filmov
tv
What is Electric Flux? (Gauss Law) #1

Показать описание
In Gauss Law, understanding electric flux is important. It is a measure of amount of electric field passing through a given area. It connect the charge value and the value of E generated by the charge
Well, all this while we have been finding what is the electric field at a point due to a charge or a collection of charges… but you could look at the whole discussion in another way. What if we know the electric field pattern in a region, then what can we say about the charge distribution in the region?”
So what if we have a box and we are not told if there is an electric charge inside it. What we know is that the material of the box is inert and has has no affect on any electric field. Or to make things simpler let us say that there is an imaginary surface in shape of a box that may or may not have a charge inside. And we will call this imaginary box as a closed surface since you can see that it encloses a certain volume. So then, the question for you is- can you tell if there is any charge inside the box… and if there is one… then how much is it including the sign of the charge.
So to answer the questions, one of the things you could do is to recognize the fact that if there is a charge inside the box, it will generate an electric field…and if you put a test charge say “qo” around the box…you could measure the force at various points on qo and therefore the electric field at various points.. as E = F/qo.
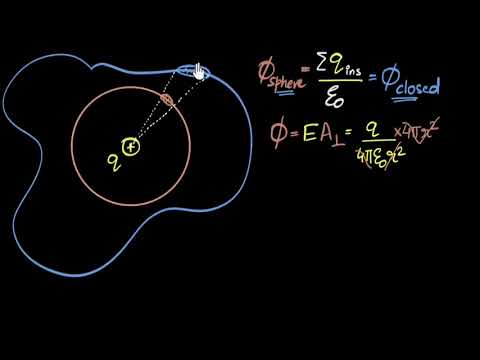
So in a way you could actually make a 3D map of the field around the box. So in this case, if you see the direction of the field map, you can clearly make out that there is a +ve charge inside the box. And if you really get into the details of the field map, you can also find the value of the charge inside the enclosed surface
Infact to determine what is the value and sign of the charge inside the box, all we need to measure is the value of E on the surface of the box.
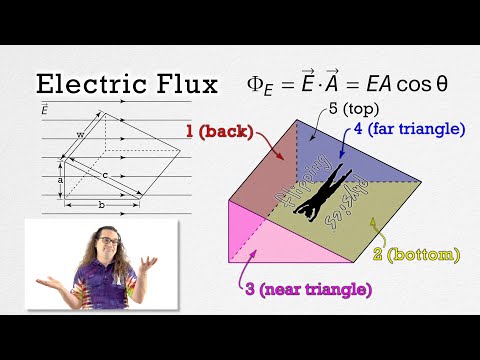
So value of flux through this side of the box is the product of the average E value through the face multiplied by the area of the face then we could say the flux is E times a(sq)
So the 3 important take away from this lesson are-
1. The direction of the flux is determined by the sign of the charge inside the box or the imaginary surface
2. If you have charge outside the box, then there is no net flux attributable to the surface under consideration
3. The net flux depends only on the magnitude of the charge enclosed by the surface and has no relation to the size of the surface being considered
So, now the question you should ask is that do these statements apply to other surfaces as well that may not be as geometric as a box. The answer is yes and that is what we will explore in the next lesson
Who can use:
Class 11 and 12 students (CBSE, ICSE, NCERT)
IIT-JEE Preparation (JEE Main and JEE advanced)
K-12
Advanced Placement (AP Physics)
Subject SAT
Well, all this while we have been finding what is the electric field at a point due to a charge or a collection of charges… but you could look at the whole discussion in another way. What if we know the electric field pattern in a region, then what can we say about the charge distribution in the region?”
So what if we have a box and we are not told if there is an electric charge inside it. What we know is that the material of the box is inert and has has no affect on any electric field. Or to make things simpler let us say that there is an imaginary surface in shape of a box that may or may not have a charge inside. And we will call this imaginary box as a closed surface since you can see that it encloses a certain volume. So then, the question for you is- can you tell if there is any charge inside the box… and if there is one… then how much is it including the sign of the charge.
So to answer the questions, one of the things you could do is to recognize the fact that if there is a charge inside the box, it will generate an electric field…and if you put a test charge say “qo” around the box…you could measure the force at various points on qo and therefore the electric field at various points.. as E = F/qo.
So in a way you could actually make a 3D map of the field around the box. So in this case, if you see the direction of the field map, you can clearly make out that there is a +ve charge inside the box. And if you really get into the details of the field map, you can also find the value of the charge inside the enclosed surface
Infact to determine what is the value and sign of the charge inside the box, all we need to measure is the value of E on the surface of the box.
So value of flux through this side of the box is the product of the average E value through the face multiplied by the area of the face then we could say the flux is E times a(sq)
So the 3 important take away from this lesson are-
1. The direction of the flux is determined by the sign of the charge inside the box or the imaginary surface
2. If you have charge outside the box, then there is no net flux attributable to the surface under consideration
3. The net flux depends only on the magnitude of the charge enclosed by the surface and has no relation to the size of the surface being considered
So, now the question you should ask is that do these statements apply to other surfaces as well that may not be as geometric as a box. The answer is yes and that is what we will explore in the next lesson
Who can use:
Class 11 and 12 students (CBSE, ICSE, NCERT)
IIT-JEE Preparation (JEE Main and JEE advanced)
K-12
Advanced Placement (AP Physics)
Subject SAT
Комментарии
 0:13:12
0:13:12
 0:18:56
0:18:56
 0:04:45
0:04:45
 0:09:04
0:09:04
 0:15:52
0:15:52
 0:15:05
0:15:05
 0:10:04
0:10:04
 0:06:03
0:06:03
 0:43:24
0:43:24
 0:15:02
0:15:02
 0:07:00
0:07:00
 0:32:27
0:32:27
 0:28:05
0:28:05
 0:11:51
0:11:51
 0:05:52
0:05:52
 0:12:16
0:12:16
 0:09:26
0:09:26
 0:04:24
0:04:24
 0:13:24
0:13:24
 0:05:18
0:05:18
 0:02:22
0:02:22
 0:00:54
0:00:54
 0:07:53
0:07:53
 0:06:27
0:06:27