filmov
tv
Bernoulli's Law Derived & Explained Using BASIC Physics - The Conservation of Energy
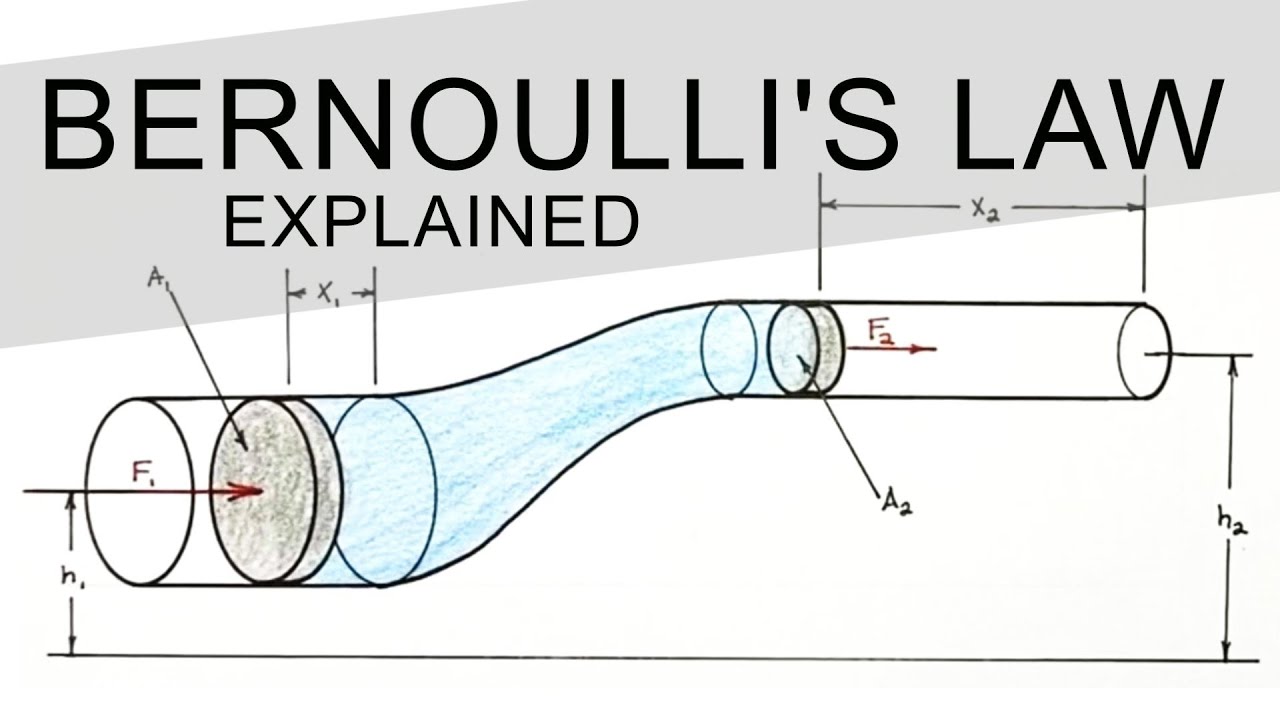
Показать описание
The entirety of this equation is based on the conservation of energy. Derive Bernoullis Equation using a basic set of high school level physics equations. By combining continuity in fluid flow with the work energy theorem we can come up with an equation that includes the kinetic energy, potential energy and pressure energy terms. We derive the energy form of Bernoullis Law but it can easily be turned into the head form with a bit of algebra.
Pascals Law does not apply when talking about Bernoulli's Law because pressure is not equal at all points in the fluid.
Take a look at pressure energy and how it actually is just non- conservative work done on the fluid in the system.
The subject of Bernoulli's Principle comes up in physics and mechanics courses such as AP Physics 1, as well as PLTW POE .
Pascals Law does not apply when talking about Bernoulli's Law because pressure is not equal at all points in the fluid.
Take a look at pressure energy and how it actually is just non- conservative work done on the fluid in the system.
The subject of Bernoulli's Principle comes up in physics and mechanics courses such as AP Physics 1, as well as PLTW POE .
Bernoulli's Law Derived & Explained Using BASIC Physics - The Conservation of Energy
Bernoulli's principle
Understanding Bernoulli's Equation
Physics: Fluid Dynamics: Fluid Flow (1.6 of 7) Bernoulli's Equation Derived
Bernoulli's Equation
Bernoulli's principle 3d animation
Bernoulli's Equation
Bernoulli's Equation Example Problems, Fluid Mechanics - Physics
Why Does Fluid Pressure Decrease and Velocity Increase in a Tapering Pipe?
How Do You Show Bernoulli's Principle? | Visualizing Bernoulli's Principle | #Shorts
Bernoulli's Principle: How it Works and Real-World Applications #vigyanrecharge #bernoulli
Bernoulli's Theorem In Real Life🔥💯#pw #shorts #physicswallah #alakhgk
Bernoulli's Theorem Class 11 Physics Term 2 Chapter 10 Important Topics
Bernoulli's Theorem (in Shorts)
PLUS ONE PHYSICS || IMPORTANT DERIVATION || PROOF OF BERNOULLI'S THEOREM 👍🔥🔥🔥🔥
Bernoulli's Theorem | 5 Real life examples of Bernoulli's Principle.
IIT Bombay Lecture Hall | IIT Bombay Motivation | #shorts #ytshorts #iit
Bernoulli's Equation | Derivation | Assumptions | Bernoulli's theorem statement
Bernoulli's principle
Bernoulli’s Equation form Euler’s Equation
Physics 34.1 Bernoulli's Equation & Flow in Pipes (21 of 38) Flow with Pump***
Bernoulli's equation derivation from Euler's equation of motion
Isaac Newton's INSANE Sleep Habits 😬
This chapter closes now, for the next one to begin. 🥂✨.#iitbombay #convocation
Комментарии
 0:13:57
0:13:57
 0:05:40
0:05:40
 0:13:44
0:13:44
 0:11:57
0:11:57
 0:07:33
0:07:33
 0:03:25
0:03:25
 0:10:12
0:10:12
 0:31:43
0:31:43
 0:05:45
0:05:45
 0:00:58
0:00:58
 0:10:28
0:10:28
 0:00:40
0:00:40
 0:12:38
0:12:38
 0:01:00
0:01:00
 0:00:05
0:00:05
 0:22:48
0:22:48
 0:00:12
0:00:12
 0:12:38
0:12:38
 0:01:01
0:01:01
 0:04:07
0:04:07
 0:02:01
0:02:01
 0:11:16
0:11:16
 0:00:24
0:00:24
 0:00:16
0:00:16