filmov
tv
File Systems in OS III - File Allocation Table in OS | Directory Structure | inode technique

Показать описание
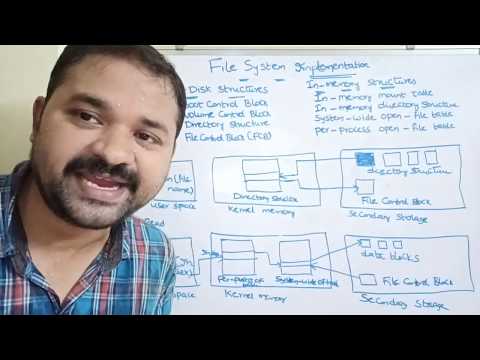
File Allocation Table (FAT) and inode structures are examples of windows and LINUX operating systems respectively. FAT file system is based on linked list and inode is an index based method used in Linux file system. File systems are computational structures that provide another level of abstraction that allows the user to manipulate and manage their files and directories.
This video talks in detail about some examples of how a real file system works in the os. The video also talks at length about the file and directory structures in FAT. This would lay a foundation of understanding the different variants of FAT file system such as the FAT12, FAT16, FAT32 etc.
Because the statistical data of years of analysis shows that most of the files are small, however, most of the disk drive space is eaten up by the larger files. So the video also talks about the i-node structure that was introduced to waive off the limitations of the single index allocation method that did not support larger files, which could not be represented just by a single block.
The links to the first two videos on File Systems are as follows:
(1/3) Technologies and performance model of disk drives
(2/3) Requirements of a File System and data allocation methods
This video talks in detail about some examples of how a real file system works in the os. The video also talks at length about the file and directory structures in FAT. This would lay a foundation of understanding the different variants of FAT file system such as the FAT12, FAT16, FAT32 etc.
Because the statistical data of years of analysis shows that most of the files are small, however, most of the disk drive space is eaten up by the larger files. So the video also talks about the i-node structure that was introduced to waive off the limitations of the single index allocation method that did not support larger files, which could not be represented just by a single block.
The links to the first two videos on File Systems are as follows:
(1/3) Technologies and performance model of disk drives
(2/3) Requirements of a File System and data allocation methods
Комментарии
 0:09:55
0:09:55
 0:02:44
0:02:44
 0:12:03
0:12:03
 0:23:34
0:23:34
 0:35:15
0:35:15
 0:11:05
0:11:05
 0:06:38
0:06:38
 0:05:16
0:05:16
 0:00:59
0:00:59
 0:06:03
0:06:03
 0:10:27
0:10:27
 0:08:01
0:08:01
 0:05:46
0:05:46
 0:06:01
0:06:01
 0:07:54
0:07:54
 0:05:12
0:05:12
 0:08:04
0:08:04
 0:15:59
0:15:59
 0:09:17
0:09:17
 0:05:05
0:05:05
 0:07:18
0:07:18
 0:21:20
0:21:20
 0:03:15
0:03:15
 0:05:40
0:05:40