filmov
tv
Specific Heat Capacity | Matter | Physics | FuseSchool

Показать описание
Specific Heat Capacity | Matter | Physics | FuseSchool
You might have noticed that if you are trying to boil a lot of water it takes longer than if you only wish to boil a small amount of water.
This is all because of something called ‘heat capacity’. Keep watching to learn more.
Before we get into the details, it is important to realise that there is a difference between ‘heat’ and ‘temperature’. Temperature is a way of describing how hot or cold an object is and is measured in °C, whereas heat is a form of energy and is measured in Joules (J). The more heat energy transferred to an object, the more its temperature will rise. So heat and temperature are related but are not the same.
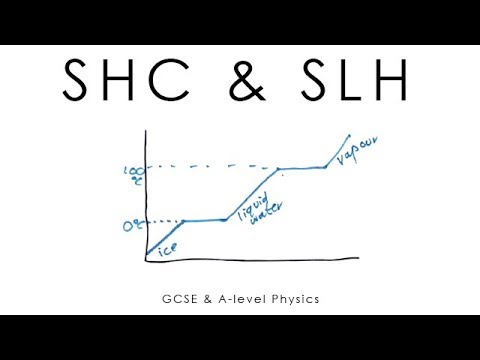
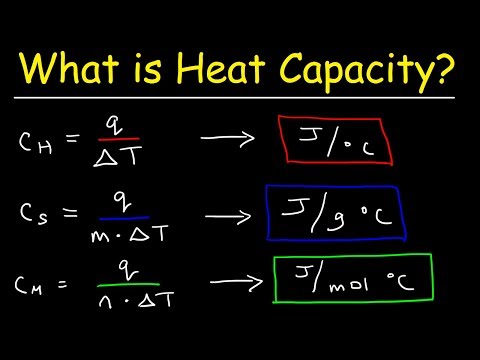
So what is heat capacity? The heat capacity of a substance is defined as the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of a material by 1°C. However, what’s more useful for us to think about is the specific heat capacity of a substance. This is, as it says in the name, a little more specific. It is the amount of heat required to raise 1 kilogram of a material by 1°C.
Different materials have different known specific heat capacities, but we aren't always given a table like this so, we need to know how to calculate specific heat capacities ourselves.
We have this equation, which can be written as symbols like this. The energy transferred is the heat energy absorbed or released. This equation can also be rearranged.
To work out the temperature change, subtract the old temperature from a new temperature.
Let's have a look at the problem. Pause the video and attempt to calculate the specific heat capacity of lead. How did you get on?
The energy transferred is this. The mass is this and the temperature change 10 °C because it's this, take away this. Using the rearranged equations substitute in the values and we get a hundred and twenty-eight joules per kilogram Celsius.
Here is another practice problem, pause the video and attempt to calculate the energy transferred to the LED. Did you get it right? We could divide it by 1000 to turn the answer into kilojoules. Notice that the answer is negative this time, it's because we called the LED the temperature change will always be negative if it is being cooled and positive is it being heated.
To summarise, specific heat capacity is the amount of energy needed to raise one kilogram of a substance by one °C. It's helpful because it allows us to work out how much energy we need to heat up or cool down the substance to decide the temperature. To calculate use the following equation.
SUPPORT US ON PATREON
SUBSCRIBE to the FuseSchool YouTube channel for many more educational videos. Our teachers and animators come together to make fun & easy-to-understand videos in Chemistry, Biology, Physics, Maths & ICT.
These videos can be used in a flipped classroom model or as a revision aid.
You might have noticed that if you are trying to boil a lot of water it takes longer than if you only wish to boil a small amount of water.
This is all because of something called ‘heat capacity’. Keep watching to learn more.
Before we get into the details, it is important to realise that there is a difference between ‘heat’ and ‘temperature’. Temperature is a way of describing how hot or cold an object is and is measured in °C, whereas heat is a form of energy and is measured in Joules (J). The more heat energy transferred to an object, the more its temperature will rise. So heat and temperature are related but are not the same.
So what is heat capacity? The heat capacity of a substance is defined as the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of a material by 1°C. However, what’s more useful for us to think about is the specific heat capacity of a substance. This is, as it says in the name, a little more specific. It is the amount of heat required to raise 1 kilogram of a material by 1°C.
Different materials have different known specific heat capacities, but we aren't always given a table like this so, we need to know how to calculate specific heat capacities ourselves.
We have this equation, which can be written as symbols like this. The energy transferred is the heat energy absorbed or released. This equation can also be rearranged.
To work out the temperature change, subtract the old temperature from a new temperature.
Let's have a look at the problem. Pause the video and attempt to calculate the specific heat capacity of lead. How did you get on?
The energy transferred is this. The mass is this and the temperature change 10 °C because it's this, take away this. Using the rearranged equations substitute in the values and we get a hundred and twenty-eight joules per kilogram Celsius.
Here is another practice problem, pause the video and attempt to calculate the energy transferred to the LED. Did you get it right? We could divide it by 1000 to turn the answer into kilojoules. Notice that the answer is negative this time, it's because we called the LED the temperature change will always be negative if it is being cooled and positive is it being heated.
To summarise, specific heat capacity is the amount of energy needed to raise one kilogram of a substance by one °C. It's helpful because it allows us to work out how much energy we need to heat up or cool down the substance to decide the temperature. To calculate use the following equation.
SUPPORT US ON PATREON
SUBSCRIBE to the FuseSchool YouTube channel for many more educational videos. Our teachers and animators come together to make fun & easy-to-understand videos in Chemistry, Biology, Physics, Maths & ICT.
These videos can be used in a flipped classroom model or as a revision aid.
Комментарии
 0:03:14
0:03:14
 0:04:14
0:04:14
 0:04:36
0:04:36
 0:03:55
0:03:55
 0:09:50
0:09:50
 0:06:26
0:06:26
 0:00:09
0:00:09
 0:13:20
0:13:20
 1:07:54
1:07:54
 0:22:21
0:22:21
 0:00:09
0:00:09
 0:03:58
0:03:58
 0:07:04
0:07:04
 0:13:53
0:13:53
 0:07:59
0:07:59
 0:05:21
0:05:21
 0:04:13
0:04:13
 0:05:23
0:05:23
 0:12:45
0:12:45
 0:00:06
0:00:06
 0:00:13
0:00:13
 0:03:20
0:03:20
 0:12:29
0:12:29
 0:00:55
0:00:55