filmov
tv
Computer Skills Course: Bits, Bytes, Kilobytes, Megabytes, Gigabytes, Terabytes (OLD VERSION)

Показать описание
PLEASE SEE NEW UPDATED VERSION:
Free Computer Skills Course: Digital Storage Terminology.
Learn about Bits, Bytes, Kilobytes (KB), Megabytes (MB), Gigabytes (GB), Terabytes (TB).
Transcript:
Let’s continue learning about how computers store data. As we learned earlier, computers use the Binary number system, which has only two numbers, one and zero.
The word that’s used to describe these binary digits, which can be either one or zero, is Bit – B-I-T = It’s short for ‘binary digit’ and it is the smallest unit of data in a computer.
Now, these Bits – these ones and zeroes – are used to store all kinds of information, from the text that appears on your screen, to the colors of an image, to the sounds that come out of your speakers. To store information like this, we use a bunch of bits together. The number of bits we have determines how much information we can store.
Now for our next term: It turns out, if you take 8 of these bits – 8 of these ones and zeroes - and put them together, that’s called a Byte. Sounds like a mouthful of food, but it’s spelled with a ‘y’ and it refers to 8 bits put together. In everyday terms, you can think of one byte as the amount of space it takes to store one single letter or symbol in a text document. If you wrote a short story with 1000 words, this would take up 1000 bytes of storage space.
That brings us to our next term. If you take 1000 bytes and put them together, that’s called a Kilobyte, often abbreviated as “kb”. Now, I will mention just once, that technically there are 1024 bytes in a kilobyte, and that’s because computers use binary and everything comes in powers of two. That said, it doesn’t really matter, it’s ok to think of a kilobyte simply as 1000 bytes, similar to how a kilometer is 1000 meters. One Kilobyte is enough space to hold about two pages of text. Back in the late 1970s and early 1980s, the 5.25” floppy disk was a popular storage option, and it could hold 360kb of information.
So now, what’s it called if you have 1000 kilobytes? It’s called a Megabyte, often abbreviated as capital “MB”. One megabyte is enough space to hold about 5 books, or one photo, or one minute of music. Back in the 1980s, we had these things called floppy disks. This was a 3.5” floppy disk that held 1.44MB of data, which was pretty good at the time, because most files were pretty small.
Alright, now you’re probably wondering, what’s it called if you have 1000 megabytes? 1000 megabytes is called a Gigabyte, and it’s enough space to hold about 400 books, or a thousand pictures, or 16 hours of music. By the mid 1990s, you could buy a 1GB hard drive for a couple hundred bucks. Today, you can buy 1 GB flash drive for about $5.
Ok, so what’s it called when you have 1000 gigabytes? 1000 gigabytes is called a Terabyte, and is often abbreviated as “TB”, and it’s enough space to hold about 400,000 large books (that’s about 30 school libraries), a million pictures, or two years of continuous music. Today, you can buy a 1TB hard drive for under $50. Yes, it’s pretty amazing.
So, to recap, we talked about Bits, how there are 8 bits in 1 byte, how there are 1000 bytes in 1 kilobyte, and 1000 kilobytes in 1 megabyte, and 1000 megabytes in 1 gigabyte, and 1000 gigabytes in 1 terabyte. I hope you’ve enjoyed this video and that you have a better understanding of digital storage terminology.
Free Computer Skills Course: Digital Storage Terminology.
Learn about Bits, Bytes, Kilobytes (KB), Megabytes (MB), Gigabytes (GB), Terabytes (TB).
Transcript:
Let’s continue learning about how computers store data. As we learned earlier, computers use the Binary number system, which has only two numbers, one and zero.
The word that’s used to describe these binary digits, which can be either one or zero, is Bit – B-I-T = It’s short for ‘binary digit’ and it is the smallest unit of data in a computer.
Now, these Bits – these ones and zeroes – are used to store all kinds of information, from the text that appears on your screen, to the colors of an image, to the sounds that come out of your speakers. To store information like this, we use a bunch of bits together. The number of bits we have determines how much information we can store.
Now for our next term: It turns out, if you take 8 of these bits – 8 of these ones and zeroes - and put them together, that’s called a Byte. Sounds like a mouthful of food, but it’s spelled with a ‘y’ and it refers to 8 bits put together. In everyday terms, you can think of one byte as the amount of space it takes to store one single letter or symbol in a text document. If you wrote a short story with 1000 words, this would take up 1000 bytes of storage space.
That brings us to our next term. If you take 1000 bytes and put them together, that’s called a Kilobyte, often abbreviated as “kb”. Now, I will mention just once, that technically there are 1024 bytes in a kilobyte, and that’s because computers use binary and everything comes in powers of two. That said, it doesn’t really matter, it’s ok to think of a kilobyte simply as 1000 bytes, similar to how a kilometer is 1000 meters. One Kilobyte is enough space to hold about two pages of text. Back in the late 1970s and early 1980s, the 5.25” floppy disk was a popular storage option, and it could hold 360kb of information.
So now, what’s it called if you have 1000 kilobytes? It’s called a Megabyte, often abbreviated as capital “MB”. One megabyte is enough space to hold about 5 books, or one photo, or one minute of music. Back in the 1980s, we had these things called floppy disks. This was a 3.5” floppy disk that held 1.44MB of data, which was pretty good at the time, because most files were pretty small.
Alright, now you’re probably wondering, what’s it called if you have 1000 megabytes? 1000 megabytes is called a Gigabyte, and it’s enough space to hold about 400 books, or a thousand pictures, or 16 hours of music. By the mid 1990s, you could buy a 1GB hard drive for a couple hundred bucks. Today, you can buy 1 GB flash drive for about $5.
Ok, so what’s it called when you have 1000 gigabytes? 1000 gigabytes is called a Terabyte, and is often abbreviated as “TB”, and it’s enough space to hold about 400,000 large books (that’s about 30 school libraries), a million pictures, or two years of continuous music. Today, you can buy a 1TB hard drive for under $50. Yes, it’s pretty amazing.
So, to recap, we talked about Bits, how there are 8 bits in 1 byte, how there are 1000 bytes in 1 kilobyte, and 1000 kilobytes in 1 megabyte, and 1000 megabytes in 1 gigabyte, and 1000 gigabytes in 1 terabyte. I hope you’ve enjoyed this video and that you have a better understanding of digital storage terminology.
Комментарии
 0:04:16
0:04:16
 0:05:28
0:05:28
 0:04:51
0:04:51
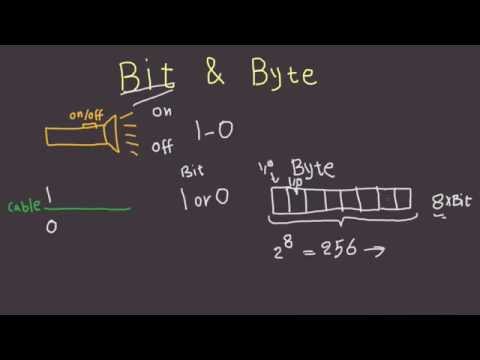 0:06:26
0:06:26
 0:02:39
0:02:39
 0:00:16
0:00:16
 0:01:49
0:01:49
 0:05:11
0:05:11
 0:11:31
0:11:31
 0:05:02
0:05:02
 0:07:00
0:07:00
 0:00:34
0:00:34
 0:00:58
0:00:58
 0:07:33
0:07:33
 0:12:34
0:12:34
 0:16:28
0:16:28
 0:05:05
0:05:05
 0:04:04
0:04:04
 0:06:47
0:06:47
 0:02:31
0:02:31
 0:42:32
0:42:32
 0:00:49
0:00:49
 0:04:33
0:04:33
 0:08:04
0:08:04