filmov
tv
Work- Energy Theorem-Practice Problems- Gr 9 &Gr10

Показать описание
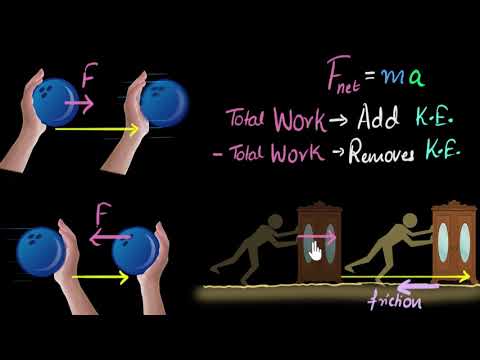
1b. A toy car with a mass of 2 kg stars at rest, A spring performs 196 Joules of work on the car. What is the toy car’s final velocity
2. A skateboarder with a mass of 30 kg ends up with a final velocity of 7 m/s after a push of 360 joules of work. What was the skateboarder initial velocity?
3. A student wearing frictionless in-line skates on a horizontal surface is pushed by a friend with a constant force of 45 N. How far must the student be pushed, starting from rest, so that her final kinetic energy is 352 J?
4. A 75 kg bobsled is pushed along a horizontal surface by two athletes. After the bobsled is pushed a distance of 4.5 m starting from rest, its speed is 6.0 m/s. Find the magnitude of the net force on the bobsled
5. A 2.0 × 10^3 kg car accelerates from rest under the actions of two forces. One is a forward force of 1140 N provided by traction between the wheels and the road. The other is a 950 N resistive force due to various frictional forces. Use the work–kinetic energy theorem to determine how far the car must travel for its speed to reach 2.0 m/s.
6. A student slides a 0.75 kg textbook across a table, and it comes to rest after traveling 1.2 m. Given that the coefficient of kinetic friction between the book and the table is 0.34, use the work–kinetic energy theorem to find the book’s initial speed.
Work energy, power play list
intro (0:00)
Qc#1 (2:41)
Qc#2 (5:08)
Qc#3 (9:08)
Qc#4 (12:11)
Qc#5 (15:23)
Qc#6 (19:02)
2. A skateboarder with a mass of 30 kg ends up with a final velocity of 7 m/s after a push of 360 joules of work. What was the skateboarder initial velocity?
3. A student wearing frictionless in-line skates on a horizontal surface is pushed by a friend with a constant force of 45 N. How far must the student be pushed, starting from rest, so that her final kinetic energy is 352 J?
4. A 75 kg bobsled is pushed along a horizontal surface by two athletes. After the bobsled is pushed a distance of 4.5 m starting from rest, its speed is 6.0 m/s. Find the magnitude of the net force on the bobsled
5. A 2.0 × 10^3 kg car accelerates from rest under the actions of two forces. One is a forward force of 1140 N provided by traction between the wheels and the road. The other is a 950 N resistive force due to various frictional forces. Use the work–kinetic energy theorem to determine how far the car must travel for its speed to reach 2.0 m/s.
6. A student slides a 0.75 kg textbook across a table, and it comes to rest after traveling 1.2 m. Given that the coefficient of kinetic friction between the book and the table is 0.34, use the work–kinetic energy theorem to find the book’s initial speed.
Work energy, power play list
intro (0:00)
Qc#1 (2:41)
Qc#2 (5:08)
Qc#3 (9:08)
Qc#4 (12:11)
Qc#5 (15:23)
Qc#6 (19:02)
 0:23:43
0:23:43
 0:13:05
0:13:05
 0:07:00
0:07:00
 0:16:17
0:16:17
 0:05:32
0:05:32
 0:30:24
0:30:24
 0:03:19
0:03:19
 0:14:31
0:14:31
 0:04:11
0:04:11
 0:10:15
0:10:15
 0:26:09
0:26:09
 1:01:44
1:01:44
 0:17:07
0:17:07
 0:05:31
0:05:31
 0:06:58
0:06:58
 0:22:10
0:22:10
 0:05:58
0:05:58
 0:13:18
0:13:18
 0:04:50
0:04:50
 0:04:57
0:04:57
 0:20:45
0:20:45
 0:01:01
0:01:01
 0:12:34
0:12:34
 0:16:46
0:16:46