filmov
tv
Myocardial Infarction (Heart Attack) Ischemia Pathophysiology, ECG, Nursing, Signs, Symptoms Part 1

Показать описание
Myocardial infarction (heart attack or MI) ischemia lecture on the pathophysiology, ECG, nursing role, complications, signs and symptoms. This video on myocardial infarction will help students prepare for the NCLEX exam.
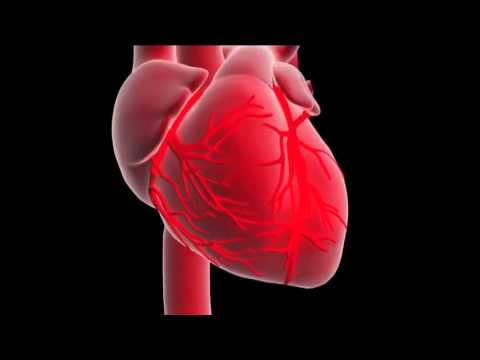
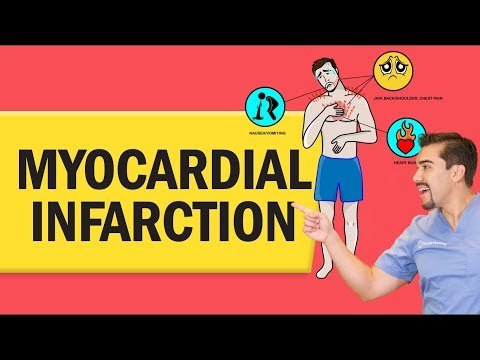
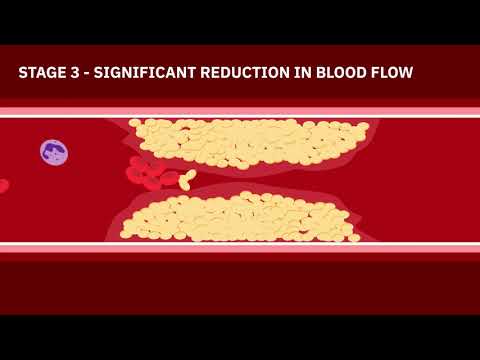
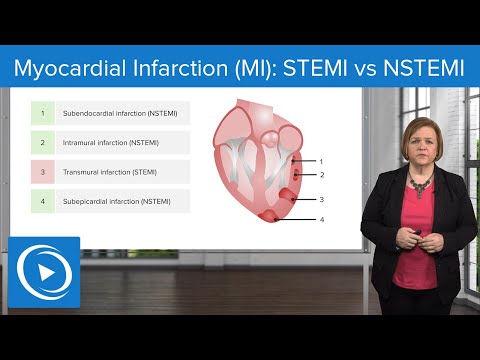
Myocardial infarction is when blood supplied to the heart muscle is limited which causes injury to the heart tissue. Injury from an MI causes complications such as pericarditis, cardiac rupture, cardiogenic shock, arrhythmias, ventricular aneurysm, heart failure, and depression. Signs of symptoms of an MI include: chest pain that radiates, is heavy/intense, and is not relieved by nitroglycerin or rest, nausea/vomiting, cold sweat, anxiety, increased heart rate or blood pressure, irregular heart rate. Tools used to diagnose a myocardial infarction include: cardiac markers (troponins, myoglobin, CK or CK-MB levels), EKG, echocardiogram, stress test with myocardial perfusion imaging, or heart catheterization. As the nurse it is important you know the basics about how to read an EKG during a possible myocardial infarction. You must know what areas of the leads reflect which heart wall and what type of EKG changes you are looking for: ST-segment depression or elevation, T-wave inversion or hyperacute, or pathological Q-wave. Don't forget to watch Part 2.
Popular Playlists:
Myocardial infarction is when blood supplied to the heart muscle is limited which causes injury to the heart tissue. Injury from an MI causes complications such as pericarditis, cardiac rupture, cardiogenic shock, arrhythmias, ventricular aneurysm, heart failure, and depression. Signs of symptoms of an MI include: chest pain that radiates, is heavy/intense, and is not relieved by nitroglycerin or rest, nausea/vomiting, cold sweat, anxiety, increased heart rate or blood pressure, irregular heart rate. Tools used to diagnose a myocardial infarction include: cardiac markers (troponins, myoglobin, CK or CK-MB levels), EKG, echocardiogram, stress test with myocardial perfusion imaging, or heart catheterization. As the nurse it is important you know the basics about how to read an EKG during a possible myocardial infarction. You must know what areas of the leads reflect which heart wall and what type of EKG changes you are looking for: ST-segment depression or elevation, T-wave inversion or hyperacute, or pathological Q-wave. Don't forget to watch Part 2.
Popular Playlists:
Комментарии
 0:00:29
0:00:29
 0:24:55
0:24:55
 0:36:04
0:36:04
 0:10:23
0:10:23
 0:05:26
0:05:26
 0:25:14
0:25:14
 0:12:11
0:12:11
 0:01:58
0:01:58
 0:24:25
0:24:25
 0:52:22
0:52:22
 0:04:43
0:04:43
 0:15:04
0:15:04
 0:00:44
0:00:44
 0:11:49
0:11:49
 0:02:18
0:02:18
 0:59:20
0:59:20
 0:05:03
0:05:03
 0:01:23
0:01:23
 0:16:33
0:16:33
![Myocardial Infarction[Heart Attack];](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/DszMPdokBBU/hqdefault.jpg) 0:23:00
0:23:00
 0:06:32
0:06:32
 0:02:38
0:02:38
 0:11:53
0:11:53
 0:02:43
0:02:43