filmov
tv
Thermodynamics - 4-4 Ideal Gas Specific Heat example 4

Показать описание
Calculating U (internal energy) and boundary work for the conservation of energy equation.
Ideal Gas. Like and subscribe! And get the notes here:
Ideal Gas. Like and subscribe! And get the notes here:
Thermodynamics - 4-4 Ideal Gas Specific Heat example 1
Thermodynamics - 4-4 Ideal Gas Specific Heat example 4
Thermodynamics - 4-4 Ideal Gas Specific Heat example 2
Ideal Gases - Specific Heat, Internal Energy, Enthalpy | Thermodynamics | (Solved Problems)
The Ideal Gas Equation | Thermodynamics | (Solved Examples)
Thermodynamics - 4-4 Calculating U (internal energy) and H (enthalpy) using specific heats
PV-Diagram Ideal Gas Cycle: Calculate Heat, Work, Change in Internal Energy, and Efficiency
Entropy Change of Ideal Gases | Thermodynamics | (Solved Examples)
Thermodynamics SPECIFIC HEATS - cv & cp - in 12 Minutes!
Thermodynamics - 3-7 Ideal Gas Equation with compressibility factor
How To Calculate Entropy Changes: Ideal Gases
Ideal Gas Law // Thermodynamics - Class 71
The Ideal Gas Law: Crash Course Chemistry #12
PHYSICS 9702 [Ideal gases, temperature and thermodynamics] #Part 4
Ideal Gas Equation and COMPRESSIBILITY Factor in 11 Minutes!
Adiabatic Process with Ideal Gas - First Law of Thermodynamics Derivation (Integration, Natural Log)
A sample of an ideal gas goes through the process shown
Thermodynamics - 4-5 Specific heats of solids and liquids
The First Law of Thermodynamics: Internal Energy, Heat, and Work
Ideal Gas Law Problems Thermodynamics
Thermodynamics 4-65 An insulated rigid tank is divided into two equal parts by a partition.
Piston-Cylinder ENTHALPY Using Specific Heat in 4 Minutes!
First Law of Thermodynamics, Basic Introduction - Internal Energy, Heat and Work - Chemistry
Quantitative Description of Isothermal (Constant Temperature) Process with Ideal Gas on P-V Diagram
Комментарии
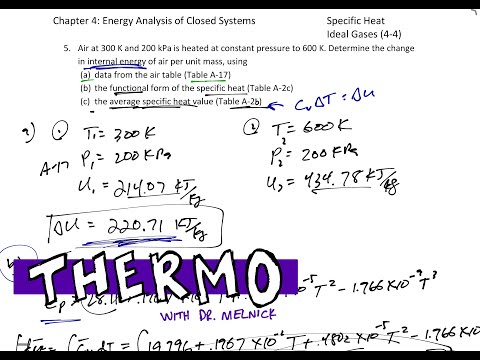 0:11:18
0:11:18
 0:14:58
0:14:58
 0:09:11
0:09:11
 0:11:25
0:11:25
 0:05:28
0:05:28
 0:22:24
0:22:24
 0:16:41
0:16:41
 0:12:32
0:12:32
 0:12:39
0:12:39
 0:12:44
0:12:44
 0:05:14
0:05:14
 0:07:54
0:07:54
 0:09:03
0:09:03
 2:18:50
2:18:50
 0:11:00
0:11:00
 0:16:00
0:16:00
 0:05:58
0:05:58
 0:05:39
0:05:39
 0:05:44
0:05:44
 0:18:19
0:18:19
 0:04:05
0:04:05
 0:04:22
0:04:22
 0:11:27
0:11:27
 0:10:23
0:10:23