filmov
tv
Formal Charge Practice Problems with Explanations

Показать описание
A video of formal charge practice problems (from easy to difficult) with clear, concise answers and explanations.
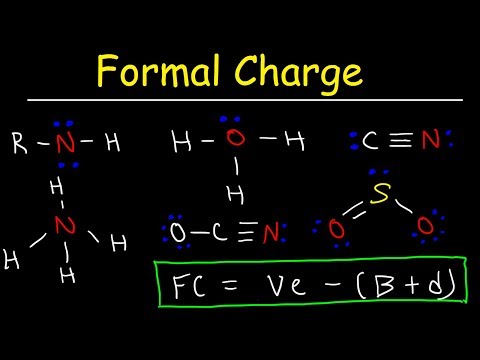
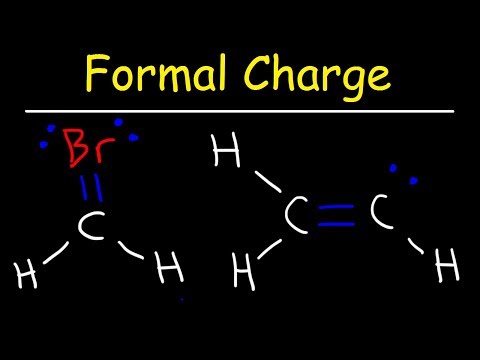
Calculating the formal charges for a molecule is a reasonably reliable way to tell what the most favorable LS is in the real world.
We start with a Lewis Structure and then calculate the charges for each atom. The most favorable or “best” Lewis Structure for a molecule is the one with formal charges closest to zero. Zero is even better.
We’ll use the equation:
Formal charge = [# of valence electrons] - [nonbonding val electrons] - [bonding electrons / 2]
The number of valence electrons for the atom of interest is found on the Periodic Table.
Nonbonding valence electrons are those around the atom of interest that are not involved in chemical bonds (they aren't being shared with another atom).
Bonding valence electrons are the ones shared between atoms. We'll divide this number by two.
Some things to note about Formal Charges:
- Formal charge is different from the oxidation number!
- If you can exceed the octet rule for the central atom it's a good idea to check the formal charges.
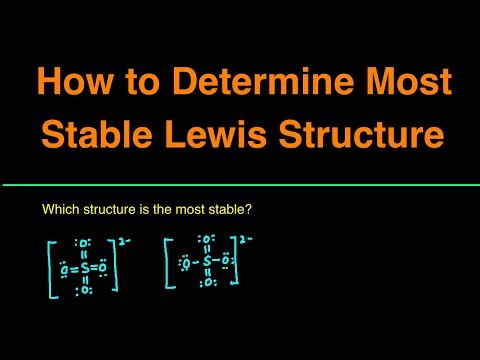
- If we have isomers or resonance -- formal charges will help us determine most stable structure.
- The closer the formal charges are to zero the more likely we have the most favorable Lewis structure for the molecule.
- We write the formal charges in (). E.g. (-1)
Helpful Videos:
Drawing/writing done in InkScape. Screen capture done with Camtasia Studio 4.0. Done on a Dell Dimension laptop computer with a Wacom digital tablet (Bamboo).
Calculating the formal charges for a molecule is a reasonably reliable way to tell what the most favorable LS is in the real world.
We start with a Lewis Structure and then calculate the charges for each atom. The most favorable or “best” Lewis Structure for a molecule is the one with formal charges closest to zero. Zero is even better.
We’ll use the equation:
Formal charge = [# of valence electrons] - [nonbonding val electrons] - [bonding electrons / 2]
The number of valence electrons for the atom of interest is found on the Periodic Table.
Nonbonding valence electrons are those around the atom of interest that are not involved in chemical bonds (they aren't being shared with another atom).
Bonding valence electrons are the ones shared between atoms. We'll divide this number by two.
Some things to note about Formal Charges:
- Formal charge is different from the oxidation number!
- If you can exceed the octet rule for the central atom it's a good idea to check the formal charges.
- If we have isomers or resonance -- formal charges will help us determine most stable structure.
- The closer the formal charges are to zero the more likely we have the most favorable Lewis structure for the molecule.
- We write the formal charges in (). E.g. (-1)
Helpful Videos:
Drawing/writing done in InkScape. Screen capture done with Camtasia Studio 4.0. Done on a Dell Dimension laptop computer with a Wacom digital tablet (Bamboo).
Комментарии
 0:10:41
0:10:41
 0:13:10
0:13:10
 0:28:30
0:28:30
 0:04:24
0:04:24
 0:06:14
0:06:14
 0:09:39
0:09:39
 0:04:27
0:04:27
 0:12:08
0:12:08
 0:05:44
0:05:44
 0:05:51
0:05:51
 0:07:44
0:07:44
 0:00:55
0:00:55
 0:12:54
0:12:54
 0:05:16
0:05:16
 0:26:27
0:26:27
 0:10:35
0:10:35
 0:06:03
0:06:03
 0:04:59
0:04:59
 0:11:29
0:11:29
 0:06:35
0:06:35
 0:06:37
0:06:37
 0:06:29
0:06:29
 0:02:47
0:02:47
 0:15:01
0:15:01