filmov
tv
IGCSE Biology - Monohybrid inheritance (17.4)

Показать описание
Cambridge IGCSE Biology (0610/0970)
Chapter 17 - Inheritance
Topic 17.4 - Monohybrid inheritance
For exams in 2023, 2024 & 2025 (core and extended)
As always this video follows the Cambridge syllabus exactly and contains absolutely everything you need to know for your final exam!
My other channels:
@igpecomplete - Cambridge IGCSE PE
@ocrpecomplete - OCR GCSE PE
Timestamps:
0:00 Contents
0:56 Inheritance
1:36 Genotype and phenotype
1:54 Dominant and recessive alleles
2:38 Homozygous and heterozygous
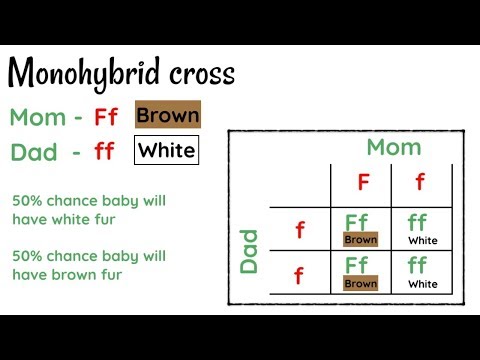
3:21 Genetic diagrams
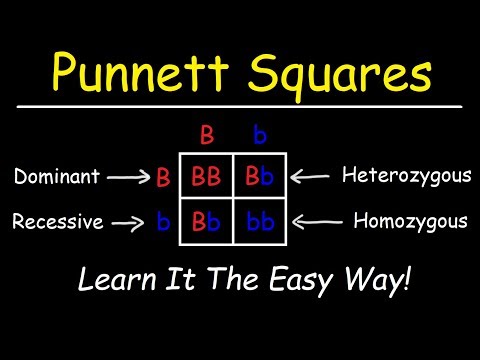
4:11 Punnett squares
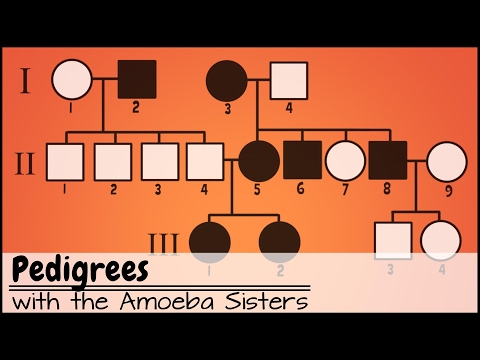
5:17 Pedigree diagrams
6:22 Test crosses (extended)
7:10 Codominance and blood groups (extended)
8:14 Sex linkage
Core content:
- Describe inheritance as the transmission of genetic information from generation to generation.
- Describe genotype as the genetic make-up of an organism and in terms of the alleles present.
- Describe phenotype as the observable features of an organism.
- Describe homozygous as having two identical alleles of a particular gene.
- State that two identical homozygous individuals that breed together will be pure-breeding.
- Describe heterozygous as having two different alleles of a particular gene.
- State that a heterozygous individual will not be pure-breeding.
- Describe a dominant allele as an allele that is expressed if it is present in the genotype.
- Describe a recessive allele as an allele that is only expressed when there is no dominant allele of the gene present in the genotype.
- Interpret pedigree diagrams for the inheritance of a given characteristic.
- Use genetic diagrams to predict the results of monohybrid crosses and calculate phenotypic ratios, limited to 1 : 1 and 3 : 1 ratios.
- Use Punnett squares in crosses which result in more than one genotype to work out and show the possible different genotypes.
Extended content:
- Explain how to use a test cross to identify an unknown genotype.
- Describe codominance as a situation in which both alleles in heterozygous organisms contribute to the phenotype.
- Explain the inheritance of ABO blood groups: phenotypes are A, B, AB and O blood groups and alleles are IA, IB and Io.
- Describe a sex-linked characteristic as a feature in which the gene responsible is located on
a sex chromosome and that this makes the characteristic more common in one sex than in the other.
- Describe red-green colour blindness as an example of sex linkage
- Use genetic diagrams to predict the results of monohybrid crosses involving codominance or sex linkage and calculate phenotypic ratios.
Комментарии
 0:08:50
0:08:50
 0:09:49
0:09:49
 0:05:26
0:05:26
 0:04:16
0:04:16
 0:07:01
0:07:01
 0:13:25
0:13:25
 0:05:43
0:05:43
 0:10:34
0:10:34
 0:29:11
0:29:11
 0:06:53
0:06:53
 0:24:05
0:24:05
 0:10:53
0:10:53
 0:07:05
0:07:05
 0:02:52
0:02:52
 0:09:15
0:09:15
 0:12:55
0:12:55
 0:04:12
0:04:12
 0:04:22
0:04:22
 0:15:07
0:15:07
 0:03:52
0:03:52
 0:56:45
0:56:45
 0:21:39
0:21:39
 0:09:38
0:09:38
 0:09:14
0:09:14