filmov
tv
Is Metformin Safe For You? This Is What Experts Say! Risks vs Benefits Of Taking Metformin

Показать описание
Metformin is an oral anti-diabetic medication, approved by the U.S Food and Drug Administration in the treatment of type 2 diabetes.
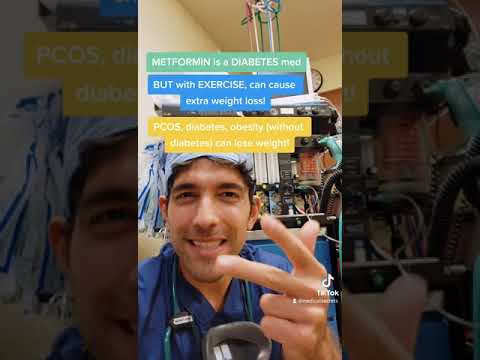
Other indications of metformin include treatment of gestational diabetes, polycystic ovarian syndrome, and to prevent diabetes in individuals with pre-diabetes.
Metformin works in the body through several mechanisms.
Its major action is to reduce gluconeogenesis, or new glucose production in the liver.
In addition, it increases the uptake of glucose from peripheral tissues, especially the adipose tissue and muscle.
It also increases the fatty acid oxidation, decreases glycogen, protein, fatty acid, and cholesterol synthesis, decreases intestinal absorption of glucose, and reduces LDL cholesterol while increasing HDL cholesterol in blood, which reduces the cardiovascular risk in patients with type 2 diabetes.
Over the years, metformin has been studied thoroughly in relation to its potential benefits and risks.
Many studies have determined that it has a very low side effect profile and many additional benefits other than lowering blood glucose levels in individuals with type 2 diabetes.
One of those benefits is protection against cancer.
A large case-control study revealed that metformin has protective effects against pancreatic cancer.
In addition, it has anti-proliferative effects on colon, pancreatic, breast, ovarian, prostate, and lung cancer cells.
Although the exact mechanism behind the anti-cancer properties of metformin is not clear, researchers believe that it may be due to the antioxidant effects of metformin, which is also beneficial in reducing the formation of atherosclerotic plaques in coronary arteries.
Prevention of nephrotoxicity is another effect of metformin.
Recent studies have shown that metformin has therapeutic or protective effects against nephrotoxic agents.
It also significantly decreases albuminuria and reduces renal damage in patients with diabetic nephropathy.
During pregnancy, metformin effectively reduces blood glucose levels in women with gestational diabetes.
It has also been suggested that women who have used metformin instead of insulin might be healthier in the post-partum period.
As already mentioned, metformin has a very low side effect profile, and it is well tolerated by most individuals.
Some mild adverse effects include gastrointestinal disturbances such as diarrhea, nausea, and vomiting.
Less common side effects include, headache, chest discomfort, increased sweating, hypoglycemia, or low blood sugar, and weakness.
Prolonged use of metformin can lead to reduced vitamin B12 levels, which can lead to peripheral neuropathy.
Metformin carries a risk of life-threatening lactic acidosis.
However, this adverse effect is very rare, affecting only about 1 in 30000 patients.
It usually occurs when lactic acid cannot be eliminated from the body quickly, especially in renal and hepatic impairment.
Therefore, in patients with decreased kidney function, when the GFR is less than 30, and in patients with advanced liver disease, metformin is contraindicated.
Finally in conclusion, metformin is a good medication with a low side effect profile and many health benefits, but it should be used with caution in patients with renal and liver disease.
#metformin #medtoday
metformin side effects,metformin,metformin diarrhea,foods to avoid while taking metformin,is metformin safe for weight loss,what are the dangers of taking metformin,signs metformin is working,what is metformin 500 mg used for,what happens if you take metformin and don't need it,is metformin safe for kidneys
Other indications of metformin include treatment of gestational diabetes, polycystic ovarian syndrome, and to prevent diabetes in individuals with pre-diabetes.
Metformin works in the body through several mechanisms.
Its major action is to reduce gluconeogenesis, or new glucose production in the liver.
In addition, it increases the uptake of glucose from peripheral tissues, especially the adipose tissue and muscle.
It also increases the fatty acid oxidation, decreases glycogen, protein, fatty acid, and cholesterol synthesis, decreases intestinal absorption of glucose, and reduces LDL cholesterol while increasing HDL cholesterol in blood, which reduces the cardiovascular risk in patients with type 2 diabetes.
Over the years, metformin has been studied thoroughly in relation to its potential benefits and risks.
Many studies have determined that it has a very low side effect profile and many additional benefits other than lowering blood glucose levels in individuals with type 2 diabetes.
One of those benefits is protection against cancer.
A large case-control study revealed that metformin has protective effects against pancreatic cancer.
In addition, it has anti-proliferative effects on colon, pancreatic, breast, ovarian, prostate, and lung cancer cells.
Although the exact mechanism behind the anti-cancer properties of metformin is not clear, researchers believe that it may be due to the antioxidant effects of metformin, which is also beneficial in reducing the formation of atherosclerotic plaques in coronary arteries.
Prevention of nephrotoxicity is another effect of metformin.
Recent studies have shown that metformin has therapeutic or protective effects against nephrotoxic agents.
It also significantly decreases albuminuria and reduces renal damage in patients with diabetic nephropathy.
During pregnancy, metformin effectively reduces blood glucose levels in women with gestational diabetes.
It has also been suggested that women who have used metformin instead of insulin might be healthier in the post-partum period.
As already mentioned, metformin has a very low side effect profile, and it is well tolerated by most individuals.
Some mild adverse effects include gastrointestinal disturbances such as diarrhea, nausea, and vomiting.
Less common side effects include, headache, chest discomfort, increased sweating, hypoglycemia, or low blood sugar, and weakness.
Prolonged use of metformin can lead to reduced vitamin B12 levels, which can lead to peripheral neuropathy.
Metformin carries a risk of life-threatening lactic acidosis.
However, this adverse effect is very rare, affecting only about 1 in 30000 patients.
It usually occurs when lactic acid cannot be eliminated from the body quickly, especially in renal and hepatic impairment.
Therefore, in patients with decreased kidney function, when the GFR is less than 30, and in patients with advanced liver disease, metformin is contraindicated.
Finally in conclusion, metformin is a good medication with a low side effect profile and many health benefits, but it should be used with caution in patients with renal and liver disease.
#metformin #medtoday
metformin side effects,metformin,metformin diarrhea,foods to avoid while taking metformin,is metformin safe for weight loss,what are the dangers of taking metformin,signs metformin is working,what is metformin 500 mg used for,what happens if you take metformin and don't need it,is metformin safe for kidneys
Комментарии
 0:03:50
0:03:50
 0:11:17
0:11:17
 0:08:54
0:08:54
 0:05:56
0:05:56
 0:04:31
0:04:31
 0:00:51
0:00:51
 0:01:20
0:01:20
 0:53:29
0:53:29
 0:03:31
0:03:31
 0:10:28
0:10:28
 0:07:06
0:07:06
 0:07:03
0:07:03
 0:05:10
0:05:10
 0:00:16
0:00:16
 0:07:33
0:07:33
 0:02:08
0:02:08
 0:07:38
0:07:38
 0:00:59
0:00:59
 0:10:51
0:10:51
 0:15:51
0:15:51
 0:10:20
0:10:20
 0:00:36
0:00:36
 0:07:42
0:07:42
 0:08:27
0:08:27