filmov
tv
How E2 Elimination Reactions Work (Animation) | Mechanism & Orbitals | Organic Chemistry

Показать описание
👀 This video explains E2 eliminations: basics of geometries, orbitals, selectivities...
🚀 Thanks to all channel supporters!!!
👉 Follow me on Instagram for updates on random research, chemistry problems and interesting news!
00:00 E2 elimination basics and orbitals
01:14 Ask yourself these questions
01:31 Level 1: 2-Bromobutane elimination and stereoselectivity
02:46 Level 2: Kinetic isotope effects and stereospecificity
04:35 Level 3: Cyclic substrates and A-values
06:25 Level 4: Peterson olefination and Brook rearrangement
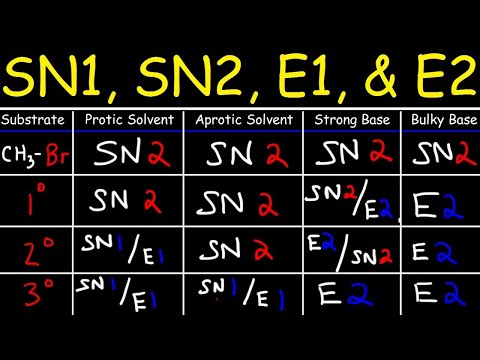
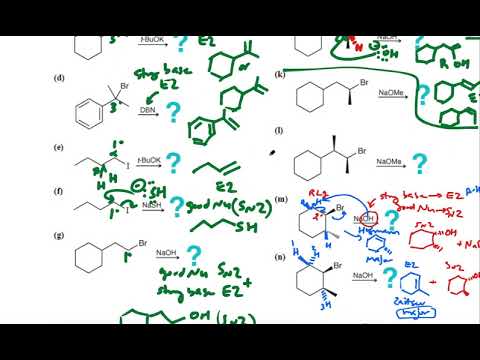
The bimolecular elimination (E2 elimination) reaction is a cornerstone of organic chemistry, particularly for synthesis of alkenes. In the E2 mechanism, a base abstracts a proton (H+) from a carbon adjacent to an sp3-hybridized carbon, which is bonded to a leaving group. Simultaneous expulsion of the leaving group, forms a double bond (alkene) - with a concerted mechanism (deprotonation and and leaving group departure occur in a single step). This contrasts with the E1 elimination mechanism, where the leaving group's departure is the rate-determining step and occurs before the deprotonation step.
Some recommended books on organic synthesis:
- Clayden, Greeves, Warren; Organic Chemistry (basic organic chemistry knowledge)
- Wyatt, Warren; Organic Synthesis: The Disconnection Approach (excellent introduction to retrosynthesis)
- Kurti, Czako; Strategic Applications of Named Reactions in Organic Synthesis (extensive toolkit of functional group reactions and applications thereof with common conditions)
- Nicolaou; Classics in Total Synthesis 1-3 (the ultimate total synthesis trilogy)
- Nicolaou; Molecules That Changed the World (the world's most important molecules and their impact on everyday life)
- Carreira, Kvaerno; Classics in Stereoselective Synthesis (compilation of the groundbreaking methods of stereoselective synthesis and application to synthesis of stereochemically complex structures)
🚀 Thanks to all channel supporters!!!
👉 Follow me on Instagram for updates on random research, chemistry problems and interesting news!
00:00 E2 elimination basics and orbitals
01:14 Ask yourself these questions
01:31 Level 1: 2-Bromobutane elimination and stereoselectivity
02:46 Level 2: Kinetic isotope effects and stereospecificity
04:35 Level 3: Cyclic substrates and A-values
06:25 Level 4: Peterson olefination and Brook rearrangement
The bimolecular elimination (E2 elimination) reaction is a cornerstone of organic chemistry, particularly for synthesis of alkenes. In the E2 mechanism, a base abstracts a proton (H+) from a carbon adjacent to an sp3-hybridized carbon, which is bonded to a leaving group. Simultaneous expulsion of the leaving group, forms a double bond (alkene) - with a concerted mechanism (deprotonation and and leaving group departure occur in a single step). This contrasts with the E1 elimination mechanism, where the leaving group's departure is the rate-determining step and occurs before the deprotonation step.
Some recommended books on organic synthesis:
- Clayden, Greeves, Warren; Organic Chemistry (basic organic chemistry knowledge)
- Wyatt, Warren; Organic Synthesis: The Disconnection Approach (excellent introduction to retrosynthesis)
- Kurti, Czako; Strategic Applications of Named Reactions in Organic Synthesis (extensive toolkit of functional group reactions and applications thereof with common conditions)
- Nicolaou; Classics in Total Synthesis 1-3 (the ultimate total synthesis trilogy)
- Nicolaou; Molecules That Changed the World (the world's most important molecules and their impact on everyday life)
- Carreira, Kvaerno; Classics in Stereoselective Synthesis (compilation of the groundbreaking methods of stereoselective synthesis and application to synthesis of stereochemically complex structures)
Комментарии
 0:08:32
0:08:32
 0:13:58
0:13:58
 0:12:20
0:12:20
 0:03:29
0:03:29
 0:06:42
0:06:42
 0:13:26
0:13:26
 0:13:31
0:13:31
 0:38:50
0:38:50
 0:06:15
0:06:15
 0:25:54
0:25:54
 0:15:26
0:15:26
 0:34:16
0:34:16
 0:02:03
0:02:03
 0:12:23
0:12:23
 0:05:17
0:05:17
 0:11:25
0:11:25
 0:10:36
0:10:36
 0:09:57
0:09:57
 0:46:33
0:46:33
 0:07:44
0:07:44
 0:09:06
0:09:06
 0:13:07
0:13:07
 0:14:34
0:14:34
 0:10:41
0:10:41