filmov
tv
What is CPU Cache?

Показать описание
CPU cache is among the fastest kinds of memory in your system, but what does it do, and why is it so important?
CPU Cache Explained - What is Cache Memory?
What is CPU Cache?
What is Cache Memory? L1, L2, and L3 Cache Memory Explained
Why do CPUs Need Caches? - Computerphile
How Cache Works In Computers to Speed Up the CPU
Differences between Cache and Registers (Computer Architecture)
Cache Memory Explained
What is CPU Cache? Explained
CPU cache L1 e L2 e que Mais tiver is so good 😊 #cpu
code::dive conference 2014 - Scott Meyers: Cpu Caches and Why You Care
How computer memory works - Kanawat Senanan
Does a large CPU cache minimise the need for fast RAM?
Principles of CPU Caches
Cache Memory Explained in Easy Language | What is Cache Memory???
AMD Ryzen Gaming, What's More Important: CPU Cores or Cache?
How a CPU Works in 100 Seconds // Apple Silicon M1 vs Intel i9
Factors Affecting CPU Performance (Clock Speed, Cache & Multiple-Cores)
What is Cache Memory? L1, L2, L3 Cache Explained (Hindi)
Why CPU GHz Doesn’t Matter!
CPU Cache Coherence + Java Concurrency
What is Cache Memory in Computer Architecture Animated. | how to increase CPU cache memory ?
Cache, from History to the Future of CPU Memory
Inside the CPU - Computerphile
How a CPU Works
Комментарии
 0:04:51
0:04:51
 0:05:02
0:05:02
 0:01:58
0:01:58
 0:06:06
0:06:06
 0:05:27
0:05:27
 0:06:15
0:06:15
 0:07:00
0:07:00
 0:08:26
0:08:26
 0:00:16
0:00:16
 1:16:58
1:16:58
 0:05:05
0:05:05
 0:03:04
0:03:04
 0:18:19
0:18:19
 0:08:41
0:08:41
 0:17:36
0:17:36
 0:12:44
0:12:44
 0:07:13
0:07:13
 0:07:36
0:07:36
 0:10:25
0:10:25
 0:05:01
0:05:01
 0:04:37
0:04:37
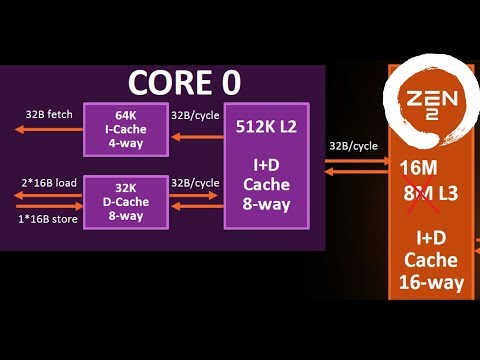 0:42:32
0:42:32
 0:11:16
0:11:16
 0:20:42
0:20:42