filmov
tv
IPConfig Command Explained in Full Tutorial
Показать описание
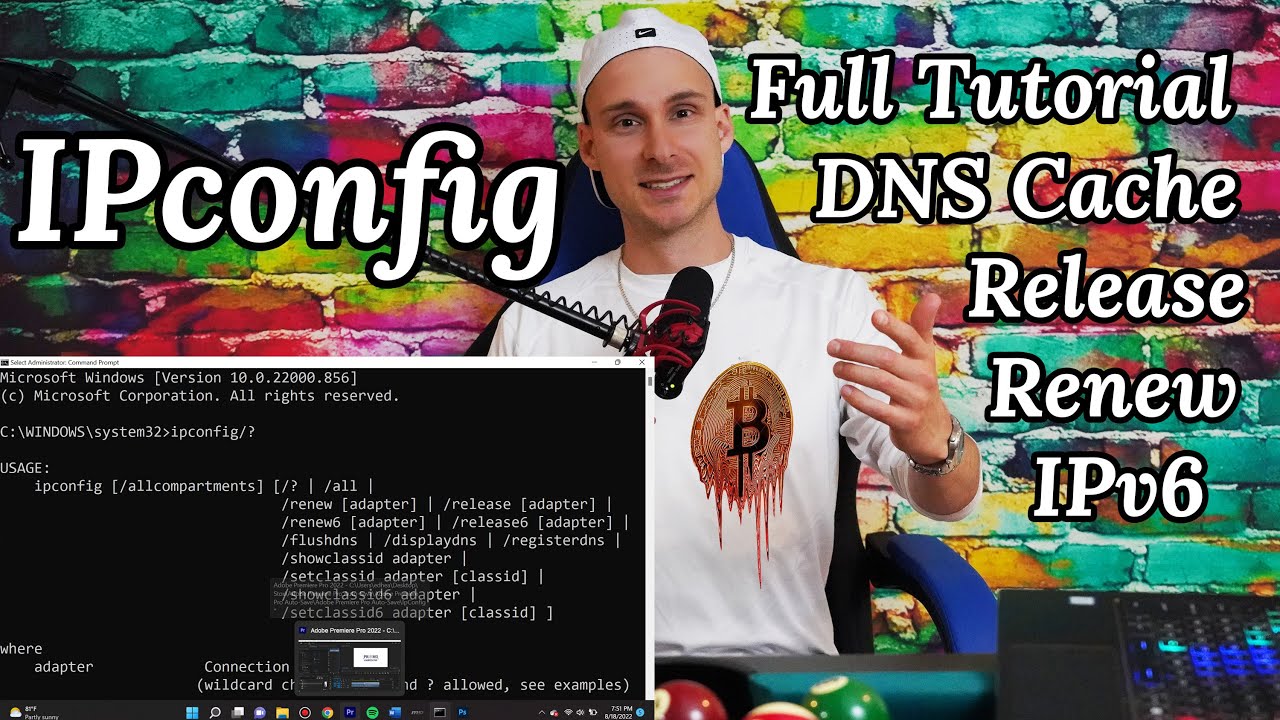
ipconfig is likely the most used command for troubleshooting networking issues. It's used a lot by web developers, designers, networking admins and cybersecurity specialists as well.
Ipconfig shows basic network information regarding your network adapters.
Ipconfig/all shows all available information regarding your network adapters including DHCP and DNS.
Ipconfig/release lets your DHCP server know that you do not want to be assigned to the current IP address any longer.
DHCP Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) this is a network management protocol whose function is to automatically provide an IP host with its IP address and other related configuration information such as the default gateway and subnet mask.
If you’re curious, IPV6 is the next generation protocol and will eventually completely replace IPV4
Ipconfig/release does the same thing as release but for the Internet Protocol Version 6 rather than the Internet Protocol Version 4 when you just do release.
You can also type which specific one to release by having a space after ipconfig/release wireless* or ipconfig/release ethernet
Ipconfig/renew is a function is typically performed after you used an ipconfig/release to go ahead and request a new IP address from the DHCP Server.
ipconfig/flushdns clears out your DNS cache where your computer requests new DNS records from the DNS servers which will be up to date. This is a popular one for web developers and designers so I’ll make a separate tutorial video on this and when and why you may you want to use this.
Ipconfig/registerdns I know it’s used in some cases when troubleshooting networking issue.
Ipconfig/display DNS To take a shortcuts, your computer often keeps local cache log of all DNS records it has visited. This temporary storage of information about previous DNS lookups has an intended purpose to quickly translate the domain names to the correct IP Address so that your computer doesn’t have to contact the DNS server every single time when visiting certain websites. It saves time but can cause problems and that is why it’s a good idea to flush DNS cache when issues arise. To view the content of the DNS cache you can use the command ipconfig/displaydns
Connect with us here:
0:00 Intro
1:05 CMD Command Prompt
1:32 IPCONFIG
2:05 IPConfig ALL
2:25 DHCP
2:42 IPConfig Release
3:33 IPv3 vs IPv4
4:12 IPConfig Renew
4:39 IPConfig FlushDNS
6:15 Cache
6:55 IPConfig DisplayDNS
7:45 Closing Thoughts
#computertutorial #ipconfig #commandprompt
Ipconfig shows basic network information regarding your network adapters.
Ipconfig/all shows all available information regarding your network adapters including DHCP and DNS.
Ipconfig/release lets your DHCP server know that you do not want to be assigned to the current IP address any longer.
DHCP Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) this is a network management protocol whose function is to automatically provide an IP host with its IP address and other related configuration information such as the default gateway and subnet mask.
If you’re curious, IPV6 is the next generation protocol and will eventually completely replace IPV4
Ipconfig/release does the same thing as release but for the Internet Protocol Version 6 rather than the Internet Protocol Version 4 when you just do release.
You can also type which specific one to release by having a space after ipconfig/release wireless* or ipconfig/release ethernet
Ipconfig/renew is a function is typically performed after you used an ipconfig/release to go ahead and request a new IP address from the DHCP Server.
ipconfig/flushdns clears out your DNS cache where your computer requests new DNS records from the DNS servers which will be up to date. This is a popular one for web developers and designers so I’ll make a separate tutorial video on this and when and why you may you want to use this.
Ipconfig/registerdns I know it’s used in some cases when troubleshooting networking issue.
Ipconfig/display DNS To take a shortcuts, your computer often keeps local cache log of all DNS records it has visited. This temporary storage of information about previous DNS lookups has an intended purpose to quickly translate the domain names to the correct IP Address so that your computer doesn’t have to contact the DNS server every single time when visiting certain websites. It saves time but can cause problems and that is why it’s a good idea to flush DNS cache when issues arise. To view the content of the DNS cache you can use the command ipconfig/displaydns
Connect with us here:
0:00 Intro
1:05 CMD Command Prompt
1:32 IPCONFIG
2:05 IPConfig ALL
2:25 DHCP
2:42 IPConfig Release
3:33 IPv3 vs IPv4
4:12 IPConfig Renew
4:39 IPConfig FlushDNS
6:15 Cache
6:55 IPConfig DisplayDNS
7:45 Closing Thoughts
#computertutorial #ipconfig #commandprompt
Комментарии
 0:08:20
0:08:20
 0:08:55
0:08:55
 0:14:11
0:14:11
 0:12:13
0:12:13
 0:08:01
0:08:01
 0:10:54
0:10:54
 0:02:46
0:02:46
 0:00:15
0:00:15
 0:04:13
0:04:13
 0:05:35
0:05:35
 0:08:30
0:08:30
 0:05:52
0:05:52
 0:04:15
0:04:15
 0:04:50
0:04:50
 0:00:19
0:00:19
 0:00:30
0:00:30
 0:14:34
0:14:34
 0:09:42
0:09:42
 0:08:02
0:08:02
 0:03:13
0:03:13
 0:06:37
0:06:37
 0:03:23
0:03:23
 0:04:38
0:04:38
 0:18:45
0:18:45