filmov
tv
Trigonal Planar Molecular Geometry/Shape and Bond Angles

Показать описание
In this video we’ll look at the Trigonal planar Molecular Geometry and Bond Angles. We'll use the example of BF3 to understand the molecular shape. To do that we'll use VSEPR Theory and the Lewis Structure for BF3 and then use interactive models and visualization to visualize the Trigonal Planar geometry.
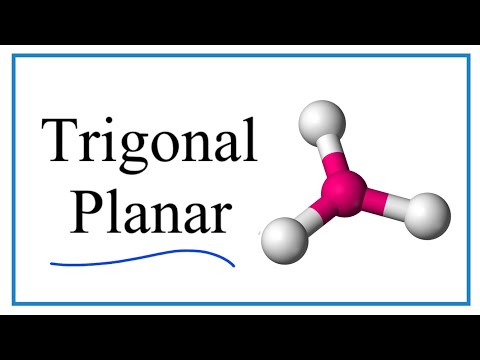
The Trigonal planar molecular shape occurs when there are three atoms attached to the central atom and no lone pairs (unbonded pairs) of electrons on the central atom. BF3 is a good example of a Trigonal planar molecular geometry.
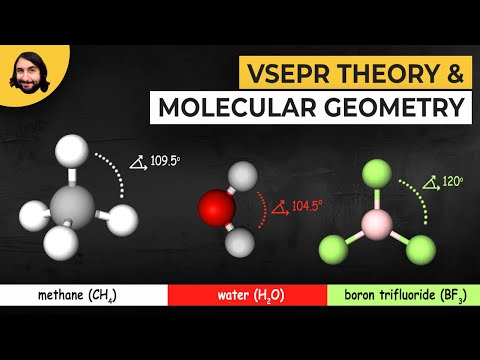
It is useful to understand the generic molecular geometry and then apply it to specific molecules using either the steric number and number of lone pairs of electrons or the AXE notation.
For the more on the molecular geometries below see my video at:
- Linear
- Bent (90 and 120-degree bond angles)
- Trigonal Planer
- Trigonal Pyramidal
- Tetrahedral
- Trigonal Bipyramidal
- Octahedral
The role of lone pairs (unbonded electron pairs) and their VSEPR influence on molecule shape will also be addressed in the video.
Molecular Shapes done with PhET's free online website:
More info on the Trigonal planar molecular geometry at:
Drawing/writing done in InkScape. Screen capture done with Camtasia Studio 4.0. Done on a Dell Dimension laptop computer with a Wacom digital tablet (Bamboo).
The Trigonal planar molecular shape occurs when there are three atoms attached to the central atom and no lone pairs (unbonded pairs) of electrons on the central atom. BF3 is a good example of a Trigonal planar molecular geometry.
It is useful to understand the generic molecular geometry and then apply it to specific molecules using either the steric number and number of lone pairs of electrons or the AXE notation.
For the more on the molecular geometries below see my video at:
- Linear
- Bent (90 and 120-degree bond angles)
- Trigonal Planer
- Trigonal Pyramidal
- Tetrahedral
- Trigonal Bipyramidal
- Octahedral
The role of lone pairs (unbonded electron pairs) and their VSEPR influence on molecule shape will also be addressed in the video.
Molecular Shapes done with PhET's free online website:
More info on the Trigonal planar molecular geometry at:
Drawing/writing done in InkScape. Screen capture done with Camtasia Studio 4.0. Done on a Dell Dimension laptop computer with a Wacom digital tablet (Bamboo).
Комментарии
 0:01:37
0:01:37
 0:13:10
0:13:10
 0:06:31
0:06:31
 0:00:29
0:00:29
 0:05:24
0:05:24
 0:11:01
0:11:01
 0:00:06
0:00:06
 0:01:49
0:01:49
 0:00:46
0:00:46
 0:10:23
0:10:23
 0:02:07
0:02:07
 0:06:35
0:06:35
 0:03:36
0:03:36
 0:00:13
0:00:13
 0:00:33
0:00:33
 0:01:00
0:01:00
 0:05:02
0:05:02
 0:01:51
0:01:51
 0:13:23
0:13:23
 0:05:38
0:05:38
 0:01:48
0:01:48
 0:02:20
0:02:20
 0:02:42
0:02:42
 0:09:06
0:09:06