filmov
tv
Distal Radius Fractures - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim

Показать описание
Dr. Ebraheim’s educational animated video describing different concepts of distal radius fractures.
Highlight points about distal radius fractures:
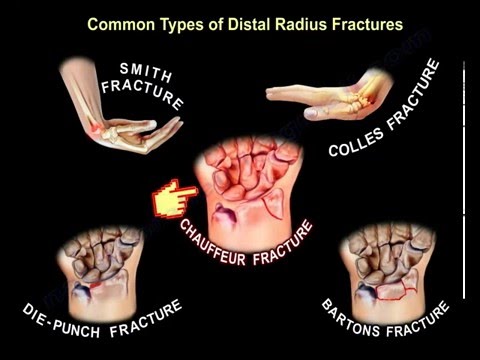
1- The fracture being extra- or intra- articular: the intra-articular fractures are usually worse than the extra- articular fractures.
Fracture of the distal radius has many types and classifications:
• Fernandes.
• Frykman.
• Melone.
• Three Column Theory.
• AO.
- Each type will require a specific management and not all of them can be treated with a cast.
2- May be DRUJ or ulnar styloid process injuries:
- Ulnar styloid process injury may not need to be fixed.
- Fix the radius first and then test the joint.
- if it is grossly unstable, fix the radioulnar joint, or you can fix the ulnarstyloid process if the fracture is big
- extensor carpi ulnaris tendon entrapment can cause irreducible dorsal dislocation of the ulna.
3- Osteoporosis:
- Osteoporosis is a decrease in bone strength.
- Osteoporitic bone is at risk of fracture at the hip, spine, and wrist.
- DEXA scan is used to study the bone mass to prevent future fracture of the spine and hip.
- Wrist fractures occur at a younger age than fractures of the spine and hip.
4- Extensor Pollicis Longus rupture:
- The EPL tendon is commonly ruptured due to nondisplaced fractures of the distal radius (attrition rupture).
- It can occur from a prominent hardware.
- When screws are used, they should not penetrate the dorsal cortex to avoid injuring the EPL tendon.
- Rupture of the EPL tendon is usually treated with transfer of the extensor indicis tendon.
- NOTE: FPL rupture can be seen with prominent volar hardware.
5- Vitamin C use for reflex sympathetic dystrophy (RSD):
- 500 milligrams of vitamin C is given every day for 50 days.
- Reflex sympathetic dystrophy is a clinical syndrome of variable course and unknown cause characterized by pain, swelling, and vasomotor dysfunction of an extremity.
- This condition is often the result of trauma or surgery.
6- Acute Carpal Tunnel Syndrome:
- Carpal tunnel syndrome is a common condition following a distal radius fracture.
- Surgical release of the carpal tunnel and fracture fixation should be performed urgently.
- It can also occur following ORIF of the distal radius fracture.
- The patient will have dense numbness in the distribution of the median nerve after surgery especially after supraclavicular regional anesthesia wear off.
- Do immediate open carpal tunnel release.
Treatment of distal radius:
• Therapy may not be needed routinely; it has the same result as home exercises.
• It is important to get the fingers moving as soon as possible (there is no need for early wrist motion even if the radius fixation is stable).
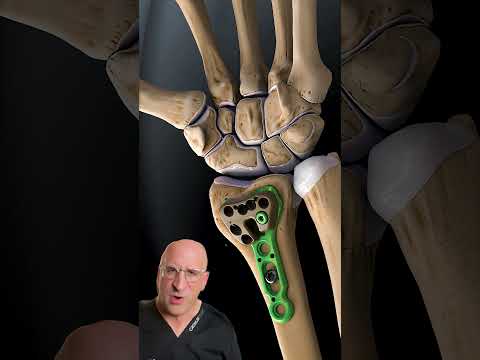
Surgery:
• Dorsal and volar planting das no difference in complication.
• Dorsal planting is used for dorsal shearing fracture.
• Volar planting is routinely used for most of these fractures.
• External fixation is less desirable.
• The American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons (AAOS) wants less than 10° of dorsal tilt; the normal amount of tilt is 12° of volar tilt.
• The AAOS wants radial inclination angle loss of less than 10°.
• The normal angle is 23°.
• Radial shortening should be less than 3 mm.
• Intra- articular step off of less than 2mm. Arthritis correlates with step off more than 2mm (may not be symptomatic).
Guidelines for Reduction:
• With older patients, you can go with nonanatomic reduction and casting.
• Patients younger than 55 years of age, surgery is recommended for optimal reduction if the fracture is displaced.
• For patients above 55 years of age, the optimal treatment is not clear.
• Radius malunion can create a DISI deformity which can be treated with osteotomy and correction of the deformity.
Become a friend on facebook:
Follow me on twitter:
Donate to the University of Toledo Foundation Department of Orthopaedic Surgery Endowed Chair Fund:
Highlight points about distal radius fractures:
1- The fracture being extra- or intra- articular: the intra-articular fractures are usually worse than the extra- articular fractures.
Fracture of the distal radius has many types and classifications:
• Fernandes.
• Frykman.
• Melone.
• Three Column Theory.
• AO.
- Each type will require a specific management and not all of them can be treated with a cast.
2- May be DRUJ or ulnar styloid process injuries:
- Ulnar styloid process injury may not need to be fixed.
- Fix the radius first and then test the joint.
- if it is grossly unstable, fix the radioulnar joint, or you can fix the ulnarstyloid process if the fracture is big
- extensor carpi ulnaris tendon entrapment can cause irreducible dorsal dislocation of the ulna.
3- Osteoporosis:
- Osteoporosis is a decrease in bone strength.
- Osteoporitic bone is at risk of fracture at the hip, spine, and wrist.
- DEXA scan is used to study the bone mass to prevent future fracture of the spine and hip.
- Wrist fractures occur at a younger age than fractures of the spine and hip.
4- Extensor Pollicis Longus rupture:
- The EPL tendon is commonly ruptured due to nondisplaced fractures of the distal radius (attrition rupture).
- It can occur from a prominent hardware.
- When screws are used, they should not penetrate the dorsal cortex to avoid injuring the EPL tendon.
- Rupture of the EPL tendon is usually treated with transfer of the extensor indicis tendon.
- NOTE: FPL rupture can be seen with prominent volar hardware.
5- Vitamin C use for reflex sympathetic dystrophy (RSD):
- 500 milligrams of vitamin C is given every day for 50 days.
- Reflex sympathetic dystrophy is a clinical syndrome of variable course and unknown cause characterized by pain, swelling, and vasomotor dysfunction of an extremity.
- This condition is often the result of trauma or surgery.
6- Acute Carpal Tunnel Syndrome:
- Carpal tunnel syndrome is a common condition following a distal radius fracture.
- Surgical release of the carpal tunnel and fracture fixation should be performed urgently.
- It can also occur following ORIF of the distal radius fracture.
- The patient will have dense numbness in the distribution of the median nerve after surgery especially after supraclavicular regional anesthesia wear off.
- Do immediate open carpal tunnel release.
Treatment of distal radius:
• Therapy may not be needed routinely; it has the same result as home exercises.
• It is important to get the fingers moving as soon as possible (there is no need for early wrist motion even if the radius fixation is stable).
Surgery:
• Dorsal and volar planting das no difference in complication.
• Dorsal planting is used for dorsal shearing fracture.
• Volar planting is routinely used for most of these fractures.
• External fixation is less desirable.
• The American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons (AAOS) wants less than 10° of dorsal tilt; the normal amount of tilt is 12° of volar tilt.
• The AAOS wants radial inclination angle loss of less than 10°.
• The normal angle is 23°.
• Radial shortening should be less than 3 mm.
• Intra- articular step off of less than 2mm. Arthritis correlates with step off more than 2mm (may not be symptomatic).
Guidelines for Reduction:
• With older patients, you can go with nonanatomic reduction and casting.
• Patients younger than 55 years of age, surgery is recommended for optimal reduction if the fracture is displaced.
• For patients above 55 years of age, the optimal treatment is not clear.
• Radius malunion can create a DISI deformity which can be treated with osteotomy and correction of the deformity.
Become a friend on facebook:
Follow me on twitter:
Donate to the University of Toledo Foundation Department of Orthopaedic Surgery Endowed Chair Fund:
Комментарии
 0:10:21
0:10:21
 0:03:55
0:03:55
 0:03:43
0:03:43
 0:00:53
0:00:53
 0:04:14
0:04:14
 0:06:33
0:06:33
 0:01:47
0:01:47
 0:01:59
0:01:59
 0:10:08
0:10:08
 0:01:11
0:01:11
 0:23:08
0:23:08
 0:00:14
0:00:14
 0:01:02
0:01:02
 0:08:18
0:08:18
 0:05:02
0:05:02
 0:27:31
0:27:31
 0:03:52
0:03:52
 0:03:44
0:03:44
 0:00:59
0:00:59
 0:01:09
0:01:09
 0:16:46
0:16:46
 0:03:08
0:03:08
 0:00:15
0:00:15