filmov
tv
Worked Example | Calculate Submerged Depth of a Floating Block | Buoyancy

Показать описание
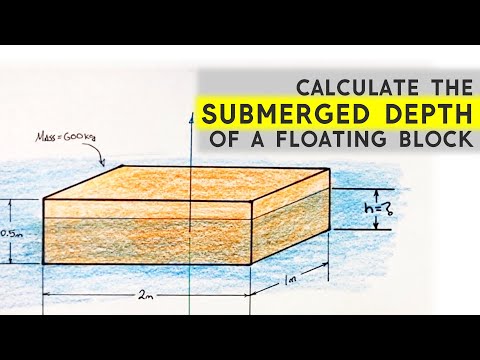
Use Archimedes Principle to find deep a floating block sits in the water. Given the length width and height of this block we can solve for the displacement of fluid by the block, which in turn produces a buoyant force. In order for the Net force on the block to equal zero, the force by gravity is equal to the buoyant force and the buoyant force is equal to the weight of water displaced by the block.
This problem comes up in introductory physics, fluid mechanics, and engineering courses.
This problem comes up in introductory physics, fluid mechanics, and engineering courses.
Worked Example | Calculate Submerged Depth of a Floating Block | Buoyancy
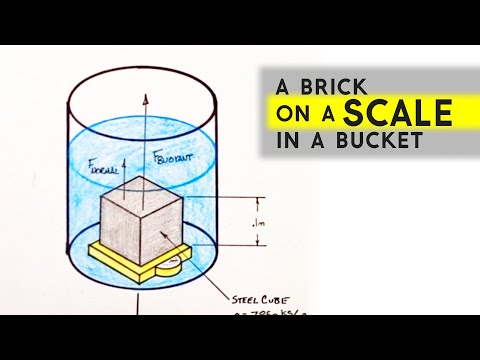
Worked Example | Calculate the Scale Reading of a Submerged Block | Apparent Weight & Buoyancy
How To Calculate The Fractional Volume Submerged & The Density of an Object In Two Fluids
Buoyancy of Floating Objects [Physics of Fluid Mechanics #31]
Solved Numerical Examples on Hydrostatic Force on Submerged Plane Surface (English)
HYDROSTATIC PRESSURE (Fluid Pressure) in 8 Minutes!
Buoyancy and Archimedes’ Principle: Example Problems
Determine Draft of a Floating Body – Fractional Volume Submerged Example Problem
Hydrostatic Force Problems - Calculus 2
How to solve manometer problems
Natural frequency of a sphere submerged in water | GATE 2020 Solved example
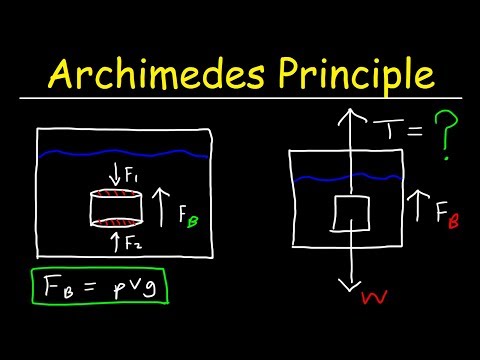
Archimedes Principle, Buoyant Force, Basic Introduction - Buoyancy & Density - Fluid Statics
Example 2.4 - Force on a submerged curved surface
Buoyancy Forces on Fully Submerged Objects Example Problems - Fluid Mechanics
Hydrostatic Pressure of SUBMERGED Gate in 2 Minutes!
Introductory Fluid Mechanics L5 p5 - Example: Plane Surface Gate
Hydrostatic Force - Submerged Trapezoid | Calculus 2
Physics 33.5 Buoyancy Force (7 of 9) Floating in Multiple Layers: 1
Fluid Mechanics 3.10 - Solved Buoyancy Example Problem- Force to Keep Glass Submerged
Fluids, Buoyancy, and Archimedes' Principle
Buoyancy Example
Fluid Mechanics: Forces on Submerged Surfaces I (3 of 34)
Sect 8 3 #6 Hydrostatic Force, Calculus 2
Buoyancy Forces on Partially Submerged Objects with Example Problem - Fluid Mechanics
Комментарии
 0:03:15
0:03:15
 0:04:18
0:04:18
 0:14:15
0:14:15
 0:08:29
0:08:29
 0:02:07
0:02:07
 0:08:46
0:08:46
 0:12:54
0:12:54
 0:09:29
0:09:29
 0:20:59
0:20:59
 0:06:15
0:06:15
 0:13:19
0:13:19
 0:15:19
0:15:19
 0:19:24
0:19:24
 0:10:46
0:10:46
 0:01:51
0:01:51
 0:12:35
0:12:35
 0:05:19
0:05:19
 0:05:30
0:05:30
 0:12:24
0:12:24
 0:04:16
0:04:16
 0:04:00
0:04:00
 1:10:59
1:10:59
 0:06:32
0:06:32
 0:08:21
0:08:21