filmov
tv
Inside The 34 Week Embryo

Показать описание
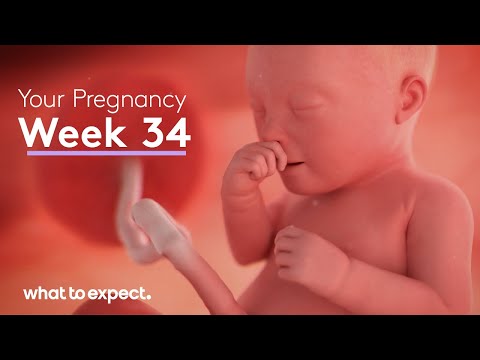
At 34 weeks, the fetus measures approximately 43 to 45 centimeters (17 to 18 inches) in length from head to heel and weighs around 2 to 2.5 kilograms (4.5 to 5.5 pounds). The fetus continues to grow steadily, with the main focus now on weight gain, lung maturation, and neurological development.
The fetus is increasingly responsive to stimuli, such as sound and light, and has developed regular sleep-wake cycles. Most of the major organ systems are in place and functional, although some, such as the respiratory and digestive systems, continue to mature.
---
2. Physical Characteristics at 34 Weeks
At this stage, the fetus closely resembles a newborn but is still developing in the following ways:
Skin and Fat Development
The skin has become thicker and less wrinkled as fat accumulates beneath it.
The presence of vernix caseosa, a white waxy substance covering the skin, provides protection from amniotic fluid exposure and helps regulate temperature after birth.
Lanugo, the fine downy hair that covered much of the body earlier in development, has mostly disappeared, remaining only on the back and shoulders.
The cheeks appear fuller, and the fetus starts to develop a more rounded appearance due to increasing fat stores.
Head and Facial Features
The head is well-formed and proportional to the body, although it remains relatively large compared to the rest of the body.
The skull bones are still soft and not fully fused, allowing for flexibility during birth.
The eyes are capable of blinking, and the fetus can detect changes in light intensity through the abdominal wall.
The ears are fully developed and capable of detecting sounds both inside and outside the womb.
Limbs and Movement
The arms and legs have grown stronger, and the fetus can perform well-coordinated movements such as stretching, kicking, and grasping.
Fingernails and toenails have grown to the tips of the fingers and toes, and fine details like fingerprints are fully developed.
The fetus responds to touch stimuli, particularly around the mouth and hands, exhibiting reflex actions such as the grasp reflex.
---
3. Neurological Development and Brain Activity
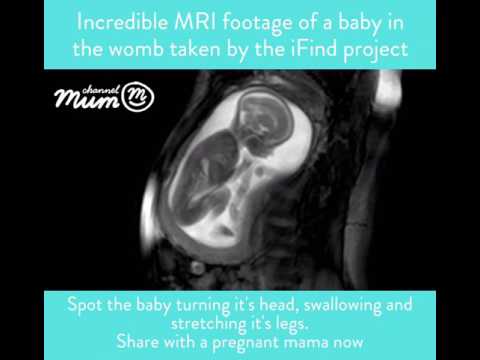
At 34 weeks, the fetal brain is growing rapidly and becoming more complex. Neural connections are forming at an accelerated rate, allowing for more refined sensory experiences and motor control.
Key Brain Developments:
The cerebral cortex, responsible for higher cognitive functions, is developing grooves and folds, increasing the brain's surface area.
The cerebellum, which controls movement and coordination, continues to mature, allowing the fetus to practice movements such as kicking and stretching.
The fetus now exhibits REM (rapid eye movement) sleep, which is associated with dreaming.
Reflexes such as the sucking reflex are well established, which helps the fetus practice for feeding after birth.
Memory and learning abilities begin to develop, as the fetus can recognize familiar voices, particularly that of the mother.
---
4. Sensory Development
By 34 weeks, the fetus has developed a sophisticated range of sensory experiences, which help prepare it for the outside world.
Hearing
The auditory system is well-developed, and the fetus can respond to loud noises by moving or changing heart rate.
The fetus recognizes and responds to familiar voices, particularly the mother’s voice, with a calming effect.
External sounds, such as music or conversations, can cause movement or changes in breathing patterns.
Vision
The eyelids can open and close, and the eyes can track light if it filters through the womb.
The fetus can distinguish between light and dark and reacts to bright light sources by turning away or blinking.
Eye color is present, though it may continue to change after birth due to pigment development.
Taste and Smell
The fetus can detect flavors from the amniotic fluid, which carries traces of the mother's diet.
Studies suggest the fetus may develop a preference for certain tastes based on maternal nutrition.
Olfactory receptors are present, though the sense of smell will fully develop after birth when exposed to air.
Touch
The fetus can respond to tactile stimulation, particularly around the face and hands.
It may explore the environment within the uterus by touching the umbilical cord or sucking its thumb. #34 weeks pregnant #34 weeks gestation #third trimester #pregnancy symptoms #developmental biology #pregnant #prenatal growth #pregnancy #34 weeks embryo #obstetrics insight #34 week fetus #prenatal education #pregnancy week 34 #pregnancy stages #early pregnancy symptoms
 0:06:51
0:06:51
 0:01:40
0:01:40
 0:03:09
0:03:09
 0:03:47
0:03:47
 0:00:06
0:00:06
 0:01:06
0:01:06
 0:00:14
0:00:14
 0:00:21
0:00:21
 0:04:12
0:04:12
 0:00:21
0:00:21
 0:00:24
0:00:24
 0:00:10
0:00:10
 0:08:31
0:08:31
 0:00:16
0:00:16
 0:00:23
0:00:23
 0:00:12
0:00:12
 0:07:33
0:07:33
 0:00:12
0:00:12
 0:00:05
0:00:05
 0:00:14
0:00:14
 0:00:13
0:00:13
 0:00:27
0:00:27
 0:00:13
0:00:13
 0:02:25
0:02:25