filmov
tv
AQA A Level PE (2018) - Cardiovascular System Lesson

Показать описание
Learn today, as The PE Tutor covers 'The Impact of Physical Activity and Sport on Health and Fitness' from the AQA A Level PE Paper 1.
Paper 1: Factors affecting participation in physical activity and sport
Section A: Applied Anatomy and Physiology
The Cardiovascular System
Impact of physical activity and sport on health
Emotional
Physical activity can release endorphins in a participants brain, boosting mood, relieving anxiety and helping in the removal of stress.
Social
Particularly in teams sports, participants have the opportunity to develop leadership, teamwork and communicative skills, as well as friendships with other performers.
Physical
Regular physical activity raises heart rate, blood flow and the demand for energy. As a result, coronary blood vessels (those that supply the blood with oxygenated blood) experience regular changes and use. This reduces the risk of a build up of fatty deposits or cholesterol against the vessel walls.
Mental
Sport and physical activity challenge a performer to make decisions, apply tactics and solve problems, over time improving their mental capacity to deal with more demanding sporting situations, and cope better with the relatively simple cognitive tasks they face day to day.
Coronary Heart Disease
• Exercise ensures blood vessel tissue remains pliable and responsive to neural commands and vasoconstricts or vasodilates appropriately.
• This means that when blood pressure rises, they are capable of expanding and coping with increasing peripheral resistance and blood flow.
• Failure to do so could cause the vessel to rupture, or the cardiac muscle to be starved of oxygen (heart attack).
• Smoking, alcohol, sedentary lifestyle and high-fat diet are four causes of deteriorating coronary blood vessels.
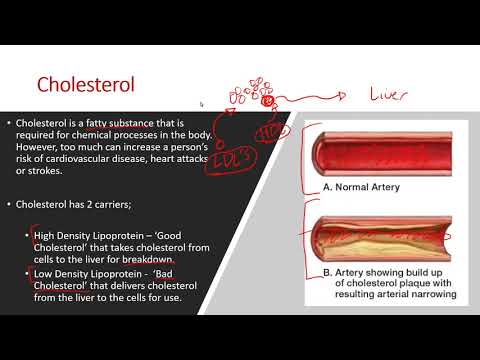
Cholesterol
• Cholesterol is a fatty substance that is required for chemical processes in the body. However, too much can increase a person’s risk of cardiovascular disease, heart attacks or strokes.
Cholesterol has 2 carriers;
• High Density Lipoprotein – ‘Good Cholesterol’ that takes cholesterol from cells to the liver for breakdown.
• Low Density Lipoprotein - ‘Bad Cholesterol’ that delivers cholesterol from the liver to the cells for use.
• Too much LDL can cause a gradual build up of cholesterol at cells as there is a surplus to requirement, and not enough HDL to remove it.
• Physical activity, particular aerobic activities, utilise fat stores to supply muscles with the energy they require. Some of this demand can be met using the fats within cholesterol.
• Overtime, with a low-fat diet and regular exercise, a person is able to lower their LDL count and cholesterol build up.
• There is a similar reduction in stroke risk. As blood vessels clear up, there is less chance of blood clotting and impeding blood flow destined for the brain.
Impact of physical activity and sport on fitness
• The heart is a muscle, therefore placing it under regular strain causes positive adaptions in it to occur. This is known as Cardiac Hypertrophy.
• It becomes bigger, stronger and more pliable leading to;
• More forceful contractions
• Increased stroke volume
• Increased cardiac output
• Increased ejection fraction
• Bradycardia
• Increased capillarization
• Sub-max exercise causes a significant increase in venous return due to vascular shunt mechanisms. The result of this increase, is the chambers of the heart become gradually stretched overtime, increasing diastolic fill.
• Maximum exercise on the other hand causes muscles to contract fully, which press on nearby blood vessels, restricting the blood flow through them. This causes a sharp increase in blood pressure. Frequent training of this nature causes the cardiac muscle to become stronger as it has to adapt to eject blood against higher levels of resistance.
Exam Question
Explain factors that can reduce a performer’s cardiovascular health, as well as two cardiovascular benefits they could experience from exercise.
Poor diet and lack of physical activity could lead to a decline in blood vessel and coronary blood vessel health. Due to infrequent response to changing blood pressures and cardiac output, vessels could become rigid (arteriosclerosis) and become susceptible to deposition of fatty substances and cholesterol. In both cases, blood flow could become restricted, limiting the supply of oxygen to the proceeding tissue. By engaging in maximal exerc
Paper 1: Factors affecting participation in physical activity and sport
Section A: Applied Anatomy and Physiology
The Cardiovascular System
Impact of physical activity and sport on health
Emotional
Physical activity can release endorphins in a participants brain, boosting mood, relieving anxiety and helping in the removal of stress.
Social
Particularly in teams sports, participants have the opportunity to develop leadership, teamwork and communicative skills, as well as friendships with other performers.
Physical
Regular physical activity raises heart rate, blood flow and the demand for energy. As a result, coronary blood vessels (those that supply the blood with oxygenated blood) experience regular changes and use. This reduces the risk of a build up of fatty deposits or cholesterol against the vessel walls.
Mental
Sport and physical activity challenge a performer to make decisions, apply tactics and solve problems, over time improving their mental capacity to deal with more demanding sporting situations, and cope better with the relatively simple cognitive tasks they face day to day.
Coronary Heart Disease
• Exercise ensures blood vessel tissue remains pliable and responsive to neural commands and vasoconstricts or vasodilates appropriately.
• This means that when blood pressure rises, they are capable of expanding and coping with increasing peripheral resistance and blood flow.
• Failure to do so could cause the vessel to rupture, or the cardiac muscle to be starved of oxygen (heart attack).
• Smoking, alcohol, sedentary lifestyle and high-fat diet are four causes of deteriorating coronary blood vessels.
Cholesterol
• Cholesterol is a fatty substance that is required for chemical processes in the body. However, too much can increase a person’s risk of cardiovascular disease, heart attacks or strokes.
Cholesterol has 2 carriers;
• High Density Lipoprotein – ‘Good Cholesterol’ that takes cholesterol from cells to the liver for breakdown.
• Low Density Lipoprotein - ‘Bad Cholesterol’ that delivers cholesterol from the liver to the cells for use.
• Too much LDL can cause a gradual build up of cholesterol at cells as there is a surplus to requirement, and not enough HDL to remove it.
• Physical activity, particular aerobic activities, utilise fat stores to supply muscles with the energy they require. Some of this demand can be met using the fats within cholesterol.
• Overtime, with a low-fat diet and regular exercise, a person is able to lower their LDL count and cholesterol build up.
• There is a similar reduction in stroke risk. As blood vessels clear up, there is less chance of blood clotting and impeding blood flow destined for the brain.
Impact of physical activity and sport on fitness
• The heart is a muscle, therefore placing it under regular strain causes positive adaptions in it to occur. This is known as Cardiac Hypertrophy.
• It becomes bigger, stronger and more pliable leading to;
• More forceful contractions
• Increased stroke volume
• Increased cardiac output
• Increased ejection fraction
• Bradycardia
• Increased capillarization
• Sub-max exercise causes a significant increase in venous return due to vascular shunt mechanisms. The result of this increase, is the chambers of the heart become gradually stretched overtime, increasing diastolic fill.
• Maximum exercise on the other hand causes muscles to contract fully, which press on nearby blood vessels, restricting the blood flow through them. This causes a sharp increase in blood pressure. Frequent training of this nature causes the cardiac muscle to become stronger as it has to adapt to eject blood against higher levels of resistance.
Exam Question
Explain factors that can reduce a performer’s cardiovascular health, as well as two cardiovascular benefits they could experience from exercise.
Poor diet and lack of physical activity could lead to a decline in blood vessel and coronary blood vessel health. Due to infrequent response to changing blood pressures and cardiac output, vessels could become rigid (arteriosclerosis) and become susceptible to deposition of fatty substances and cholesterol. In both cases, blood flow could become restricted, limiting the supply of oxygen to the proceeding tissue. By engaging in maximal exerc
 0:22:24
0:22:24
 0:13:45
0:13:45
 0:01:01
0:01:01
 1:40:51
1:40:51
 0:00:37
0:00:37
 0:00:10
0:00:10
 0:00:16
0:00:16
 0:11:20
0:11:20
 0:06:50
0:06:50
 0:00:07
0:00:07
 0:00:37
0:00:37
 0:03:42
0:03:42
 0:09:35
0:09:35
 0:06:51
0:06:51
 0:00:37
0:00:37
 0:04:48
0:04:48
 0:00:51
0:00:51
 1:11:16
1:11:16
 0:07:42
0:07:42
 0:00:27
0:00:27
 0:55:26
0:55:26
 0:01:00
0:01:00
 1:05:30
1:05:30
 0:01:15
0:01:15