves and causes the pencil to appear broken.
Spectacles, binoculars and telescopes refract light through their arrangement of lenses. As light passes from air through the glass of the lenses, it slows down and bends. As it leaves the lens and enters the air again, it speeds up.
Light can be refracted to bring the light rays closer together and make objects appear closer. It can also be refracted to spread out the rays and cause objects to appear further away.
What is Light?
Light is a form of energy that is made of vibrating magnetic and electric fields which travel out from its source as light waves. Light waves vibrate perpendicular to one another and also perpendicular to the direction the light wave is traveling. Light waves are transverse waves. Wavelength is the distance between two similar points in the repeating pattern of a wave. We are able to see light when the wavelengths of the light waves are in a certain range. This light is called visible light. Light waves with wavelengths shorter or longer than visible light cannot be seen with our eyes.
How Light Travels
Like thermal energy, light can travel through solids, liquids, gases and in a vacuum. In the vacuum of space, light travels at almost
300,000 km/s (186,000 mi/s). It takes the light from the Sun – our main source of light, about eight minutes to reach the Earth. Light travels slightly slower in air and slower still in liquids
and solids.
Light waves travel out from their source in straight lines called rays. Rays do not bend or curve, but can act in different ways when they
hit an object.
When you hold a tennis ball out and release it, it falls in a straight line until it hits the floor. It then bounces up in the direction in which it was dropped. The angle at which the ball bounces off is equal to the angle at which it hit the ground.
Reflection of light works in a similar way. Reflection is the change in direction of waves.
When waves pass through one medium into another medium of different density, the speed of the waves changes. The change in speed causes the waves to change direction. This change in speed and direction is
called refraction.
The amount of light that is refracted depends on the difference in density between the two mediums. The greater the difference in densities between two mediums, the more light bends as it passes through them. Look at the pencil in the glass of water below. The change in density as light moves from the air to the water bends the light waves and causes the pencil to appear broken.
Spectacles, binoculars and telescopes refract light through their arrangement of lenses. As light passes from air through the glass of the lenses, it slows down and bends. As it leaves the lens and enters the air again, it speeds up.
Light can be refracted to bring the light rays closer together and make objects appear closer. It can also be refracted to spread out the rays and cause objects to appear further away.
What is Light?
Light is a form of energy that is made of vibrating magnetic and electric fields which travel out from its source as light waves. Light waves vibrate perpendicular to one another and also perpendicular to the direction the light wave is traveling. Light waves are transverse waves. Wavelength is the distance between two similar points in the repeating pattern of a wave. We are able to see light when the wavelengths of the light waves are in a certain range. This light is called visible light. Light waves with wavelengths shorter or longer than visible light cannot be seen with our eyes.
How Light Travels
Like thermal energy, light can travel through solids, liquids, gases and in a vacuum. In the vacuum of space, light travels at almost
300,000 km/s (186,000 mi/s). It takes the light from the Sun – our main source of light, about eight minutes to reach the Earth. Light travels slightly slower in air and slower still in liquids
and solids.
Light waves travel out from their source in straight lines called rays. Rays do not bend or curve, but can act in different ways when they
hit an object.
When you hold a tennis ball out and release it, it falls in a straight line until it hits the floor. It then bounces up in the direction in which it was dropped. The angle at which the ball bounces off is equal to the angle at which it hit the ground.
Reflection of light works in a similar way. Reflection is the change in direction of waves.
 0:00:59
0:00:59
 0:04:53
0:04:53
 0:13:36
0:13:36
 0:02:01
0:02:01
 0:29:24
0:29:24
 0:03:30
0:03:30
 0:01:35
0:01:35
 0:11:24
0:11:24
 0:07:26
0:07:26
 0:02:35
0:02:35
 0:04:32
0:04:32
 0:01:17
0:01:17
 0:01:00
0:01:00
 0:05:28
0:05:28
 0:13:25
0:13:25
 0:05:55
0:05:55
 0:04:44
0:04:44
 0:04:15
0:04:15
 0:04:54
0:04:54
 0:00:21
0:00:21
 0:03:59
0:03:59
 0:01:03
0:01:03
 0:06:20
0:06:20
 0:00:33
0:00:33