filmov
tv
Live Super Nova Explosion of a Star

Показать описание
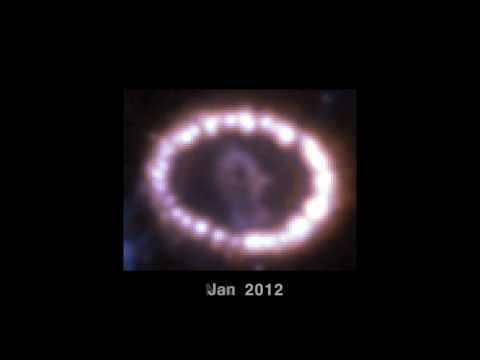
A supernova is a stellar explosion that briefly outshines an entire galaxy, radiating as much energy as the Sun or any ordinary star is expected to emit over its entire life span, before fading from view over several weeks or months.The extremely luminous burst of radiation expels much or all of a star's material at a velocity of up to 30,000 km/s (10% of the speed of light), driving a shock wave into the surrounding interstellar medium. This shock wave sweeps up an expanding shell of gas and dust called a supernova remnant. Supernovae are potentially strong galactic sources of gravitational waves.A great proportion of primary cosmic rays comes from supernovae.
Supernovae are more energetic than a nova. Nova means "new" in Latin, referring to what appears to be a very bright new star shining in the celestial sphere; the prefix "super-" distinguishes supernovae from ordinary novae, which are far less luminous. The word supernova was coined by Walter Baade and Fritz Zwicky in 1931.It is pronounced /ˌsuːpərnoʊvə/ with the plural supernovae /ˌsuːpərnoʊviː/ or supernovas (abbreviated SN, plural SNe after "supernovae").
Supernovae can be triggered in one of two ways: by the sudden re-ignition of nuclear fusion in a degenerate star; or by the gravitational collapse of the core of a massive star. In the first case, a degenerate white dwarf may accumulate sufficient material from a companion, either through accretion or via a merger, to raise its core temperature, ignite carbon fusion, and trigger runaway nuclear fusion, completely disrupting the star. In the second case, the core of a massive star may undergo sudden gravitational collapse, releasing gravitational potential energy that can create a supernova explosion.
The last directly observed supernova in the Milky Way was Kepler's Star of 1604 (SN 1604); remnants of two more recent supernovae have been found retrospectively.[7] Observations in other galaxies indicate that supernovae should occur on average about three times every century in the Milky Way, and that any galactic supernova would almost certainly be observable in modern astronomical equipment.[8] They play a significant role in enriching the interstellar medium with higher mass elements.Furthermore, the expanding shock waves from supernova explosions can trigger the formation of new stars.Betelgeuse explosion footage will be soon seen from Earth.
Supernovae are more energetic than a nova. Nova means "new" in Latin, referring to what appears to be a very bright new star shining in the celestial sphere; the prefix "super-" distinguishes supernovae from ordinary novae, which are far less luminous. The word supernova was coined by Walter Baade and Fritz Zwicky in 1931.It is pronounced /ˌsuːpərnoʊvə/ with the plural supernovae /ˌsuːpərnoʊviː/ or supernovas (abbreviated SN, plural SNe after "supernovae").
Supernovae can be triggered in one of two ways: by the sudden re-ignition of nuclear fusion in a degenerate star; or by the gravitational collapse of the core of a massive star. In the first case, a degenerate white dwarf may accumulate sufficient material from a companion, either through accretion or via a merger, to raise its core temperature, ignite carbon fusion, and trigger runaway nuclear fusion, completely disrupting the star. In the second case, the core of a massive star may undergo sudden gravitational collapse, releasing gravitational potential energy that can create a supernova explosion.
The last directly observed supernova in the Milky Way was Kepler's Star of 1604 (SN 1604); remnants of two more recent supernovae have been found retrospectively.[7] Observations in other galaxies indicate that supernovae should occur on average about three times every century in the Milky Way, and that any galactic supernova would almost certainly be observable in modern astronomical equipment.[8] They play a significant role in enriching the interstellar medium with higher mass elements.Furthermore, the expanding shock waves from supernova explosions can trigger the formation of new stars.Betelgeuse explosion footage will be soon seen from Earth.
Комментарии
 0:00:15
0:00:15
 0:01:10
0:01:10
 0:02:12
0:02:12
 0:00:13
0:00:13
 0:00:34
0:00:34
 0:01:07
0:01:07
 0:00:12
0:00:12
 0:00:52
0:00:52
 10:48:24
10:48:24
 0:02:12
0:02:12
 0:19:10
0:19:10
 0:00:44
0:00:44
 0:00:11
0:00:11
 0:30:16
0:30:16
 0:10:21
0:10:21
 0:00:32
0:00:32
 0:00:25
0:00:25
 0:00:46
0:00:46
 0:01:03
0:01:03
 0:01:34
0:01:34
 0:11:25
0:11:25
 0:12:12
0:12:12
 0:09:47
0:09:47
 0:00:46
0:00:46