filmov
tv
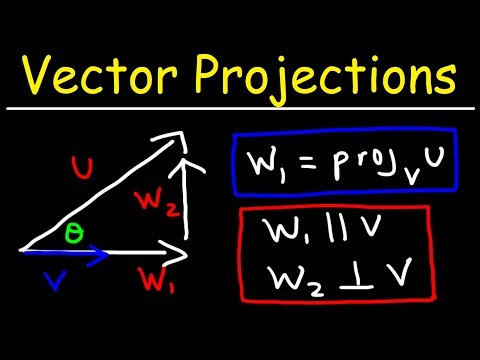
Find the Projection of a Vector onto Another Vector || Scalar & Vector Projections

Показать описание
Find the Projection of a Vector onto Another Vector || Scalar & Vector Projections
The Gram Schmidt procedure is used for orthogonalizing or orthonormalizing the given set of Vectors. If we are given the set of vectors
V1,V2,V3,……,Vn
We can orthogonalize them if they are linearly independent. If the given set of vector does not consist of linearly independent vectors then we can not orthogonalize them using Gram Schmidt Procedure.
Procedure
This method uses the idea of components of a vector and then finding the projection of a vector. Since we all know that a vector can be represented as a summation of its components. So, if A is a vector in 2D then it can be written as
#projectionofavector #scalarprojection #vectorprojection
#projectionofavector
The Gram Schmidt procedure is used for orthogonalizing or orthonormalizing the given set of Vectors. If we are given the set of vectors
V1,V2,V3,……,Vn
We can orthogonalize them if they are linearly independent. If the given set of vector does not consist of linearly independent vectors then we can not orthogonalize them using Gram Schmidt Procedure.
Procedure
This method uses the idea of components of a vector and then finding the projection of a vector. Since we all know that a vector can be represented as a summation of its components. So, if A is a vector in 2D then it can be written as
#projectionofavector #scalarprojection #vectorprojection
#projectionofavector
 0:12:14
0:12:14
 0:02:29
0:02:29
 0:05:17
0:05:17
 0:06:12
0:06:12
 0:03:21
0:03:21
 0:09:51
0:09:51
 0:07:51
0:07:51
 0:07:39
0:07:39
 0:36:13
0:36:13
 0:03:36
0:03:36
 0:03:03
0:03:03
 0:10:36
0:10:36
 0:14:20
0:14:20
 0:02:49
0:02:49
 0:14:37
0:14:37
 0:01:59
0:01:59
 0:04:50
0:04:50
 0:09:08
0:09:08
 0:06:48
0:06:48
 0:10:09
0:10:09
 0:08:45
0:08:45
 0:03:55
0:03:55
 0:09:14
0:09:14
 0:03:05
0:03:05