filmov
tv
When does the derivative equal the integral?

Показать описание
We find a function such that its antiderivative equals its derivative #shorts
#calculus,#derivative,integral,numbers,integration,differentiation,derivative,integral,math elite,mathelite,maths,mathematics
#calculus,#derivative,integral,numbers,integration,differentiation,derivative,integral,math elite,mathelite,maths,mathematics
When does the derivative equal the integral?
A fascinating differential equation: when does the derivative equal the composition?
Derivative as a concept | Derivatives introduction | AP Calculus AB | Khan Academy
Definition of the Derivative
What is a derivative?
What is a Derivative? Deriving the Power Rule
The meaning behind the first and second derivative
Difference Between Partial and Total Derivative
Chain Rule Method of Differentiation | Derivatives #excellenceacademy #jonahemmanuel
Alternate Form of The Limit Definition of the Derivative - Calculus
Calculus - Lesson 10 | When does the Derivative Not Exist? | Don't Memorise
What's so special about Euler's number e? | Chapter 5, Essence of calculus
Calculus - How to find the derivative of a function using the power rule
Calculus 1 - Derivatives
What does area have to do with slope? | Chapter 9, Essence of calculus
Why is the derivative of e^x equal to e^x?
when two functions have the same derivative
Where a function is not differentiable | Taking derivatives | Differential Calculus | Khan Academy
Derivative by first principle- Example 2.
The derivative of e^x.
Exponential derivative visual
Given fx sketch the first and second derivative graph
What is a derivative in Calculus? Derivatives explained in simple language...finally.
The paradox of the derivative | Chapter 2, Essence of calculus
Комментарии
 0:10:31
0:10:31
 0:07:16
0:07:16
 0:23:31
0:23:31
 0:10:43
0:10:43
 0:10:05
0:10:05
 0:02:55
0:02:55
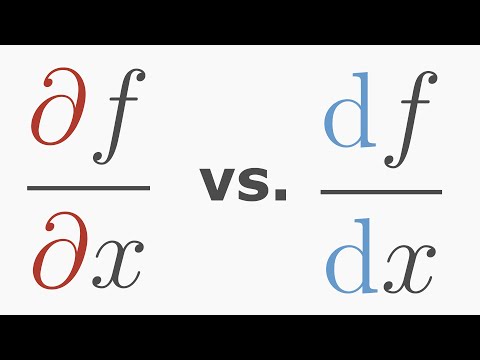 0:01:44
0:01:44
 0:01:00
0:01:00
 0:08:10
0:08:10
 0:11:03
0:11:03
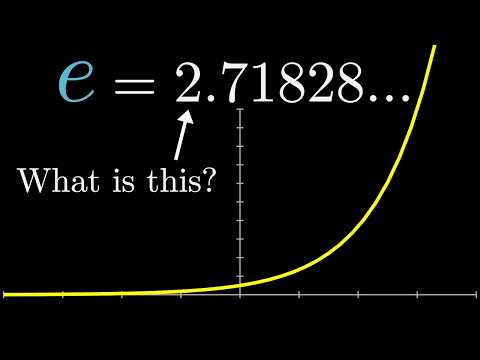 0:13:50
0:13:50
 0:05:21
0:05:21
 0:52:51
0:52:51
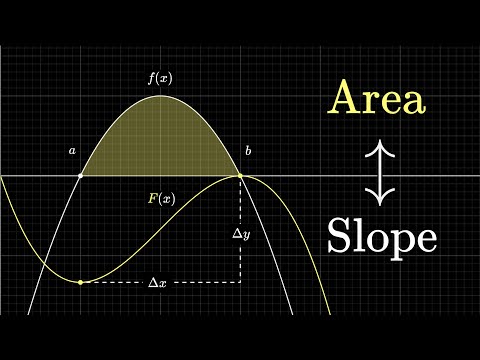 0:12:39
0:12:39
 0:11:59
0:11:59
 0:06:20
0:06:20
 0:03:35
0:03:35
 0:04:54
0:04:54
 0:02:10
0:02:10
 0:00:57
0:00:57
 0:04:09
0:04:09
 0:01:46
0:01:46
 0:16:50
0:16:50