filmov
tv
Intro to Einstein's Special Relativity | Doc Physics

Показать описание
We'll talk about fat walruses, the equivalence of all inertial reference frames for all physical observations, and the constancy of the speed of light for all inertial observers. Enjoy getting your head mashed to a pulp.
Simple Relativity - Understanding Einstein's Special Theory of Relativity
Special Relativity Part 1: From Galileo to Einstein
General Relativity Explained simply & visually
Einstein and the clock - an intro to special relativity
Time Dilation - Einstein's Theory Of Relativity Explained!
Special Relativity: Crash Course Physics #42
Introduction to Special Relativity
Intro to Einstein's Special Relativity | Doc Physics
Do you know that Albert Einstein was offered to be the president of Isarel?
Einstein's special relativity: an introduction | WildTrig: Intro to Rational Trigonometry
Visualization of Einstein's special relativity [HD]
Relativity 101b: Introduction to Special Relativity
Einstein and The Special Theory of Relativity
An Introduction to Special Relativity
Introduction to the Lorentz transformation | Special relativity | Physics | Khan Academy
General Relativity Explained in 7 Levels of Difficulty
WSU: Special Relativity with Brian Greene
Introduction to special relativity and Minkowski spacetime diagrams | Khan Academy
Special Relativity simplified using no math. Einstein thought experiments
Einstein's Special Theory of Relativity explained
What is the difference between Special and General Relativity?
Special Relativity: This Is Why You Misunderstand It
Special Relativity
How Einstein Thought of the Theory of Relativity
Комментарии
 0:05:56
0:05:56
 0:05:49
0:05:49
 0:14:04
0:14:04
 0:11:36
0:11:36
 0:08:06
0:08:06
 0:08:59
0:08:59
 0:20:59
0:20:59
 0:14:00
0:14:00
 0:00:40
0:00:40
 0:09:50
0:09:50
 0:04:34
0:04:34
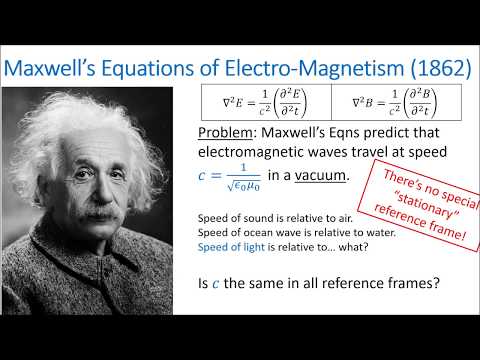 0:15:20
0:15:20
 0:01:50
0:01:50
 0:04:31
0:04:31
 0:08:20
0:08:20
 0:06:09
0:06:09
 11:29:00
11:29:00
 0:13:43
0:13:43
 0:12:19
0:12:19
 0:00:37
0:00:37
 0:00:55
0:00:55
 0:21:15
0:21:15
 0:12:59
0:12:59
 0:09:05
0:09:05