filmov
tv
Flow Cytometry

Показать описание
Flow cytometry is a powerful technique used in biology and medicine to analyze and quantify various physical and chemical characteristics of cells and particles. It provides insights into cell populations, their properties, and their behaviors based on the detection of fluorescent signals. Flow cytometry is widely used in fields such as immunology, hematology, cancer research, microbiology, and more.
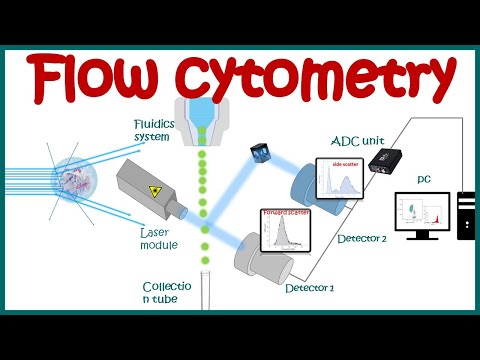
The basic principle of flow cytometry involves the measurement of scattered light and fluorescent emissions from individual cells or particles as they pass through a laser beam and a series of detectors. Here's how the process generally works:
1. Sample Preparation: The sample is typically a suspension of cells or particles that have been treated with fluorescent dyes or antibodies. These dyes can bind to specific cellular components, such as proteins or DNA, allowing researchers to target and analyze specific features.
2. Laser Excitation: The sample is injected into a flow cytometer, a specialized instrument that contains a fluidics system to transport the sample in a controlled manner. The sample stream passes through a laser beam, which excites the fluorescent dyes bound to the cells or particles.
3. Scattered Light Detection: As the cells pass through the laser beam, they scatter light in different directions. The scattered light can be captured by detectors placed at various angles to provide information about cell size, shape, and granularity.
4. Fluorescent Emission Detection: If the cells are labeled with fluorescent dyes or antibodies, they will emit light at specific wavelengths when excited by the laser. Multiple detectors are used to capture this emitted light at various wavelengths, allowing researchers to measure different characteristics of the cells, such as the expression of specific proteins, the presence of certain molecules, or cell viability.
5. Data Analysis: The data collected from the detectors are processed and analyzed using specialized software. Researchers can create plots called "scatter plots" to visualize the data and identify different cell populations based on their unique characteristics. This analysis helps researchers understand the heterogeneity of cell populations within a sample.
Flow cytometry offers several advantages:
- High Throughput: Flow cytometers can analyze thousands of cells per second, allowing for quick and efficient analysis of large cell populations.
- Multiparametric Analysis: Researchers can simultaneously measure multiple characteristics of cells, such as size, shape, and multiple fluorescence signals, providing a comprehensive view of cellular populations.
- Cell Sorting: Some advanced flow cytometers are equipped with cell sorting capabilities, allowing researchers to isolate specific cell populations for further study.
Applications of flow cytometry include immunophenotyping (identifying cell types based on surface markers), cell cycle analysis, apoptosis studies, intracellular ion concentration measurements, DNA content analysis, and more.
In summary, flow cytometry is a versatile and powerful tool that enables researchers to analyze and quantify cellular characteristics with high precision and efficiency, contributing to advancements in various scientific and medical fields.
The basic principle of flow cytometry involves the measurement of scattered light and fluorescent emissions from individual cells or particles as they pass through a laser beam and a series of detectors. Here's how the process generally works:
1. Sample Preparation: The sample is typically a suspension of cells or particles that have been treated with fluorescent dyes or antibodies. These dyes can bind to specific cellular components, such as proteins or DNA, allowing researchers to target and analyze specific features.
2. Laser Excitation: The sample is injected into a flow cytometer, a specialized instrument that contains a fluidics system to transport the sample in a controlled manner. The sample stream passes through a laser beam, which excites the fluorescent dyes bound to the cells or particles.
3. Scattered Light Detection: As the cells pass through the laser beam, they scatter light in different directions. The scattered light can be captured by detectors placed at various angles to provide information about cell size, shape, and granularity.
4. Fluorescent Emission Detection: If the cells are labeled with fluorescent dyes or antibodies, they will emit light at specific wavelengths when excited by the laser. Multiple detectors are used to capture this emitted light at various wavelengths, allowing researchers to measure different characteristics of the cells, such as the expression of specific proteins, the presence of certain molecules, or cell viability.
5. Data Analysis: The data collected from the detectors are processed and analyzed using specialized software. Researchers can create plots called "scatter plots" to visualize the data and identify different cell populations based on their unique characteristics. This analysis helps researchers understand the heterogeneity of cell populations within a sample.
Flow cytometry offers several advantages:
- High Throughput: Flow cytometers can analyze thousands of cells per second, allowing for quick and efficient analysis of large cell populations.
- Multiparametric Analysis: Researchers can simultaneously measure multiple characteristics of cells, such as size, shape, and multiple fluorescence signals, providing a comprehensive view of cellular populations.
- Cell Sorting: Some advanced flow cytometers are equipped with cell sorting capabilities, allowing researchers to isolate specific cell populations for further study.
Applications of flow cytometry include immunophenotyping (identifying cell types based on surface markers), cell cycle analysis, apoptosis studies, intracellular ion concentration measurements, DNA content analysis, and more.
In summary, flow cytometry is a versatile and powerful tool that enables researchers to analyze and quantify cellular characteristics with high precision and efficiency, contributing to advancements in various scientific and medical fields.
 0:13:24
0:13:24
 0:01:34
0:01:34
 0:12:05
0:12:05
 0:08:50
0:08:50
 0:33:55
0:33:55
 0:04:35
0:04:35
 0:06:35
0:06:35
 0:04:42
0:04:42
 0:56:07
0:56:07
 0:01:36
0:01:36
 0:06:18
0:06:18
 0:04:00
0:04:00
 0:17:41
0:17:41
 0:49:41
0:49:41
 0:35:53
0:35:53
 0:42:37
0:42:37
 0:03:39
0:03:39
 0:11:13
0:11:13
 0:01:11
0:01:11
 1:34:54
1:34:54
 0:28:50
0:28:50
 0:56:05
0:56:05
 0:02:01
0:02:01
 0:02:58
0:02:58