filmov
tv
Ionic Bonds - Ionic Compounds: What is the ionic bond and how does the ionic compound form?
Показать описание
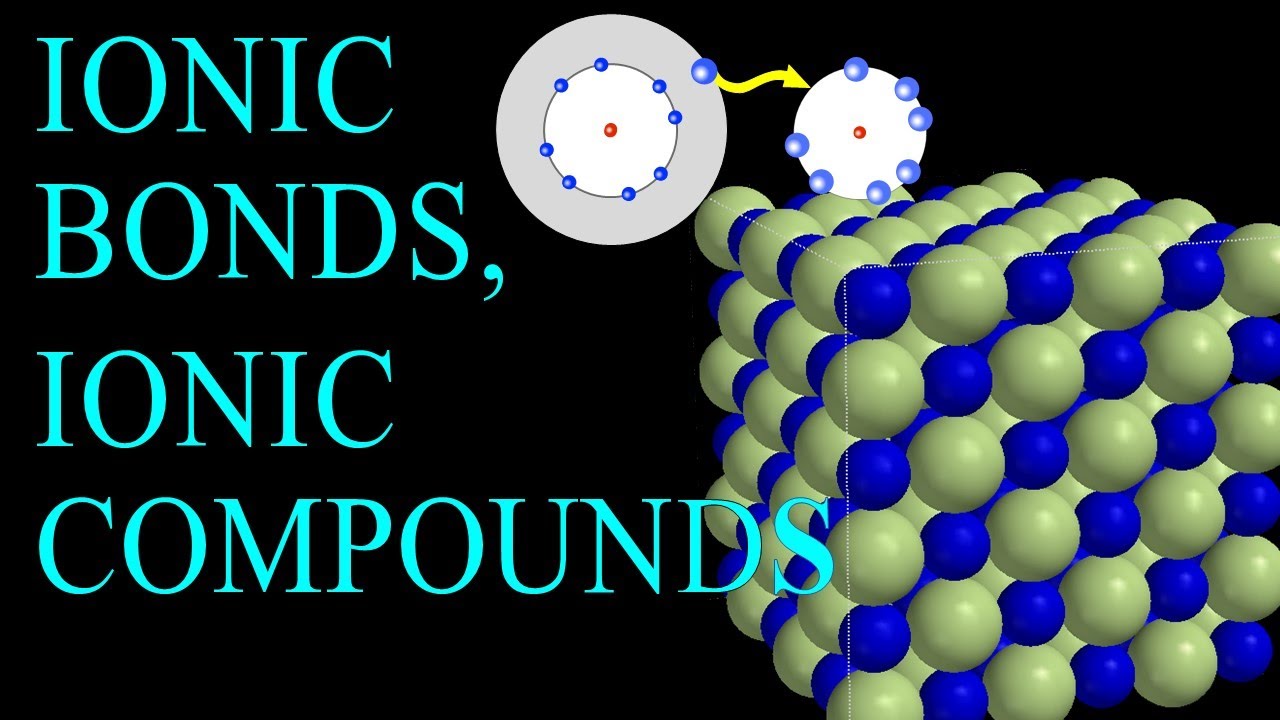
This video tells how ionic bonds form in a chemical reaction, showing electron transfer from metal to non-metal and resulting charge formation resulting in ions that attract due to opposite charge, forming the ionic bond. Writing correct formulas is shown by balancing charges to create a neutral compound. The video also details ion size and resulting compound formation from two examples, NaF and MgF2.
CC Academy videos for Chemistry help on your chemistry homework, problems, and experiments.
Check out other CC Academy videos on this channel:
-Stoichiometry Tutorial, step by step
-Types of Chemical Reactions: How to classify five basic reaction types
-Solution Stoichiometry
-Orbitals the Basics: Atomic Orbitals Tutorial
-Hybrid Orbitals Explained
-Polar Molecules Tutorial: How to determine polarity in a molecule
-Metallic Bonding and Metallic Properties Explained
-Covalent Bonding Tutorial
-Ionic Bonds, Ionic Compounds: What is an ionic bond and how do ionic compounds form
-Electronegativity and bond character (bond type): non-polar covalent, polar, ionic
-Metric Unit Prefix Conversions: How to Convert Metric System Prefixes
-Metric unit conversions shortcut: fast, easy how-to with examples
-Mole Conversions Tutorial: how to convert mole - mass, mole - particle, mass - particle problems
-Frequency, Wavelength, and the Speed of Light
-The Bohr Model of the Atom and Atomic Emission Spectra
-What is Heat: A brief introduction at the particle level
-Rutherford's Gold Foil Experiment
-Unit Conversion Using Dimensional Analysis Tutorial
-What is Fire: Combustion Reaction Tutorial
-Quantum Numbers Tutorial
-Electron Configurations Tutorial and How to Derive Electron Configurations from the Periodic Table
-Concentration and Molarity Explained
-Heating Curves Tutorial
-Naming Ionic Compounds
-Limiting Reactant Tutorial
-PV=nRT The Ideal Gas Law: What is it, What is R, Four practice problems solved including molar mass
-Gas density and PV=nRT, the ideal gas law
-Surface Tension - What is it, how does it form, what properties does it impart
—More on ionic bonds | Wikipedia— Dec 2019
Ionic bonding is a type of chemical bonding that involves the electrostatic attraction between oppositely charged ions, and is the primary interaction occurring in ionic compounds. It is one of the main bonds along with Covalent bond and Metallic bonding. Ions are atoms that have either gained or lost one or more electrons. Ions that have gained an electron are negatively charged. They are anions. Ions that have lost an electron are positively charged. They are cations. This transfer of electrons is known as electrovalence in contrast to covalence. In the simplest case, the cation is a metal atom and the anion is a nonmetal atom, but these ions can be of a more complex nature, e.g. molecular ions like NH4 1+ or SO4 2−. In simpler words, an ionic bond is the transfer of electrons from a metal to a non-metal in order to obtain a full valence shell for both atoms.
It is important to recognize that clean ionic bonding—in which one atom or molecule completely transfers an electron to another—cannot exist: all ionic compounds have some degree of covalent bonding, or electron sharing. Thus, the term "ionic bonding" is given when the ionic character is greater than the covalent character – that is, a bond in which a large electronegativity difference exists between the two atoms, causing the bonding to be more polar (ionic) than in covalent bonding where electrons are shared more equally. Bonds with partially ionic and partially covalent character are called polar covalent bonds.
Ionic compounds conduct electricity when molten or in solution, typically as a solid. Ionic compounds generally have a high melting point, depending on the charge of the ions they consist of. The higher the charges the stronger the cohesive forces and the higher the melting point. They also tend to be soluble in water; the stronger the cohesive forces, the lower the solubility.
Atoms that have an almost full or almost empty valence shell tend to be very reactive. Atoms that are strongly electronegative (as is the case with halogens) often have only one or two empty orbitals in their valence shell, and frequently bond with other molecules or gain electrons to form anions. Atoms that are weakly electronegative (such as alkali metals) have relatively few valence electrons, which can easily be shared with atoms that are strongly electronegative. As a result, weakly electronegative atoms tend to distort their electron cloud and form cations.
from Wikipedia "Ionic Bonding" 12/19/2019
CC Academy videos for Chemistry help on your chemistry homework, problems, and experiments.
Check out other CC Academy videos on this channel:
-Stoichiometry Tutorial, step by step
-Types of Chemical Reactions: How to classify five basic reaction types
-Solution Stoichiometry
-Orbitals the Basics: Atomic Orbitals Tutorial
-Hybrid Orbitals Explained
-Polar Molecules Tutorial: How to determine polarity in a molecule
-Metallic Bonding and Metallic Properties Explained
-Covalent Bonding Tutorial
-Ionic Bonds, Ionic Compounds: What is an ionic bond and how do ionic compounds form
-Electronegativity and bond character (bond type): non-polar covalent, polar, ionic
-Metric Unit Prefix Conversions: How to Convert Metric System Prefixes
-Metric unit conversions shortcut: fast, easy how-to with examples
-Mole Conversions Tutorial: how to convert mole - mass, mole - particle, mass - particle problems
-Frequency, Wavelength, and the Speed of Light
-The Bohr Model of the Atom and Atomic Emission Spectra
-What is Heat: A brief introduction at the particle level
-Rutherford's Gold Foil Experiment
-Unit Conversion Using Dimensional Analysis Tutorial
-What is Fire: Combustion Reaction Tutorial
-Quantum Numbers Tutorial
-Electron Configurations Tutorial and How to Derive Electron Configurations from the Periodic Table
-Concentration and Molarity Explained
-Heating Curves Tutorial
-Naming Ionic Compounds
-Limiting Reactant Tutorial
-PV=nRT The Ideal Gas Law: What is it, What is R, Four practice problems solved including molar mass
-Gas density and PV=nRT, the ideal gas law
-Surface Tension - What is it, how does it form, what properties does it impart
—More on ionic bonds | Wikipedia— Dec 2019
Ionic bonding is a type of chemical bonding that involves the electrostatic attraction between oppositely charged ions, and is the primary interaction occurring in ionic compounds. It is one of the main bonds along with Covalent bond and Metallic bonding. Ions are atoms that have either gained or lost one or more electrons. Ions that have gained an electron are negatively charged. They are anions. Ions that have lost an electron are positively charged. They are cations. This transfer of electrons is known as electrovalence in contrast to covalence. In the simplest case, the cation is a metal atom and the anion is a nonmetal atom, but these ions can be of a more complex nature, e.g. molecular ions like NH4 1+ or SO4 2−. In simpler words, an ionic bond is the transfer of electrons from a metal to a non-metal in order to obtain a full valence shell for both atoms.
It is important to recognize that clean ionic bonding—in which one atom or molecule completely transfers an electron to another—cannot exist: all ionic compounds have some degree of covalent bonding, or electron sharing. Thus, the term "ionic bonding" is given when the ionic character is greater than the covalent character – that is, a bond in which a large electronegativity difference exists between the two atoms, causing the bonding to be more polar (ionic) than in covalent bonding where electrons are shared more equally. Bonds with partially ionic and partially covalent character are called polar covalent bonds.
Ionic compounds conduct electricity when molten or in solution, typically as a solid. Ionic compounds generally have a high melting point, depending on the charge of the ions they consist of. The higher the charges the stronger the cohesive forces and the higher the melting point. They also tend to be soluble in water; the stronger the cohesive forces, the lower the solubility.
Atoms that have an almost full or almost empty valence shell tend to be very reactive. Atoms that are strongly electronegative (as is the case with halogens) often have only one or two empty orbitals in their valence shell, and frequently bond with other molecules or gain electrons to form anions. Atoms that are weakly electronegative (such as alkali metals) have relatively few valence electrons, which can easily be shared with atoms that are strongly electronegative. As a result, weakly electronegative atoms tend to distort their electron cloud and form cations.
from Wikipedia "Ionic Bonding" 12/19/2019
Комментарии
 0:04:12
0:04:12
 0:02:55
0:02:55
 0:04:10
0:04:10
 0:06:08
0:06:08
 0:07:20
0:07:20
 0:07:02
0:07:02
 0:47:35
0:47:35
 0:01:47
0:01:47
 0:13:24
0:13:24
 0:02:01
0:02:01
 0:04:48
0:04:48
 0:04:39
0:04:39
 0:02:15
0:02:15
 0:03:36
0:03:36
 0:03:34
0:03:34
 0:06:12
0:06:12
 0:04:30
0:04:30
 0:05:44
0:05:44
 0:14:22
0:14:22
 0:03:33
0:03:33
 0:40:30
0:40:30
 0:09:46
0:09:46
 0:06:23
0:06:23
 0:21:57
0:21:57