filmov
tv
Tritone Substitution: the one jazz piano trick you need to know

Показать описание
► Free Jazz Piano Crash Course:
Tritone Substitution is a reharmonisation technique that can be used to add harmonic interest and variety to a chord progression.
Tritone substitutions are also knows as substitute dominants or sub 5's so be aware that these 3 terms refer to the same thing.
This lesson will explain what tritone substitution is, why it works and how to apply it to a major 251 progression.
What Is A Tritone?
A tritone is an interval of 3 whole steps or 6 half steps on the piano. The tritone marks exactly half of the octave.
Here’s a few examples:
C to F# is a tritone.
D to Ab is a tritone
F to B is a tritone
You will be glad to hear that there are only 6 tritones that you need to learn. This is because tritones are symmetrical when inverted in the sense that you still have a tritone interval.
What Is Tritone Substitution?
Tritone substitution is when a dominant 7 chord is substituted for the dominant 7th chord a tritone away.
You might ask how is this possible?
The answer is because dominant chords that are a tritone apart share the same 3rd and 7th. Remember that the 3rd and 7th are what gives the chord it’s unique harmonic quality so therefore, chords that share the same 3rd and 7th are harmonically very similar.
Let’s look at an example:
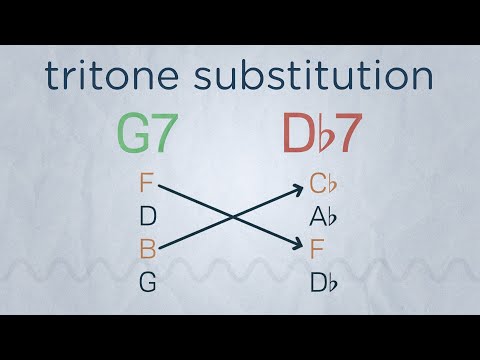
The root of G7 is a tritone away from the root of Db7 which makes them tritone substitutes.
Let’s compare the notes of G7 and Db7:
G, B, D, F
Db, F, Ab, Cb
Db7 and G7 share the same 3rd and 7th notes but in reverse order.
It’s worth noting here that B (3rd of G7) and Cb (7th of Db7) are enharmonic equivalents, meaning that they are the exact same note but they are spelt or notated differently.
Tritone Substitution and the 251 Progression:
A tritone substitution is an easy way to add variety to a 251 progression.
In the key of C, a 251 progression contains the chords:
Dm7, G7 and Cmaj7.
The tritone substitution for the 5 chord G7 would be Db7.
G7 and Db7 share the same tritone interval which gives both chords their dominant quality and makes these two chords interchangeable.
All that changes is the bass note but this then has an effect on the extensions and alterations.
Why do we use tritone substitution?
To create very smooth voice leading in a 251 progression, the root of each chord moves down by a half step to resolution rather than moving by 5ths intervals.
Chromatic, step wise bass line movement
Access different scales and arpeggios for improvisation
Alternative ways to harmonize the melody to add dynamics and interest to your performance.
Tritone Substitution is a reharmonisation technique that can be used to add harmonic interest and variety to a chord progression.
Tritone substitutions are also knows as substitute dominants or sub 5's so be aware that these 3 terms refer to the same thing.
This lesson will explain what tritone substitution is, why it works and how to apply it to a major 251 progression.
What Is A Tritone?
A tritone is an interval of 3 whole steps or 6 half steps on the piano. The tritone marks exactly half of the octave.
Here’s a few examples:
C to F# is a tritone.
D to Ab is a tritone
F to B is a tritone
You will be glad to hear that there are only 6 tritones that you need to learn. This is because tritones are symmetrical when inverted in the sense that you still have a tritone interval.
What Is Tritone Substitution?
Tritone substitution is when a dominant 7 chord is substituted for the dominant 7th chord a tritone away.
You might ask how is this possible?
The answer is because dominant chords that are a tritone apart share the same 3rd and 7th. Remember that the 3rd and 7th are what gives the chord it’s unique harmonic quality so therefore, chords that share the same 3rd and 7th are harmonically very similar.
Let’s look at an example:
The root of G7 is a tritone away from the root of Db7 which makes them tritone substitutes.
Let’s compare the notes of G7 and Db7:
G, B, D, F
Db, F, Ab, Cb
Db7 and G7 share the same 3rd and 7th notes but in reverse order.
It’s worth noting here that B (3rd of G7) and Cb (7th of Db7) are enharmonic equivalents, meaning that they are the exact same note but they are spelt or notated differently.
Tritone Substitution and the 251 Progression:
A tritone substitution is an easy way to add variety to a 251 progression.
In the key of C, a 251 progression contains the chords:
Dm7, G7 and Cmaj7.
The tritone substitution for the 5 chord G7 would be Db7.
G7 and Db7 share the same tritone interval which gives both chords their dominant quality and makes these two chords interchangeable.
All that changes is the bass note but this then has an effect on the extensions and alterations.
Why do we use tritone substitution?
To create very smooth voice leading in a 251 progression, the root of each chord moves down by a half step to resolution rather than moving by 5ths intervals.
Chromatic, step wise bass line movement
Access different scales and arpeggios for improvisation
Alternative ways to harmonize the melody to add dynamics and interest to your performance.
Комментарии
 0:15:42
0:15:42
 0:17:02
0:17:02
 0:17:11
0:17:11
 0:01:00
0:01:00
 0:00:51
0:00:51
 0:11:06
0:11:06
 0:13:23
0:13:23
 0:00:27
0:00:27
 0:06:01
0:06:01
 0:00:59
0:00:59
 0:12:26
0:12:26
 0:27:56
0:27:56
 0:09:36
0:09:36
 0:00:47
0:00:47
 0:00:50
0:00:50
 0:11:35
0:11:35
 0:00:29
0:00:29
 0:06:36
0:06:36
 0:00:17
0:00:17
 0:12:04
0:12:04
 0:06:25
0:06:25
 0:06:02
0:06:02
 0:00:56
0:00:56
 0:05:29
0:05:29