filmov
tv
Lymphocytes | T cells

Показать описание
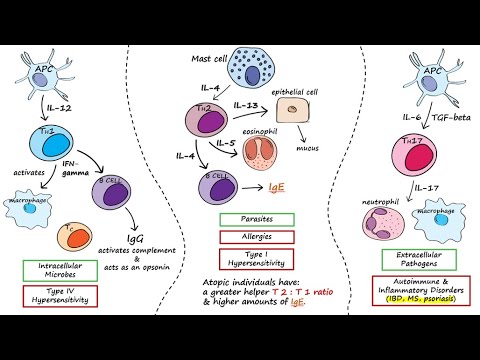
A lymphocyte is a type of white blood cell (leukocyte) in the immune system of most vertebrates. Lymphocytes include T cells (for cell-mediated, cytotoxic adaptive immunity), B cells (for humoral, antibody-driven adaptive immunity),and Innate lymphoid cells (ILCs) ("innate T cell-like" cells involved in mucosal immunity and homeostasis), of which natural killer cells are an important subtype (which functions in cell-mediated, cytotoxic innate immunity). They are the main type of cell found in lymph, which prompted the name "lymphocyte" (with cyte meaning cell).Lymphocytes make up between 18% and 42% of circulating white blood cells.
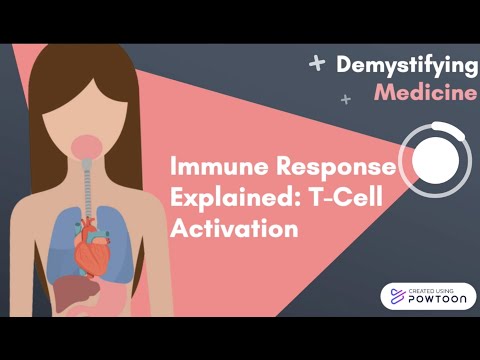
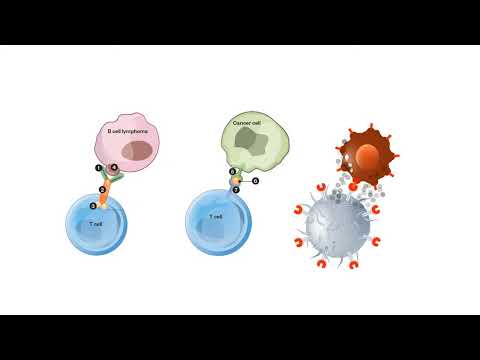
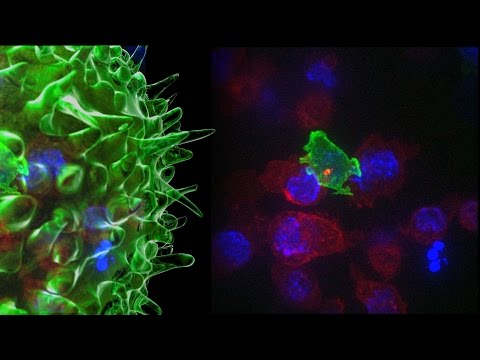
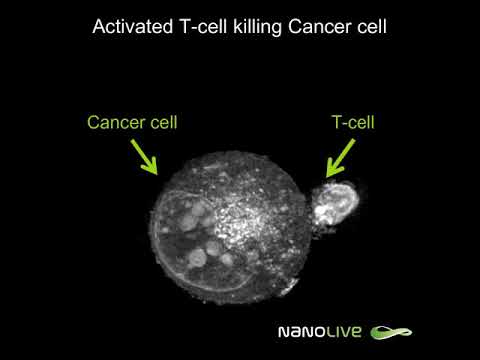
T cells are one of the important types of white blood cells of the immune system and play a central role in the adaptive immune response. T cells can be distinguished from other lymphocytes by the presence of a T-cell receptor (TCR) on their cell surface.
T cells are born from hematopoietic stem cells,[1] found in the bone marrow. Developing T cells then migrate to the thymus gland to develop (or mature). T cells derive their name from the thymus.[2][3] After migration to the thymus, the precursor cells mature into several distinct types of T cells. T cell differentiation also continues after they have left the thymus. Groups of specific, differentiated T cell subtypes have a variety of important functions in controlling and shaping the immune response.
Комментарии
 0:05:49
0:05:49
 0:06:53
0:06:53
 0:07:15
0:07:15
 0:23:50
0:23:50
 0:00:16
0:00:16
 0:09:01
0:09:01
 0:05:01
0:05:01
 0:04:31
0:04:31
 0:36:39
0:36:39
 0:11:07
0:11:07
 0:16:48
0:16:48
 0:00:45
0:00:45
 0:01:02
0:01:02
 0:20:34
0:20:34
 0:16:31
0:16:31
 0:06:39
0:06:39
 0:01:55
0:01:55
 0:09:13
0:09:13
 0:15:29
0:15:29
 0:00:16
0:00:16
 0:25:29
0:25:29
 0:06:23
0:06:23
 0:06:26
0:06:26
 1:27:48
1:27:48