filmov
tv
Common Types Of Distal Radius Fractures - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim

Показать описание
Dr. Ebraheim’s educational animated video describes the common types of distal radius wrist fractures.
Anatomy associated with distal radius fractures:
- Radioulnar joint.
- Sigmiid notch.
- Lunate fossa.
- Scaphoid fossa.
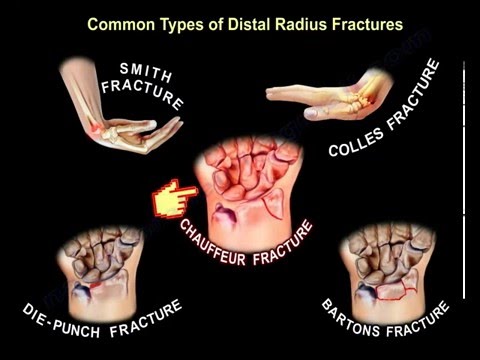
The most common types of the distal radius fractures:
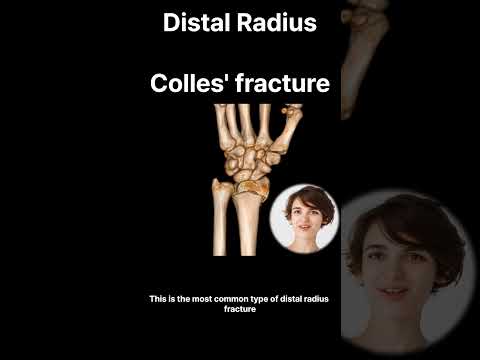
- Colles fracture:
• the most common type,
• It is a distal radius fracture in the wrist, has a characteristic backwards displacement of the hand.
• It’s a low energy fracture, extra articular fracture with dorsal displacement of the distal fracture fragment.
• It typically occurs in patients more than 50 years old from attempting to break a fall with an outstretched hand.
• This fracture some times is referred to as “dinner fork” deformity, due to the shape of the fractured forearm.
• TFCC tears occurs in 50% of extra-articular distal radius fractures versus 1/3 of intra articular fractures.
• Dorsal comminution is frequent and if comminution is to 50% of the dorsal cortex, then treatment with a cast will not work. The more dorsal flexion, then the more comminution and more chance of fracture failure when using a cast.
• Colles fracture that extends to the DRUJ has a worse prognosis.
- Smith fracture:
• Is an extra articular transverse fracture that is palmarly displaced and can be thought of as a reverse Colles fracture.
• It could occur from a fall onto a flexed wrist.
• This fracture has multiple types:
1- Type I: fracture is extra articular transverse fracture through the distal radius (most common)
2- Type II: fracture crosses into the dorsal articular surface.
3- Type III: fracture enters the radiocarpal joint (volar barton fracture equals a Smith type III fracture), both will involve the intra- articular distal radius and includes possible dissociation of the carpal bones.
- Die- Punch fracture:
• Is a depressed fracture of the lunate fossa that results from axial loading forces on the distal radius that is transmitted through the lunate bone.
• It is intra- articular fractures of the lunate fossa of the distal radius.
• Check to see if there is any carpal bone dissociation.
- Bartons fracture:
• Intra articular fracture of the distal radius with dislocation of the radiocarpal joint.
• These fractures can be dorsal or volar.
• Check for carpal bone disruption or dissociation.
• It is caused by a fall on an extended and pronated wrist with the volar type being the most common type. The fracture fragment is usually smaller with the dorsal barton fracture.
• The volar barton fracture is the fracture of the volar margin of the of the distal radius, which is associated with subluxation of the radio-carpal joint.
• The most striking finding is subluxation or dislocation of the wrist with that small fragment.
• You can see in the picture the strong volar radiocarpal ligament avulses the volar lip of the radius.
• This fracture is very similler to the Smith type III fracture.
• Treatment of volar barton fracture is usually surgery with a volar approach and volar plate.
• Dorsal Barton: the dorsal shearing force, distal radius fracture with dislocation of the radiocarpal joint, fracture ia intra-articular and involves the dorsal lip.
Dislocation is the most striking x-ray finding. The avulsed fragment is usually small.
Treatment is open reduction internal fixation through a dorsal approach.
- Chauffer fracture:
• Is fracture of the radial styloid process in association with scapholunate dissociation.
• It is caused by compression of the scaphoid bone of the hand against the styloid process of the distal radius.
• Evaluation of the radial styloid fracture should always include supinated view x-rays so that scapholunate dissociation can be ruled out.
• Look for major swelling of the wrist and distal DISI deformity on lateral x-rays with a widening gap between the lunate and scphoid bones on AP view.
• DISI deformity: the scapholunate angle is usually about 47° and can be up to 60°, any angle that is greater than 60° is considered abnormal; this is usually seen with a DISI deformity due to the palmar flexion of the scaphoid. This means that there is scaphoid dissociation. The scaphoid and lunate bones turn in opposite directions.
• Treatment of this fracture is: compression screw fixation of the radial styloid process.
• Assess the scapholunate joint for possible stabilization.
In conclusion:
- During assessment of the x-rays, you need to see if there is any involvement of the dorsal or volar rim of the radius.
- Check for involvement of the DRUJ and look for die-punch lesions.
- Check for dislocation of the wrist and the direction of the displacement.
- Check the carpal distribution to see if there is any dissociation between the carpal bones.
Anatomy associated with distal radius fractures:
- Radioulnar joint.
- Sigmiid notch.
- Lunate fossa.
- Scaphoid fossa.
The most common types of the distal radius fractures:
- Colles fracture:
• the most common type,
• It is a distal radius fracture in the wrist, has a characteristic backwards displacement of the hand.
• It’s a low energy fracture, extra articular fracture with dorsal displacement of the distal fracture fragment.
• It typically occurs in patients more than 50 years old from attempting to break a fall with an outstretched hand.
• This fracture some times is referred to as “dinner fork” deformity, due to the shape of the fractured forearm.
• TFCC tears occurs in 50% of extra-articular distal radius fractures versus 1/3 of intra articular fractures.
• Dorsal comminution is frequent and if comminution is to 50% of the dorsal cortex, then treatment with a cast will not work. The more dorsal flexion, then the more comminution and more chance of fracture failure when using a cast.
• Colles fracture that extends to the DRUJ has a worse prognosis.
- Smith fracture:
• Is an extra articular transverse fracture that is palmarly displaced and can be thought of as a reverse Colles fracture.
• It could occur from a fall onto a flexed wrist.
• This fracture has multiple types:
1- Type I: fracture is extra articular transverse fracture through the distal radius (most common)
2- Type II: fracture crosses into the dorsal articular surface.
3- Type III: fracture enters the radiocarpal joint (volar barton fracture equals a Smith type III fracture), both will involve the intra- articular distal radius and includes possible dissociation of the carpal bones.
- Die- Punch fracture:
• Is a depressed fracture of the lunate fossa that results from axial loading forces on the distal radius that is transmitted through the lunate bone.
• It is intra- articular fractures of the lunate fossa of the distal radius.
• Check to see if there is any carpal bone dissociation.
- Bartons fracture:
• Intra articular fracture of the distal radius with dislocation of the radiocarpal joint.
• These fractures can be dorsal or volar.
• Check for carpal bone disruption or dissociation.
• It is caused by a fall on an extended and pronated wrist with the volar type being the most common type. The fracture fragment is usually smaller with the dorsal barton fracture.
• The volar barton fracture is the fracture of the volar margin of the of the distal radius, which is associated with subluxation of the radio-carpal joint.
• The most striking finding is subluxation or dislocation of the wrist with that small fragment.
• You can see in the picture the strong volar radiocarpal ligament avulses the volar lip of the radius.
• This fracture is very similler to the Smith type III fracture.
• Treatment of volar barton fracture is usually surgery with a volar approach and volar plate.
• Dorsal Barton: the dorsal shearing force, distal radius fracture with dislocation of the radiocarpal joint, fracture ia intra-articular and involves the dorsal lip.
Dislocation is the most striking x-ray finding. The avulsed fragment is usually small.
Treatment is open reduction internal fixation through a dorsal approach.
- Chauffer fracture:
• Is fracture of the radial styloid process in association with scapholunate dissociation.
• It is caused by compression of the scaphoid bone of the hand against the styloid process of the distal radius.
• Evaluation of the radial styloid fracture should always include supinated view x-rays so that scapholunate dissociation can be ruled out.
• Look for major swelling of the wrist and distal DISI deformity on lateral x-rays with a widening gap between the lunate and scphoid bones on AP view.
• DISI deformity: the scapholunate angle is usually about 47° and can be up to 60°, any angle that is greater than 60° is considered abnormal; this is usually seen with a DISI deformity due to the palmar flexion of the scaphoid. This means that there is scaphoid dissociation. The scaphoid and lunate bones turn in opposite directions.
• Treatment of this fracture is: compression screw fixation of the radial styloid process.
• Assess the scapholunate joint for possible stabilization.
In conclusion:
- During assessment of the x-rays, you need to see if there is any involvement of the dorsal or volar rim of the radius.
- Check for involvement of the DRUJ and look for die-punch lesions.
- Check for dislocation of the wrist and the direction of the displacement.
- Check the carpal distribution to see if there is any dissociation between the carpal bones.
Комментарии
 0:10:21
0:10:21
 0:07:00
0:07:00
 0:08:57
0:08:57
 0:04:14
0:04:14
 0:03:55
0:03:55
 0:05:13
0:05:13
 0:13:26
0:13:26
 0:04:52
0:04:52
 0:00:32
0:00:32
 0:00:53
0:00:53
 0:00:15
0:00:15
 0:11:13
0:11:13
 0:00:15
0:00:15
 0:01:47
0:01:47
 0:00:46
0:00:46
 0:10:04
0:10:04
 0:27:31
0:27:31
 0:01:11
0:01:11
 0:16:46
0:16:46
 0:00:52
0:00:52
 0:03:44
0:03:44
 0:01:40
0:01:40
 0:10:08
0:10:08
 0:17:31
0:17:31