filmov
tv
calculus 2 mixing problem, CSTR, differential equation application

Показать описание
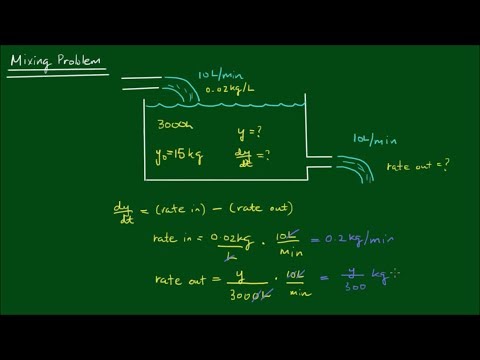
The mixing problem is an application in separable differential equation. This is also known as continuous stirred tank reactor (CSTR).
@bprpcalculusbasics
@bprpcalculusbasics
calculus 2 mixing problem, CSTR, differential equation application
Differential Equation Mixing Problem, calculus 2 tutorial
Mixing Problems and Separable Differential Equations - Calculus 2
❖ Mixing Problems and Separable Differential Equations ❖
Mixing Problem Differential Equation (Application)
ODE | A model for mixing problems
Mixing Salt and Water - First Order Differential Equations
Mixing Problem Example
Differential Equation - Mixing Problem
Mixture Problem-Big Idea
Mixing problems with separable differential equations (KristaKingMath)
Mixing Problems in Calculus: Alcohol Percentages in Beer Tank
Example #2: Mixing Problem with Differential Equations
Example #1: Mixing Problem with Differential Equations
Mixing Problems Part 1: Setting up a differential Equation
DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS PART 13 MIXING PROBLEMS
1.5 Mixing problems
Recap: Applying Differential Equations to Mixing Problems
The Mixing Problem modeling with separable differential equations
Mixing Problems and Separable Differential Equations
Mixing Problems and Separable Differential Equations
Ordinary Differential Equation-Mixing Problem
ODE | Mixing problem example
Applications of First Order Differential Equations - Mixing Concentrations 2
Комментарии
 0:17:38
0:17:38
 0:11:47
0:11:47
 0:24:45
0:24:45
 0:10:09
0:10:09
 0:09:31
0:09:31
 0:06:02
0:06:02
 0:11:49
0:11:49
 0:11:20
0:11:20
 0:28:01
0:28:01
 0:06:27
0:06:27
 0:11:14
0:11:14
 0:07:34
0:07:34
 0:13:25
0:13:25
 0:20:48
0:20:48
 0:01:08
0:01:08
 0:16:14
0:16:14
 0:05:02
0:05:02
 0:04:14
0:04:14
 0:16:45
0:16:45
 0:05:30
0:05:30
 0:06:32
0:06:32
 0:19:58
0:19:58
 0:04:57
0:04:57
 0:11:33
0:11:33