filmov
tv
Ketone Bodies (Part 1 of 4) - Intro

Показать описание
In this video, I give brief introduction to ketone bodies, describing what they are, what their purpose/function is, and where they are made.
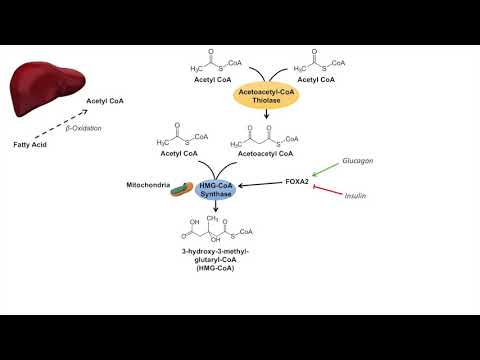
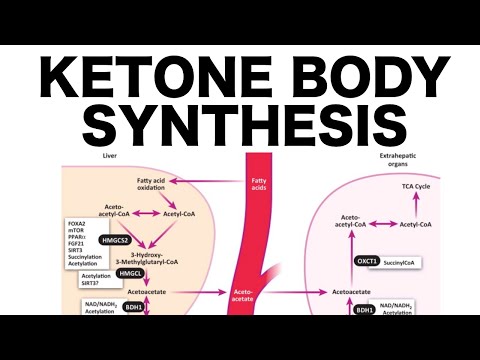
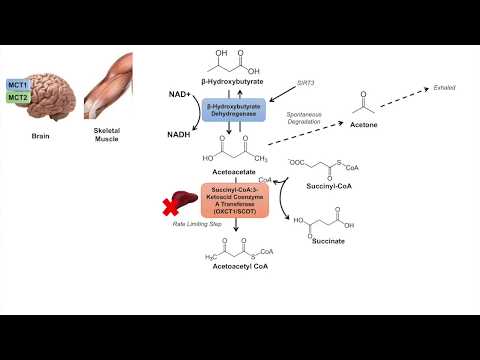
There are three Ketone Bodies: Acetone, Acetoacetate, and D--Hydroxybutyrate (structures shown in the video). They are all made in the mitochondrial matrix of liver cells (hepatocytes) from Acetyl-CoA (from beta oxidation) that built up due to lack of flux through the Krebs Cycle. Acetyl-CoA, being an activated 2-carbon unit, does not hang around very long, and if it’s not going through the Krebs Cycle, it’s diverted off to Ketone Body Synthesis, otherwise known as Ketogenesis. Between the three ketone bodies, acetone is produced to a lesser extent, while acetoacetate and D--Hydroxybutyrate are produced to a greater extent. Ketone Bodies function as an energy source for extrahepatic tissues, meaning tissues other than the liver. The liver produces ketone bodies to be sent in the blood to be used by other tissues. Even the brain, which prefers to use glucose as its sole energy source, adapts to using ketone bodies for energy during starvation.
Don't forget to LIKE, COMMENT, and SUBSCRIBE:
Комментарии
 0:05:44
0:05:44
 0:31:23
0:31:23
 0:02:02
0:02:02
 0:07:04
0:07:04
 0:21:11
0:21:11
 0:09:06
0:09:06
 0:12:07
0:12:07
 0:01:37
0:01:37
 0:09:27
0:09:27
 0:09:27
0:09:27
 0:29:40
0:29:40
 0:03:07
0:03:07
 0:14:23
0:14:23
 0:18:59
0:18:59
 0:14:46
0:14:46
 0:07:23
0:07:23
 0:09:27
0:09:27
 0:02:39
0:02:39
 0:00:35
0:00:35
 0:15:37
0:15:37
 0:00:53
0:00:53
 0:04:28
0:04:28
 0:36:42
0:36:42
 0:00:45
0:00:45