filmov
tv
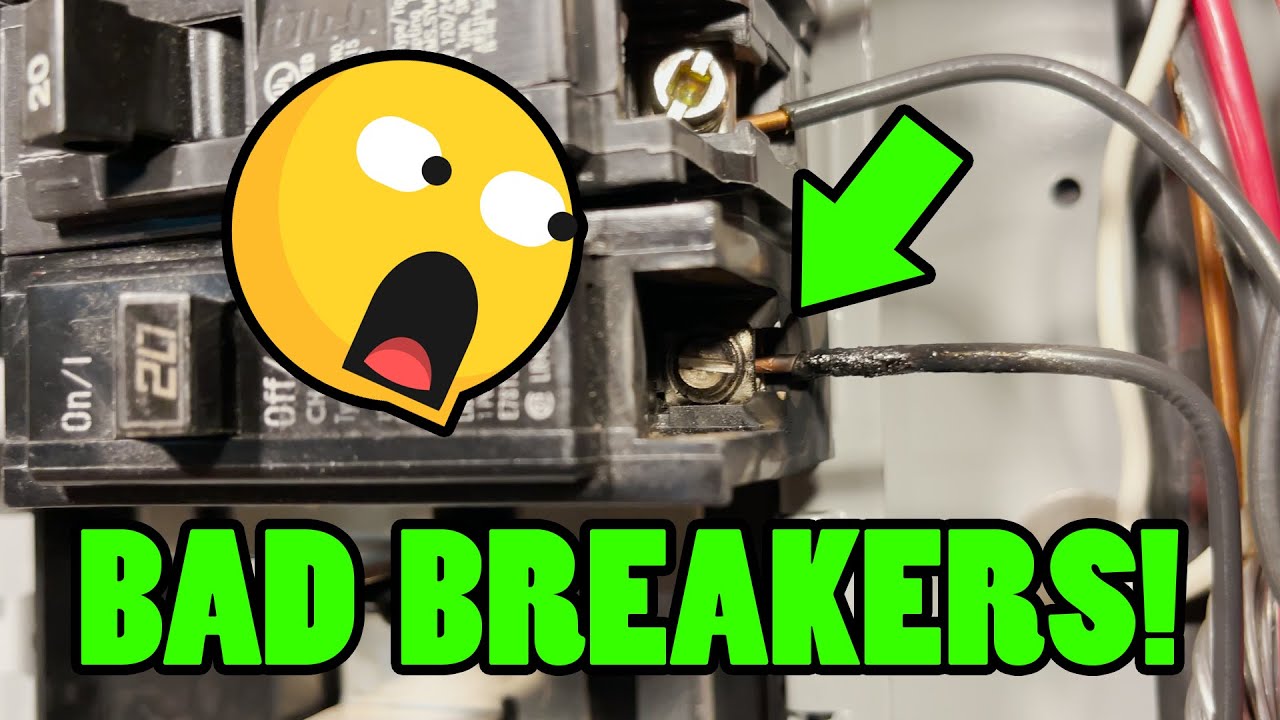
How to Tell if a Breaker is Bad
Показать описание
There will undoubtedly come a time in your electrical career where you will need to troubleshoot a bad breaker. How do you go about diagnosing whether or not a breaker is bad?
🤘⚡️EU Learning System⚡️🤘
-Video courses on every side of the electrical trade (theory, code, safety, wiring, install, troubleshooting, leadership, and more)
-Practice exams for 2017, 2020, 2023 code
-YouTube videos categorized and searchable
-Audio lessons
-Forum
-Business version has admin portal and ability to assign learning to technicians and monitor progress
-Any business size from 2 techs to 2,000!
🎓💡CONTINUING EDUCATION💡🎓
-State Approved
-Video Based
✍📝PRACTICE EXAMS📝✍
-2017, 2020, and 2023 NEC versions
-Online Residential Wireman Exam
-Online Journeyman Exam
-Online Master Exam
-300 Question Online Code Cannon (not license specific, all code)
-Take as many times as you want
-All of the above come with printable PDFs
🎤🎧PODCAST🎧🎤
Spotify:
Apple Podcast:
📱👍SOCIALS👍📱
🎧🎹Music, Editing, and Videography by Drake Descant and Rob LeBlanc🎹🎧
SPONSOR:
Make sure you use Coupon Code ELECTRICIANU for a 15% discount on all products
#electrician #electrical #electricity
Over the course of a circuit-breaker's life it can become damaged. It is a simple mechanical object that always has a certain level of heat it's experiencing, when current is flowing through it. So excessive heat can cause the components inside to weaken over time. Moisture and extreme fluctuations in temperature can also cause breakers to fail over time.
For non-general-use breakers such as smart-breakers, AFCI, GFCI, Dual Function, and shunt-trip breakers, they may have additional internal computer boards and components that can fail too. Many times these utilize more intricate/weaker secondary components that fail more often than the primary components of the breaker.
There are several ways to diagnose a bad breaker, including a simple visual inspection of the handle, the terminal, and the back side of the breaker where it attaches to the panel's busbar. Often times you'll see signs of melted plastic where excess heating occurs, and it's usually where there's a termination or a point where two things are making contact. Other things to watch out for are a breaker not tripping when it is intentionally short circuited. Lastly, if there are no physical signs of damage to the breaker, you can test the internal circuitry of the breaker by testing the terminals with a multimeter. The breaker should have voltage from the output terminal to ground and/or neutral. If it is a 2-pole or 3-pole breaker there should be voltage between each of the terminals of the breaker - typically around 208-240volts from terminal to terminal.
🤘⚡️EU Learning System⚡️🤘
-Video courses on every side of the electrical trade (theory, code, safety, wiring, install, troubleshooting, leadership, and more)
-Practice exams for 2017, 2020, 2023 code
-YouTube videos categorized and searchable
-Audio lessons
-Forum
-Business version has admin portal and ability to assign learning to technicians and monitor progress
-Any business size from 2 techs to 2,000!
🎓💡CONTINUING EDUCATION💡🎓
-State Approved
-Video Based
✍📝PRACTICE EXAMS📝✍
-2017, 2020, and 2023 NEC versions
-Online Residential Wireman Exam
-Online Journeyman Exam
-Online Master Exam
-300 Question Online Code Cannon (not license specific, all code)
-Take as many times as you want
-All of the above come with printable PDFs
🎤🎧PODCAST🎧🎤
Spotify:
Apple Podcast:
📱👍SOCIALS👍📱
🎧🎹Music, Editing, and Videography by Drake Descant and Rob LeBlanc🎹🎧
SPONSOR:
Make sure you use Coupon Code ELECTRICIANU for a 15% discount on all products
#electrician #electrical #electricity
Over the course of a circuit-breaker's life it can become damaged. It is a simple mechanical object that always has a certain level of heat it's experiencing, when current is flowing through it. So excessive heat can cause the components inside to weaken over time. Moisture and extreme fluctuations in temperature can also cause breakers to fail over time.
For non-general-use breakers such as smart-breakers, AFCI, GFCI, Dual Function, and shunt-trip breakers, they may have additional internal computer boards and components that can fail too. Many times these utilize more intricate/weaker secondary components that fail more often than the primary components of the breaker.
There are several ways to diagnose a bad breaker, including a simple visual inspection of the handle, the terminal, and the back side of the breaker where it attaches to the panel's busbar. Often times you'll see signs of melted plastic where excess heating occurs, and it's usually where there's a termination or a point where two things are making contact. Other things to watch out for are a breaker not tripping when it is intentionally short circuited. Lastly, if there are no physical signs of damage to the breaker, you can test the internal circuitry of the breaker by testing the terminals with a multimeter. The breaker should have voltage from the output terminal to ground and/or neutral. If it is a 2-pole or 3-pole breaker there should be voltage between each of the terminals of the breaker - typically around 208-240volts from terminal to terminal.
Комментарии
 0:04:43
0:04:43
 0:00:26
0:00:26
 0:01:34
0:01:34
 0:00:41
0:00:41
 0:01:19
0:01:19
 0:05:53
0:05:53
 0:07:20
0:07:20
 0:00:37
0:00:37
 0:12:15
0:12:15
 0:14:00
0:14:00
 0:09:56
0:09:56
 0:05:25
0:05:25
 0:09:13
0:09:13
 0:04:05
0:04:05
 0:06:18
0:06:18
 0:07:23
0:07:23
 0:07:38
0:07:38
 0:10:00
0:10:00
 0:06:05
0:06:05
 0:00:40
0:00:40
 0:06:21
0:06:21
 0:00:27
0:00:27
 0:08:36
0:08:36
 0:03:48
0:03:48