filmov
tv
Math Olympiad | A Very Nice Geometry Problem | 2 Different Methods

Показать описание
Math Olympiad | A Very Nice Geometry Problem | 2 Methods
Math Olympiad | A Very Nice Geometry Problem | 2 Different Methods
The United States | Maths Olympiad | A Very tricky Algebra problems |
Math Olympiad | A Very Nice Geometry Problem
A beautiful international math olympiad problem
Norway Math Olympiad Question | You should be able to solve this!
A Very Nice Math Olympiad Problem | Solve for a, b and c | Algebra
The unexpectedly hard windmill question (2011 IMO, Q2)
Luxembourg - Math Olympiad Question | You should know this trick
Math Olympiad Question | Equation solving | You should learn this trick to pass the exam
A Nice Math Olympiad Exponential Equation 3^x = X^9
Math Olympiad | A Very Nice Algebra Problem
France Math Olympiad | A Very Nice Geometry Problem
Math Olympiad | A Very Nice Geometry Problem | 2 Different Methods
A Nice Olympiad Exponential Multiplication Problem #short #olympiad #mathematics #maths #exponents
Russian Math Olympiad | A Very Nice Geometry Problem
Canada Math Olympiad Problem | A Very Nice Geometry Challenge
Thailand | Math Olympiad Question | Nice Algebra Equation
Math Olympiad | A Very Nice Geometry Problem
Math Olympiad Practice
Math Olympiad 3^m–2^m=65 | Math Olympiad Problems | Algebra
Solving an IMO Problem in 6 Minutes!! | International Mathematical Olympiad 1979 Problem 1
Mexico - A Nice Math Olympiad Exponential Problem
Math Olympiad Question | You should know this trick!!
Комментарии
 0:13:46
0:13:46
 0:07:33
0:07:33
 0:12:05
0:12:05
 0:01:00
0:01:00
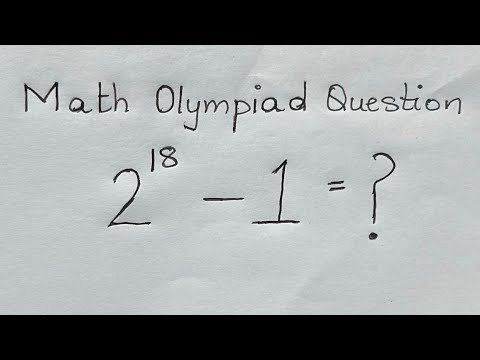 0:03:21
0:03:21
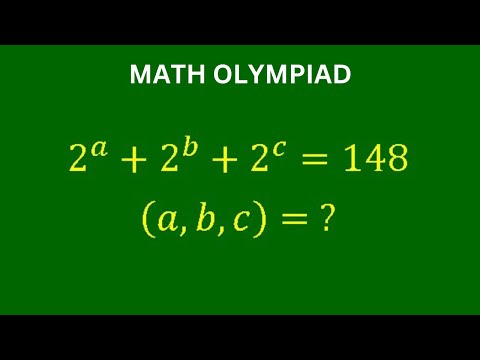 0:12:31
0:12:31
 0:16:03
0:16:03
 0:02:51
0:02:51
 0:01:54
0:01:54
 0:02:34
0:02:34
 0:08:38
0:08:38
 0:12:37
0:12:37
 0:15:27
0:15:27
 0:00:52
0:00:52
 0:14:34
0:14:34
 0:15:38
0:15:38
 0:01:26
0:01:26
 0:08:41
0:08:41
 0:01:00
0:01:00
 0:10:49
0:10:49
 0:06:40
0:06:40
 0:08:36
0:08:36
 0:00:33
0:00:33