filmov
tv
Understanding Airplane Stalls (Critical Angle of Attack)

Показать описание
Airfoils, Stalls and Critical Angle of Attack - AeroGuard Flight Training
What Is a Stall? Angle of Attack Explained
What is a Stall? What is Angle of Attack? | King Schools
What is a stall?
Understanding Airplane Stalls (Critical Angle of Attack)
Airplane Stall explained by Capt. Neha Thakare...Critical Angle AttackAerodynamic #pilot #airplane
Understanding Airplane Stalls (Critical Angle of Attack)3
Airplane Stall Explained
Understanding Deep Stall | The Super Stall.
What is angle of attack?
Understanding the critical angle of attack and elevator stall position!
What is a Stall? #shorts
How Bank Angle Affects Stall Speed | Don't Get too Slow! | Load Factor
What is a SPIN? | The Aggravated STALL
Stalls & Angle of Attack
What Causes An Airplane To Stall (Private Pilot Ground Lesson 3)
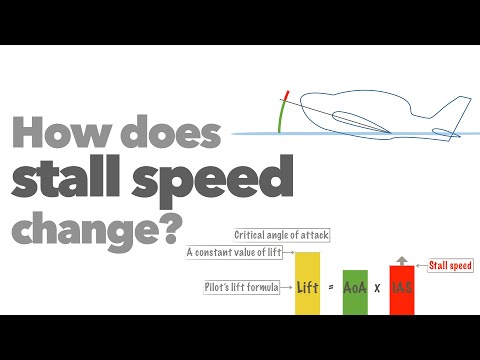
How does stall speed change?
Critical Angle Of Attack - [Are you sure you cannot stall at high speed?]
Why Stall Speed if it's all about Angle of Attack?!
What affects stall speed?
Understanding Coffin Corner | The High-Risk Zone in Aviation.
This will save your life! Understanding what Causes an Aerodynamic Stall and Why...
PPGS Lesson 5.5 | Aerodynamics: Stalls
What Causes an Airplane to STALL? | Complete PPL Ground Course (Lesson 3)
Комментарии
 0:09:48
0:09:48
 0:00:43
0:00:43
 0:03:58
0:03:58
 0:03:22
0:03:22
 0:10:34
0:10:34
 0:01:01
0:01:01
 0:10:58
0:10:58
 0:00:33
0:00:33
 0:02:27
0:02:27
 0:05:36
0:05:36
 0:00:56
0:00:56
 0:00:23
0:00:23
 0:07:13
0:07:13
 0:05:19
0:05:19
 0:04:24
0:04:24
 0:04:13
0:04:13
 0:01:20
0:01:20
 0:06:02
0:06:02
 0:09:59
0:09:59
 0:03:34
0:03:34
 0:04:24
0:04:24
 0:08:00
0:08:00
 0:08:38
0:08:38
 0:09:03
0:09:03