filmov
tv
Mathematical Fallacy (PT 1=2, 2=1, 3=4)

Показать описание
"Invalid proof" redirects here. For any type of invalid proof besides mathematics, see Fallacy.
In mathematics, certain kinds of mistaken proof are often exhibited, and sometimes collected, as illustrations of a concept called mathematical fallacy. There is a distinction between a simple mistake and a mathematical fallacy in a proof, in that a mistake in a proof leads to an invalid proof while in the best-known examples of mathematical fallacies there is some element of concealment or deception in the presentation of the proof.[1]
For example, the reason why validity fails may be attributed to a division by zero that is hidden by algebraic notation. There is a certain quality of the mathematical fallacy: as typically presented, it leads not only to an absurd result, but does so in a crafty or clever way.[2] Therefore, these fallacies, for pedagogic reasons, usually take the form of spurious proofs of obvious contradictions. Although the proofs are flawed, the errors, usually by design, are comparatively subtle, or designed to show that certain steps are conditional, and are not applicable in the cases that are the exceptions to the rules.
In mathematics, certain kinds of mistaken proof are often exhibited, and sometimes collected, as illustrations of a concept called mathematical fallacy. There is a distinction between a simple mistake and a mathematical fallacy in a proof, in that a mistake in a proof leads to an invalid proof while in the best-known examples of mathematical fallacies there is some element of concealment or deception in the presentation of the proof.[1]
For example, the reason why validity fails may be attributed to a division by zero that is hidden by algebraic notation. There is a certain quality of the mathematical fallacy: as typically presented, it leads not only to an absurd result, but does so in a crafty or clever way.[2] Therefore, these fallacies, for pedagogic reasons, usually take the form of spurious proofs of obvious contradictions. Although the proofs are flawed, the errors, usually by design, are comparatively subtle, or designed to show that certain steps are conditional, and are not applicable in the cases that are the exceptions to the rules.
 0:11:19
0:11:19
 0:02:24
0:02:24
 0:01:01
0:01:01
 0:01:14
0:01:14
 0:03:31
0:03:31
 0:01:59
0:01:59
 0:01:45
0:01:45
 0:05:45
0:05:45
 1:33:47
1:33:47
 0:13:57
0:13:57
 0:03:23
0:03:23
 0:00:58
0:00:58
 0:06:22
0:06:22
 0:12:30
0:12:30
 0:08:29
0:08:29
 0:04:19
0:04:19
 0:01:00
0:01:00
 0:03:06
0:03:06
 0:10:53
0:10:53
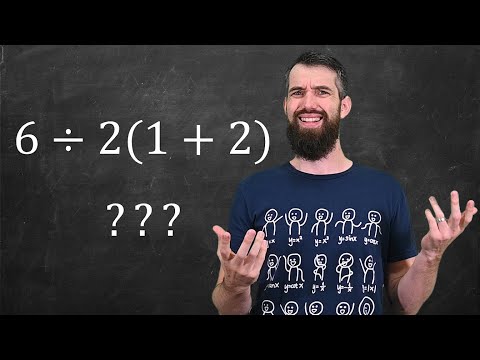 0:06:04
0:06:04
 0:13:25
0:13:25
 0:05:23
0:05:23
 0:07:34
0:07:34
 0:08:00
0:08:00