filmov
tv
HOW TO READ A CHROMATOGRAM (Step-By-Step Guide For Beginners)

Показать описание
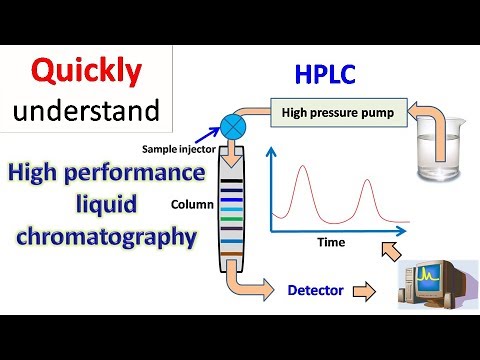
The only thing you will need to know about how chromatography works to follow this video, is that they all separate compounds based on how they interact with the stationary phase inside their column. This causes the different sub components of the sample to exit the column at different times and whenever something exits the column it is measured.
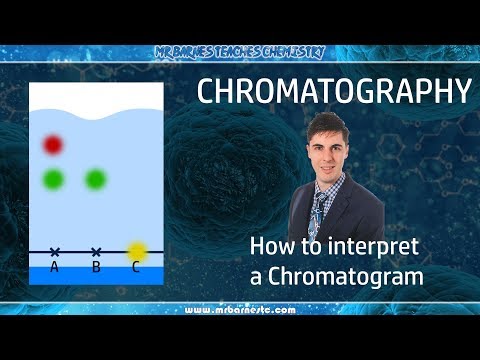
The result from a chromatography is displayed in a chromatogram. The chromatogram gives you a well of information, both in terms of the health of the gas chromatography device in addition to data which can be used for qualitative or even quantitative analysis.
The retention time is displayed on the x-axis and is the time it takes the sample, from when it was injected, to run through the column and exit. The y-axis is the measured response of the analyte peak in the detector. The baseline shows the signal from the detector when no analyte is eluting from the column. This baseline should be low and straight. A higher and/or irregular baseline compared to what is normal indicates a problem or alternatively that maintenance of the device is required. By comparing the different peaks of our sample in terms of retention and shape to that of known compounds we can identify the different compounds present in our sample. Furthermore, the concentration of a compound can be determined by taking the peak area and comparing it to an example calibration curve of the same compound at different concentrations.
The result from a chromatography is displayed in a chromatogram. The chromatogram gives you a well of information, both in terms of the health of the gas chromatography device in addition to data which can be used for qualitative or even quantitative analysis.
The retention time is displayed on the x-axis and is the time it takes the sample, from when it was injected, to run through the column and exit. The y-axis is the measured response of the analyte peak in the detector. The baseline shows the signal from the detector when no analyte is eluting from the column. This baseline should be low and straight. A higher and/or irregular baseline compared to what is normal indicates a problem or alternatively that maintenance of the device is required. By comparing the different peaks of our sample in terms of retention and shape to that of known compounds we can identify the different compounds present in our sample. Furthermore, the concentration of a compound can be determined by taking the peak area and comparing it to an example calibration curve of the same compound at different concentrations.
Комментарии
 0:02:03
0:02:03
 0:03:36
0:03:36
 0:06:24
0:06:24
 0:03:39
0:03:39
 0:06:10
0:06:10
 0:02:34
0:02:34
 0:12:22
0:12:22
 0:03:53
0:03:53
 0:02:44
0:02:44
 0:06:33
0:06:33
 0:03:19
0:03:19
 0:04:34
0:04:34
 0:05:36
0:05:36
 0:05:09
0:05:09
 0:16:12
0:16:12
 0:23:39
0:23:39
 0:04:40
0:04:40
 0:03:53
0:03:53
 0:02:45
0:02:45
 0:09:33
0:09:33
 0:33:22
0:33:22
 0:02:17
0:02:17
 0:05:13
0:05:13
 0:06:54
0:06:54