filmov
tv
Coronary Artery Disease: Types, Symptoms, Causes and treatment
Показать описание
What is the definition of Coronary Artery Disease (CAD) and what are its main types?
What are the key risk factors and underlying mechanisms of CAD?
What symptoms are commonly associated with CAD, and what is the hallmark symptom?
What differentiates unstable angina from myocardial infarction?
What diagnostic tests are used to confirm a diagnosis of CAD and which test is considered the gold standard?
What is the first, second, and third line of treatment for CAD?
What is the significance of reperfusion in the context of myocardial infarction and how is it achieved?
Important Highlights:
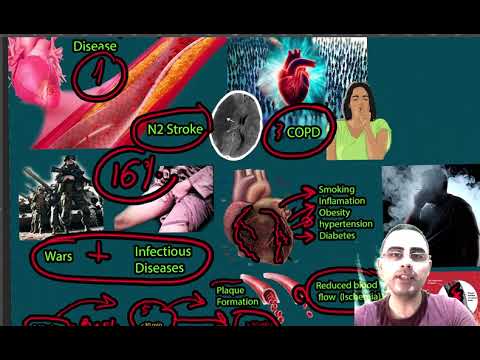
Coronary Artery Disease is a leading cause of death globally, with it being responsible for 16% of all deaths.
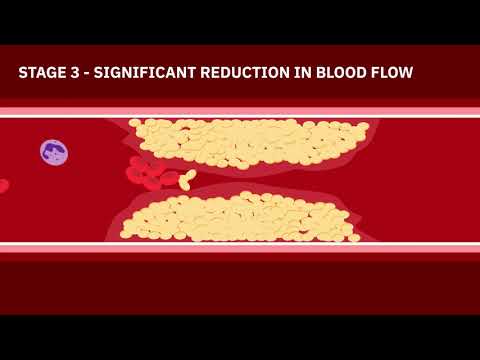
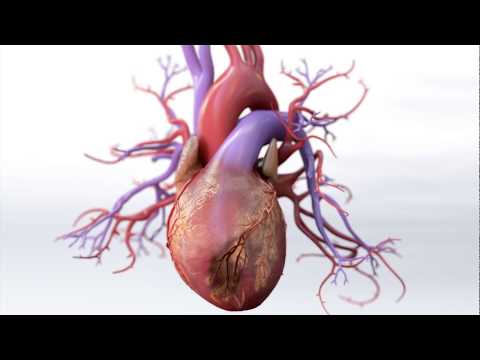
The pathophysiology of CAD involves the buildup of plaque (atherosclerosis) in the coronary arteries, reducing blood flow to the heart muscle and potentially leading to angina or heart attacks.
Angina, particularly discomfort in the chest, is the hallmark symptom of CAD.
Unstable angina, a less common but more dangerous form of CAD, causes chest pain even at rest, while myocardial infarction involves complete blockage of an artery, leading to damage or death of part of the heart muscle.
Diagnostic tests for CAD include ECG, stress tests, echocardiogram, and coronary angiogram, the latter being the gold standard.
The treatment of CAD involves lifestyle modifications, medications (like aspirin, beta-blockers, calcium channel blockers, statins, and nitroglycerin), and potentially revascularization procedures like angioplasty or bypass surgery.
Time is crucial in a myocardial infarction; the sooner reperfusion occurs, the more heart muscle can be saved, with reperfusion ideally occurring within the first hour after the onset of symptoms.
What are the key risk factors and underlying mechanisms of CAD?
What symptoms are commonly associated with CAD, and what is the hallmark symptom?
What differentiates unstable angina from myocardial infarction?
What diagnostic tests are used to confirm a diagnosis of CAD and which test is considered the gold standard?
What is the first, second, and third line of treatment for CAD?
What is the significance of reperfusion in the context of myocardial infarction and how is it achieved?
Important Highlights:
Coronary Artery Disease is a leading cause of death globally, with it being responsible for 16% of all deaths.
The pathophysiology of CAD involves the buildup of plaque (atherosclerosis) in the coronary arteries, reducing blood flow to the heart muscle and potentially leading to angina or heart attacks.
Angina, particularly discomfort in the chest, is the hallmark symptom of CAD.
Unstable angina, a less common but more dangerous form of CAD, causes chest pain even at rest, while myocardial infarction involves complete blockage of an artery, leading to damage or death of part of the heart muscle.
Diagnostic tests for CAD include ECG, stress tests, echocardiogram, and coronary angiogram, the latter being the gold standard.
The treatment of CAD involves lifestyle modifications, medications (like aspirin, beta-blockers, calcium channel blockers, statins, and nitroglycerin), and potentially revascularization procedures like angioplasty or bypass surgery.
Time is crucial in a myocardial infarction; the sooner reperfusion occurs, the more heart muscle can be saved, with reperfusion ideally occurring within the first hour after the onset of symptoms.
 0:05:17
0:05:17
 0:06:45
0:06:45
 0:05:25
0:05:25
 0:03:34
0:03:34
 0:00:44
0:00:44
 0:52:22
0:52:22
 0:13:32
0:13:32
 0:14:16
0:14:16
 0:32:56
0:32:56
 0:01:00
0:01:00
 0:04:11
0:04:11
 0:03:10
0:03:10
 0:02:38
0:02:38
 0:12:11
0:12:11
 0:19:01
0:19:01
 0:08:37
0:08:37
 0:19:57
0:19:57
 0:08:41
0:08:41
 0:14:32
0:14:32
 0:08:59
0:08:59
 0:01:31
0:01:31
 0:01:23
0:01:23
 0:04:29
0:04:29