filmov
tv
Implementing Zero Trust Architecture: A Step-by-Step Guide Part 1

Показать описание
The session begins with a comprehensive introduction to Zero Trust Architecture (ZTA) and its practical implications, led by Pushpendra, a security expert. The discussion revolves around understanding Zero Trust beyond the common "never trust, always verify" approach, emphasizing the depth of its implementation and practical use in organizations.The session provides a practical, real-world insight into Zero Trust, offering guidance for organizations at any stage of their Zero Trust journey.
Key Insights:
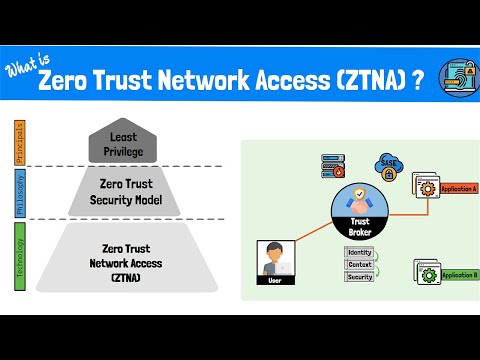
Zero Trust Defined:
Zero Trust is not just a security model or set of technologies but an evolving architecture that demands strict verification and monitoring of all access requests.
It departs from the traditional parameter-based security and focuses on securing identities, devices, networks, applications, and data with continuous monitoring and authentication at all points.
Beyond Traditional Security:
Traditional security models (e.g., VPN with Single Sign-On) rely on authenticating once and granting broad access. However, Zero Trust builds on this by providing granular authorization for each request, ensuring no free access is granted post-authentication.
Core Pillars of Zero Trust:
Identity: Ensuring the right person or entity is accessing resources.
Devices: Evaluating device posture and ensuring devices are secure.
Network: Using micro-segmentation to limit east-west traffic and prevent unauthorized access within the network.
Applications: Defining strict access to specific applications based on user identity.
Data: Classifying and protecting critical business data.
Cybersecurity Governance:
Practical Implementation Challenges:
Pushpendra highlights how Zero Trust is not a plug-and-play solution. It involves detailed analysis of current infrastructure, identifying gaps, and then bridging those gaps with tailored solutions.
Zero Trust is a journey, not a one-time project. It evolves as threats evolve, and the solution needs to be continuously monitored and refined.
Roadmap for Zero Trust:
Pushpendra lays out a high-level roadmap for implementing Zero Trust:
Conduct a risk and gap analysis.
Define goals and objectives (e.g., enabling MFA for all users).
Develop a framework for Zero Trust with clear policies and principles.
Prioritize tasks based on business needs.
Continuous monitoring and risk assessment to fine-tune processes.
Ensure proper training and education for employees.
People, Process, and Technology:
Pushpendra emphasizes that technology is just one aspect of Zero Trust.
The people and processes involved in the security architecture are equally critical.
A solid governance and communication structure is required to align security efforts across the organization.
Conclusion:
The session concludes with a reminder that Zero Trust is a holistic, business-driven architecture that should evolve with organizational needs and threats. It requires a balance of people, processes, and technology, and it’s crucial to continuously assess and adapt.
Pushpendra leaves the viewers with practical advice on adopting Zero Trust:
Avoid vendor-driven solutions and focus on business-specific needs.
Make Zero Trust part of a long-term security strategy and roadmap.
Playlist CISO Talk
Playlist Network Security
GRC Interview Questions
Internal Auditor Playlist
How to make career progression post #isc2 and #isaca
How to make career in GRC
How to Build PIMS
How to Implement 27001 in an organization
How to conduct PIA
How to Make an career in GRC
Telegram Group
Pentesting Career
Telegram Group Link
Cybersecurity Guide
#ZeroTrust #CyberSecurity #ITSecurity #PushpinderSingh #PracticalGuide #ZeroTrustImplementation #DigitalSecurity #SecureArchitecture #cyberdefense #cloudsecurity #cybersecurity
Key Insights:
Zero Trust Defined:
Zero Trust is not just a security model or set of technologies but an evolving architecture that demands strict verification and monitoring of all access requests.
It departs from the traditional parameter-based security and focuses on securing identities, devices, networks, applications, and data with continuous monitoring and authentication at all points.
Beyond Traditional Security:
Traditional security models (e.g., VPN with Single Sign-On) rely on authenticating once and granting broad access. However, Zero Trust builds on this by providing granular authorization for each request, ensuring no free access is granted post-authentication.
Core Pillars of Zero Trust:
Identity: Ensuring the right person or entity is accessing resources.
Devices: Evaluating device posture and ensuring devices are secure.
Network: Using micro-segmentation to limit east-west traffic and prevent unauthorized access within the network.
Applications: Defining strict access to specific applications based on user identity.
Data: Classifying and protecting critical business data.
Cybersecurity Governance:
Practical Implementation Challenges:
Pushpendra highlights how Zero Trust is not a plug-and-play solution. It involves detailed analysis of current infrastructure, identifying gaps, and then bridging those gaps with tailored solutions.
Zero Trust is a journey, not a one-time project. It evolves as threats evolve, and the solution needs to be continuously monitored and refined.
Roadmap for Zero Trust:
Pushpendra lays out a high-level roadmap for implementing Zero Trust:
Conduct a risk and gap analysis.
Define goals and objectives (e.g., enabling MFA for all users).
Develop a framework for Zero Trust with clear policies and principles.
Prioritize tasks based on business needs.
Continuous monitoring and risk assessment to fine-tune processes.
Ensure proper training and education for employees.
People, Process, and Technology:
Pushpendra emphasizes that technology is just one aspect of Zero Trust.
The people and processes involved in the security architecture are equally critical.
A solid governance and communication structure is required to align security efforts across the organization.
Conclusion:
The session concludes with a reminder that Zero Trust is a holistic, business-driven architecture that should evolve with organizational needs and threats. It requires a balance of people, processes, and technology, and it’s crucial to continuously assess and adapt.
Pushpendra leaves the viewers with practical advice on adopting Zero Trust:
Avoid vendor-driven solutions and focus on business-specific needs.
Make Zero Trust part of a long-term security strategy and roadmap.
Playlist CISO Talk
Playlist Network Security
GRC Interview Questions
Internal Auditor Playlist
How to make career progression post #isc2 and #isaca
How to make career in GRC
How to Build PIMS
How to Implement 27001 in an organization
How to conduct PIA
How to Make an career in GRC
Telegram Group
Pentesting Career
Telegram Group Link
Cybersecurity Guide
#ZeroTrust #CyberSecurity #ITSecurity #PushpinderSingh #PracticalGuide #ZeroTrustImplementation #DigitalSecurity #SecureArchitecture #cyberdefense #cloudsecurity #cybersecurity
Комментарии
 0:37:45
0:37:45
 0:03:43
0:03:43
 0:01:14
0:01:14
 0:07:44
0:07:44
 0:02:52
0:02:52
 0:52:23
0:52:23
 0:13:06
0:13:06
 0:27:03
0:27:03
 2:42:18
2:42:18
 0:09:57
0:09:57
 0:17:59
0:17:59
 0:53:30
0:53:30
 0:01:41
0:01:41
 0:10:05
0:10:05
 0:47:54
0:47:54
 0:47:06
0:47:06
 0:38:08
0:38:08
 0:02:37
0:02:37
 0:57:11
0:57:11
 0:45:07
0:45:07
 0:32:47
0:32:47
 0:08:57
0:08:57
 0:15:14
0:15:14
 0:26:39
0:26:39