filmov
tv
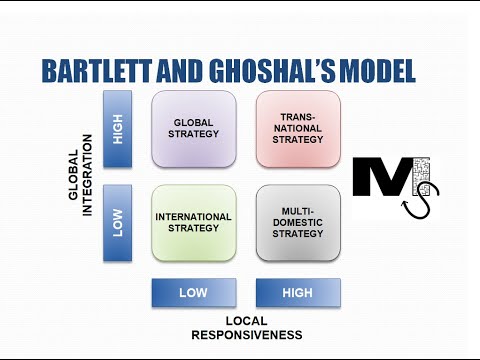
Transnational Strategy for Services (With Example of McDonalds)

Показать описание
What is a Transnational Strategy?
A transnational strategy can be termed as a plan of action whereby a company operates across international borders.
This strategy entails overseas operations and assets, linking them to every country in which the company operates.
Transnational strategies ultimately combine global integration and local responsiveness to each market.
Examples of Transnational Model
McDonalds nails the Transnational Model
McDonald’s is the world’s biggest restaurant chain, with over 37,000 restaurants in more than 120 markets. The fast-food chain divides its target markets into segments by country, region, and cities then customizes its menu.
McDonald’s modifies its product offerings in line with the geographic and cultural region.
For instance, In Japan, they factor in seasonal tastes, for example, the TeriTama Burger in springtime and Tsukimi Burger in autumn.
Further, McDonald's procures over 90% of its raw materials from local vendors or invest in resources which are not locally available.
Netflix perfects the model in a decade
At the end of 2021, Netflix had approximately 222 million paid memberships. In terms of regions, United States and Canada accounted for the maximum paid membership.
In terms of growth; 90% of the subscribers added in 2021 were outside the U.S. and Canada.
Netflix’s reach spans in more than 190 countries across the world. Additionally; Netflix offers different genre of content in more than 37 languages and has made shows in 40 different countries.
The variety in language has not stopped viewers from English speaking countries to binge watch Non-English shows. For instance; Non-English viewing in the United States witnessed a stellar growth of 71% from 2019.
Factors Favoring Transnational Strategy
1. Market Drivers
Common customer needs across different countries.
Presence of global customers who demand consistent service for supplier all around the world.
Availability of proper infrastructure such as technology, communication, supply chains, etc.
2. Technology Drivers
Technological advancements in the areas of telecommunication, computerization, software development are the technological drivers that influences the companies to adopt such strategy.
Growing availability of broadband telecommunication channels, easy access to internet facilities all round the world has helped a company to ‘Go Global’.
Firms can take advantage of favorable labor by consolidating operations of supplementary services (such as reservations) or back-office functions (such as accounting) in just one or few selected countries.
3. Cost Drivers
Operating at a global level enables the company to reduce the cost of operations thereby increasing the efficiency.
This is because globalization helps the companies to outsource its processes to such countries where same process can be completed at a cheaper rate that too with higher efficiency
Moreover, global companies can also take the advantages of economies of scale by manufacturing products and services on a large scale and by making optimum utilization of available resources.
4. Competition Drivers
Firms may be obliged to follow their competitors into new markets in order to protect their positions elsewhere.
The presence of competitors from different countries, independence of countries, and the transnational policies of competitors themselves are among the key competition drivers that exercise a powerful force in many service industries.
5. Government Drivers
Government policies can serve to encourage or development of a transnationally integrated strategy.
Among these drivers are favorable trade policies, technical assistance and granting subsidies and tax exemptions.
Characteristics of Transnational Strategy
1. Global Market Participation
Transnational strategy enables a company to operate at a global level. It enables the company to participate in the global market.
Management selects the various countries on the basis of attractiveness as well as the potential of each country to generate reasonable returns.
2. Delivering Global Products
The firm offers one or more standardized core products in many countries.
At times, firm may offer a broader product line in some countries while it may restrict itself to a narrower product line in other countries depending upon revenue generating capacity of each country.
3. Global Location of Services
When a company operates within the country, the supply chain is restricted within. However, when a company adopts a transnational strategy, the entire supply chain is spread across countries.
This video is on Transnational Strategy for Services and it has the following sub-topics.
Time Stamps
0:00 Transnational Strategy Introduction
0:32 What is a Transnational Strategy?
0:54 Examples of Transnational Model
2:17 Factors Favoring Transnational Strategy
4:08 Characteristics of Transnational Strategy
Комментарии
 0:06:02
0:06:02
 0:01:51
0:01:51
 0:05:19
0:05:19
 0:15:54
0:15:54
 0:09:32
0:09:32
 0:08:26
0:08:26
 0:04:53
0:04:53
 0:05:49
0:05:49
 0:08:46
0:08:46
 0:06:29
0:06:29
 0:03:28
0:03:28
 0:03:01
0:03:01
 0:27:08
0:27:08
 0:01:47
0:01:47
 0:10:49
0:10:49
 0:28:10
0:28:10
 0:33:38
0:33:38
 0:02:25
0:02:25
 0:04:45
0:04:45
 0:02:03
0:02:03
 0:01:38
0:01:38
 0:06:35
0:06:35
 0:02:31
0:02:31
 0:15:26
0:15:26