filmov
tv
Limitations of noisy quantum algorithms
Показать описание
Daniel Stilck França, ENS Lyon
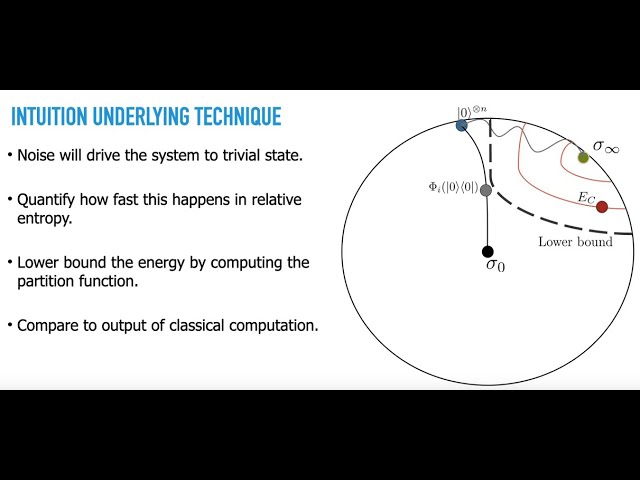
The impressive progress in quantum hardware of the last years has raised the interest of the quantum computing community in harvesting the computational power of such devices. However, in the absence of error correction, these devices can only reliably implement very shallow circuits or comparatively deeper circuits at the expense of a nontrivial density of errors. In this talk I will discuss how to use entropic inequalities to obtain limitation bounds for standard noisy intermediate scale proposals with or without error-mitigation tools. For instance, I will prove that with local depolarizing noise with probability p, at depths O(1/p) it is exponentially unlikely that the outcome of a noisy quantum circuit outperforms efficient classical algorithms for combinatorial optimization problems like Max-Cut. In addition, I am going to discuss how current error-mitigation protocols face significant barriers to overcome these conclusions.
The impressive progress in quantum hardware of the last years has raised the interest of the quantum computing community in harvesting the computational power of such devices. However, in the absence of error correction, these devices can only reliably implement very shallow circuits or comparatively deeper circuits at the expense of a nontrivial density of errors. In this talk I will discuss how to use entropic inequalities to obtain limitation bounds for standard noisy intermediate scale proposals with or without error-mitigation tools. For instance, I will prove that with local depolarizing noise with probability p, at depths O(1/p) it is exponentially unlikely that the outcome of a noisy quantum circuit outperforms efficient classical algorithms for combinatorial optimization problems like Max-Cut. In addition, I am going to discuss how current error-mitigation protocols face significant barriers to overcome these conclusions.
 1:03:01
1:03:01
 0:29:12
0:29:12
 1:30:01
1:30:01
 0:48:15
0:48:15
 0:00:48
0:00:48
 1:23:22
1:23:22
 0:50:28
0:50:28
 0:28:04
0:28:04
 0:58:55
0:58:55
 0:52:55
0:52:55
 0:35:24
0:35:24
 0:55:55
0:55:55
 0:25:05
0:25:05
 0:29:36
0:29:36
 0:00:24
0:00:24
 1:05:05
1:05:05
 0:47:52
0:47:52
 1:06:08
1:06:08
 0:15:56
0:15:56
 1:07:20
1:07:20
 0:28:15
0:28:15
 0:33:53
0:33:53
 0:50:07
0:50:07
 0:00:55
0:00:55