filmov
tv
Physics 62.1 Understanding Space, Time & Relativity (2 of 55) Special & General Relativity

Показать описание
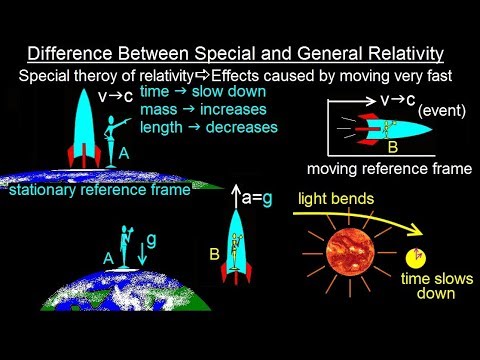
In this video I will explain the difference between special relativity and general relativity. Special relativity is the effects caused by moving very fast (closed to the speed of light. Where as general relativity has to do with the events that happens on Earth due to gravity (9.8m/s^2) are indistinguishable to the same events in a space ship accelerating at 9.8m/s^2.
Next video in this series can be seen at:
Physics 62.1 Understanding Space, Time & Relativity (1 of 55) Introduction
Physics 62.1 Understanding Space, Time & Relativity (12 of 55) What Happens to Time at v=c?
Physics 62.1 Understanding Space, Time & Relativity (5 of 55) Einstein's Brilliant Insight...
Physics 62.1 Understanding Space, Time & Relativity (15 of 55) Why Distance & Time are Rela...
Physics 62.1 Understanding Space, Time & Relativity (6 of 55) What is the Lorentz Factor?
Physics 62.1 Understanding Space, Time & Relativity (9 of 55) Einstein's Brilliant Insight...
Physics 62.1 Understanding Space, Time & Relativity (10 of 55) Einstein's Insight 3 Proved
Physics 62.1 Understanding Space, Time & Relativity (3 of 55) Is Relativity Real?
IGCSE Physics 0625 May/June 2024 P42 (Detailed discussions+ EXTRA TIPS)
Physics 62.1 Understanding Space, Time & Relativity (16 of 55) Time to Fly to the Sun
Physics 62.1 Understanding Space, Time & Relativity (19 of 55) Redshift of Receding Galaxy
Physics 62.1 Understanding Space, Time & Relativity (7 of 55) Lorentz Factor Calculated
Physics 62.1 Understanding Space, Time & Relativity (8 of 55) Einstein's Brilliant Insight...
Physics 62.1 Understanding Space, Time & Relativity (4 of 55) Einstein's Brilliant Insight...
Physics 62.1 Understanding Space, Time & Relativity (2 of 55) Special & General Relativity
Physics 62.1 Understanding Space, Time & Relativity (17 of 55) Moving Source Changes Light
Physics 62.1 Understanding Space, Time & Relativity (20 of 55) Relative Redshift of a Galaxy
Physics 62.1 Understanding Space, Time & Relativity (13 of 55) What Do You See at v=c?
Physics 62.1 Understanding Space, Time & Relativity (18 of 55) Blueshift Approaching Galaxy
Physics 62.1 Understanding Space, Time & Relativity (21 of 55) What is Relativistic z-Factor?
Physics 62.1 Understanding Space, Time & Relativity (11 of 55) What is the Twin Paradox?
All of IGCSE Physics in 5 minutes (summary)
Physics 62 Special Relativity (35 of 43) Relativistic Sample Problem - Time
The Mind Blowing Theory of General Relativity Unveiled Space and Time Warped
Комментарии
 0:04:16
0:04:16
 0:03:58
0:03:58
 0:04:28
0:04:28
 0:03:58
0:03:58
 0:03:28
0:03:28
 0:04:29
0:04:29
 0:03:05
0:03:05
 0:04:37
0:04:37
 0:47:00
0:47:00
 0:03:42
0:03:42
 0:02:12
0:02:12
 0:08:23
0:08:23
 0:03:27
0:03:27
 0:03:50
0:03:50
 0:06:52
0:06:52
 0:03:02
0:03:02
 0:02:30
0:02:30
 0:05:09
0:05:09
 0:02:54
0:02:54
 0:04:01
0:04:01
 0:04:35
0:04:35
 0:05:01
0:05:01
 0:07:52
0:07:52
 0:00:59
0:00:59