filmov
tv
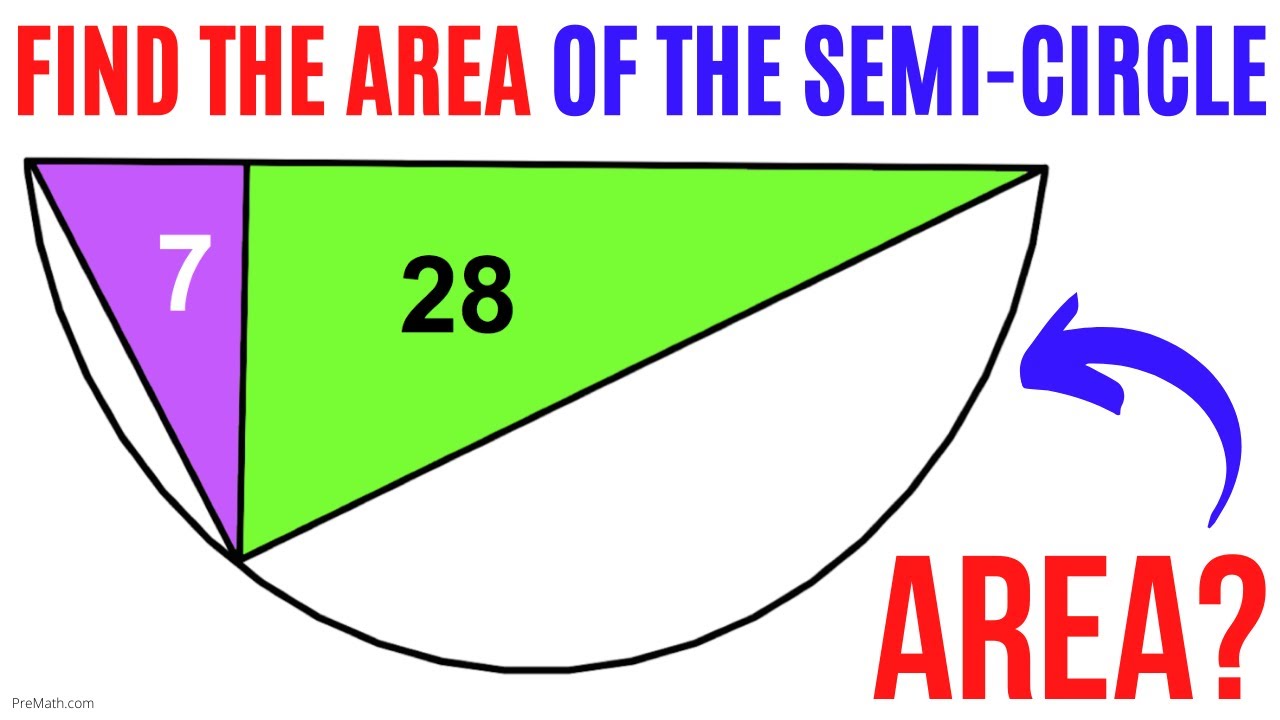
Can You Find the Area of this Semicircle? | Step-by-Step Explanation
Показать описание
Can you find area of the Green shaded region? | (Semicircle) | #math #maths | #geometry
Math Antics - Area
Finding the Area of a Composite Figure | Area of Composite Rectangles
Can you find area of the Green shaded Triangle? | (Justify) | #math #maths | #geometry
Can You Find the Area of This Figure?
Find the Area Challenge
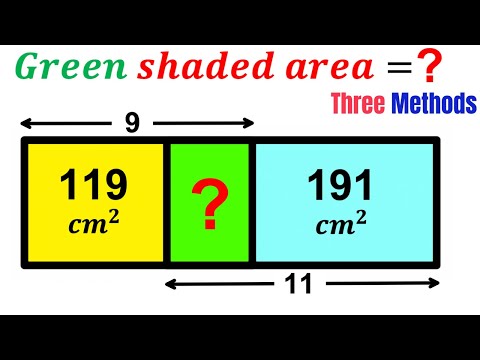
Can you find area of the Green shaded rectangle? | (3 Methods) | #math #maths | #geometry
How to Find Area | Rectangles, Squares, Triangles, & Circles | Math Mr. J
Can you find area of the Blue triangle? | (Fun Geometry Problem) | #math #maths | #geometry
How to Find the Area of a Square | Math with Mr. J
Can you find the area of this triangle??
Can you find area of Green, Yellow, and Blue squares? | (Semicircle) | #math #maths #geometry
Area for Kids
How to Find the Area of a Triangle | Calculate the Area of a Triangle
Can you find area of the Yellow shaded Square? | (Triangle) | #math #maths | #geometry
Can you find the Area of the Green shaded Region? | Quick & Easy Tutorial
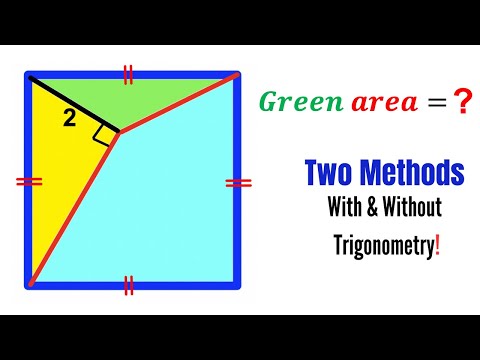
Can you find area of the Green shaded region? | (Squares) | #math #maths | #geometry
Can you find area of the big square ? #Math
Can you find area of the Green shaded Triangle? | (Two Methods) | #math #maths | #geometry
Can you find the Area of the 2 Purple Triangles in 1 minute? | Quick & Simple Explanation
Can You Find the Area of this Semicircle? | Step-by-Step Explanation
Can YOU find the area of the blue triangle ???
Can you find the area of the Purple triangle? | (Important Geometry skills explained) | #math #maths
Can you find area of the Yellow shaded Trapezoid? | (Two Methods) | #math #maths | #geometry
Комментарии
 0:11:53
0:11:53
 0:10:26
0:10:26
 0:07:14
0:07:14
 0:10:16
0:10:16
 0:03:39
0:03:39
 0:04:33
0:04:33
 0:12:49
0:12:49
 0:22:10
0:22:10
 0:13:42
0:13:42
 0:02:48
0:02:48
 0:06:10
0:06:10
 0:17:40
0:17:40
 0:08:58
0:08:58
 0:06:37
0:06:37
 0:08:42
0:08:42
 0:10:34
0:10:34
 0:08:52
0:08:52
 0:03:49
0:03:49
 0:09:08
0:09:08
 0:03:50
0:03:50
 0:09:46
0:09:46
 0:01:38
0:01:38
 0:11:19
0:11:19
 0:11:48
0:11:48