filmov
tv
E2 Reaction Mechanism - Hoffman Elimination vs Zaitsev's Rule

Показать описание
This organic chemistry video tutorial provides a basic introduction into the E2 reaction mechanism. The hoffman product is the least stable alkene and the zaitsev product is the most stable alkene. The hoffman product can be formed using a bulky base with a sterically hindered alkyl halide or using an alkyl fluoride.
Stereochemistry R/S Configuration:
Optical Activity & Specific Rotation:
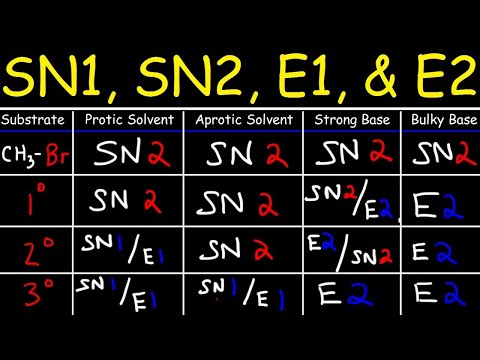
SN1, SN2, E1, E2 Reaction Mechanisms:
SN2 Reaction Mechanisms:
SN2 - Test Question:
_______________________________
SN1 Reaction Mechanisms:
Carbocation Stability - Hyperconjugation:
Carbanion Stability:
Protic Vs Aprotic Solvents:
E1 Ring Expansion:
E2 - Test Question:
________________________________
E2 Stereochemistry - Newman Projections:
SN1, SN2, E1, E2 - Practice Test:
Organic Chemistry PDF Worksheets:
Organic Chemistry 1 Exam 2 Playlist:
Full-Length Videos and Worksheets:
Stereochemistry R/S Configuration:
Optical Activity & Specific Rotation:
SN1, SN2, E1, E2 Reaction Mechanisms:
SN2 Reaction Mechanisms:
SN2 - Test Question:
_______________________________
SN1 Reaction Mechanisms:
Carbocation Stability - Hyperconjugation:
Carbanion Stability:
Protic Vs Aprotic Solvents:
E1 Ring Expansion:
E2 - Test Question:
________________________________
E2 Stereochemistry - Newman Projections:
SN1, SN2, E1, E2 - Practice Test:
Organic Chemistry PDF Worksheets:
Organic Chemistry 1 Exam 2 Playlist:
Full-Length Videos and Worksheets:
Комментарии
 0:12:20
0:12:20
 0:05:41
0:05:41
 0:13:31
0:13:31
 0:10:28
0:10:28
 0:03:29
0:03:29
 0:34:16
0:34:16
 0:25:54
0:25:54
 0:13:58
0:13:58
 0:13:26
0:13:26
 0:11:50
0:11:50
 0:07:52
0:07:52
 0:04:29
0:04:29
 0:39:33
0:39:33
 0:09:03
0:09:03
 0:38:50
0:38:50
 0:11:57
0:11:57
 0:11:25
0:11:25
 0:06:07
0:06:07
 0:10:22
0:10:22
 0:10:34
0:10:34
 0:11:32
0:11:32
 0:04:53
0:04:53
 0:08:49
0:08:49
 0:13:31
0:13:31